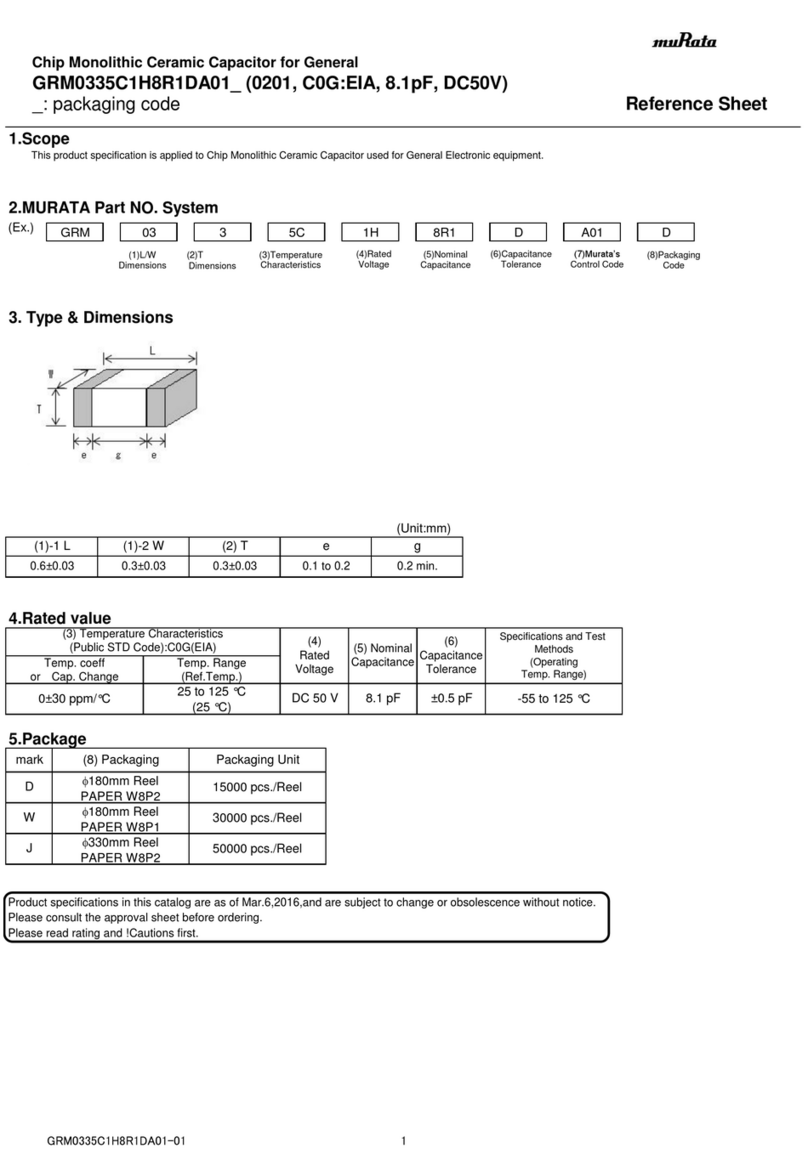
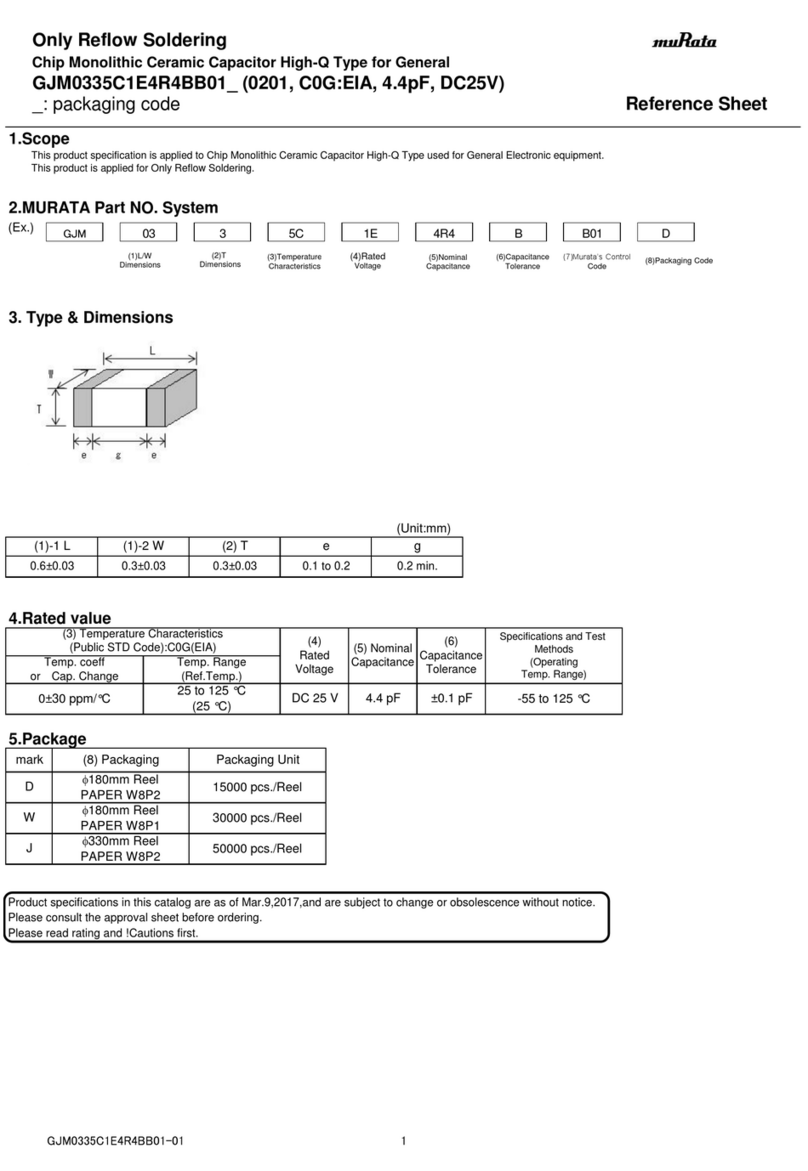
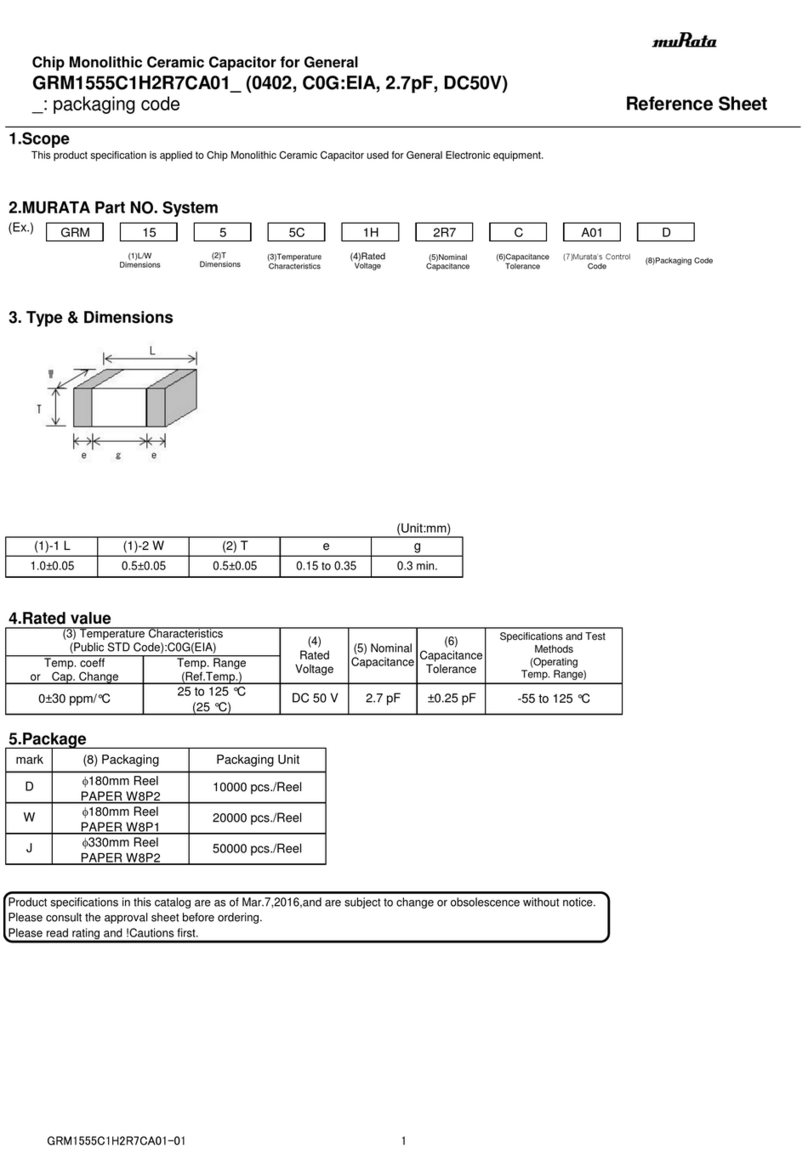
1 1 Name:Basis
KEB COMBIVERT F5-G / B
10 28.02.02
Introduction General
© KEB Antriebstechnik, 2002
All Rights reserved
Chapter Section Page Date
6.4.8 Limiter(oP.36...41).............................................................6.4.15
6.4.9 Ramp with constant time ...................................................6.4.15
6.4.10 Used Parameters...............................................................6.4.18
6.5 Voltage-/Frequency Characteristic Adjustment............................... 6.5.3
6.5.1 ControlType (ud.2) and Max Frequency Mode (only F5-B)..6.5.3
6.5.2 Rated frequency (uF.0) and Boost (uF.1) .............................6.5.4
6.5.3 Additional Rated Point (uF.2/uF.3) .......................................6.5.4
6.5.4 Delta Boost (uF.4/uF.5) ........................................................6.5.4
6.5.5 Voltage Stabilization (uF.9)..................................................6.5.5
6.5.6 Maximal voltage mode (uF.10)............................................. 6.5.6
6.5.7 Switching Frequency (uF.11) ............................................... 6.5.6
6.5.8 Used Parameters.................................................................6.5.7
6.6 Motor Data Adjustment ......................................................................6.6.3
6.6.1 Motor Name Plate................................................................ 6.6.3
6.6.2 MotorData from theName Plate (dr.0...dr.5)........................6.6.3
6.6.3 Motor Data from Data Sheets (dr.9).....................................6.6.4
6.6.4 MotorStator Resistance (dr.6) ............................................. 6.6.4
6.6.5 Used Parameters.................................................................6.6.6
6.7 Protective Functions.......................................................................... 6.7.3
6.7.1 Ramp Stop and Hardware Current Limit..............................6.7.3
6.7.2 Current Limit Constant Run (Stall-Function)........................ 6.7.5
6.7.3 Automatic Restart and Speed Search .................................6.7.7
6.7.4 Dead Time Compensation uF.18.........................................6.7.9
6.7.5 Base-Block Time (uF.12) and Voltage Level (uF.13) ............6.7.9
6.7.6 Response to Errors or Warning Signal ................................6.7.9
6.7.7 QuickStop (Pn.58...60) .....................................................6.7.13
6.7.8 Motor Protection Mode ......................................................6.7.15
6.7.9 GTR7-Control....................................................................6.7.19
6.7.10 Special Functions..............................................................6.7.20
6.8 Parameter Sets ...................................................................................6.8.3
6.8.1 Not Programmable Parameters ...........................................6.8.3
6.8.2 Security-Parameters ............................................................6.8.3
6.8.3 System-Parameters .............................................................6.8.3
6.8.4 Indirect and Direct Set Addressing ......................................6.8.3
6.8.5 Copying of Parameter Sets via Keyboard (Fr.1) ...................6.8.4
6.8.6 Copying of Parameter Sets via Bus (Fr.1, Fr.9) ....................6.8.4
6.8.7 Parameter Set Selection...................................................... 6.8.5
6.8.8 Locking of Parameter Sets...................................................6.8.8
6.8.9 ParameterSet ON/Off Delay(Fr.5, Fr.6) ...............................6.8.8
6.8.10 Used Parameters.................................................................6.8.9
6.9 Special Functions .............................................................................. 6.9.3
6.9.1 DC-Braking .........................................................................6.9.3
6.9.2 Energy Saving Function......................................................6.9.5
6.9.3 Motor Potentiometer Function..............................................6.9.7
6.9.4 Timer and Counter ............................................................6.9.11
6.9.5 Brake Control ....................................................................6.9.15