INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA
6
PL
powinien skontaktować się z producentem w
celu wymiany tabliczki znamionowej za każ-
dym razem gdy jest to konieczne.
Zagrożenia związane z wyrzucanymi częściami
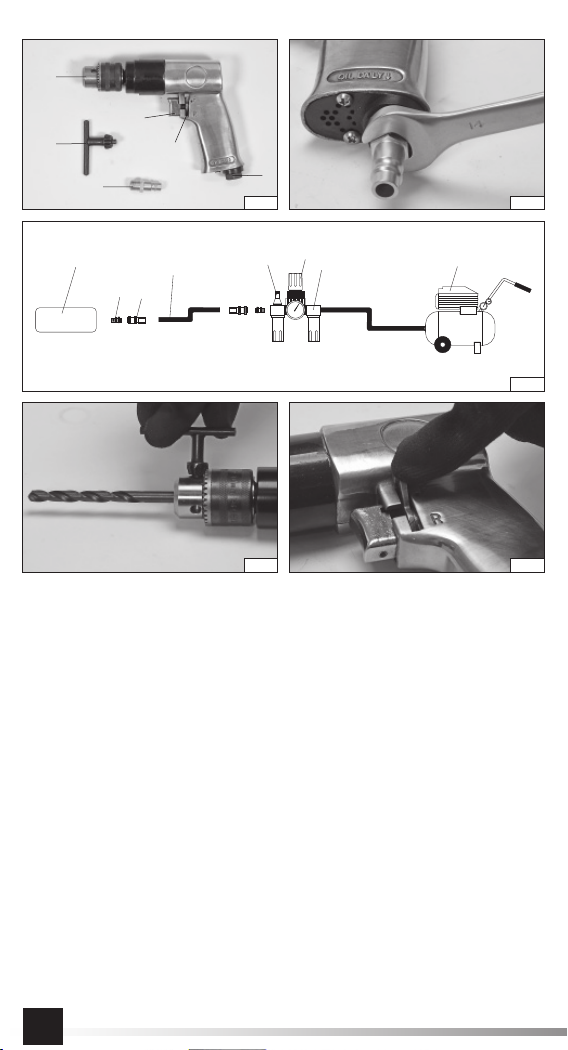
Odłączyć narzędzie od źródła zasilania przed
wymianą narzędzia wstawionego lub akce-
soria. Uszkodzenie obrabianego przedmiotu,
akcesoriów lub nawet narzędzia wstawiane-
go może spowodować wyrzucenie części z
dużą prędkością. Zawsze należy stosować
ochronę oczu odporną na uderzenia. Stopień
ochrony należy dobierać w zależności od
wykonywanej pracy. Należy się upewnić, ze
obrabiany przedmiot jest bezpiecznie zamo-
cowany. W przypadku pracy narzędziem nad
głową, stosować hełm ochronny. Należy rów-
nież brać pod uwagę ryzyko wobec osób po-
stronnych. Należy się upewnić, ze obrabiany
przedmiot jest bezpiecznie zamocowany.
Nie pracować narzędziem bez upewnienia
się, że został zainstalowany ogranicznik na-
rzędzia wstawianego. Aby uniknąć obrażeń,
należy wymieniać ogranicznik kiedy zostanie
zużyty, pęknięty lub zniekształcony. Pewnie
przyłożyć narzędzie wstawiane do obrabia-
nej powierzchni przed rozpoczęciem pracy.
Zagrożenia związane z pracą
Użytkowanie narzędzia może wystawić ręce
operatora na zagrożenia, takie jak: zmiaż-
dżenie, uderzenie, odcięcie, ścieranie oraz
gorąco. Należy ubierać właściwe rękawice
do ochrony rąk. Operator oraz personel kon-
serwujący powinni być fi zycznie zdolni do
poradzenia sobie z ilością, masą oraz mocą
narzędzia. Trzymać narzędzie poprawnie.
Zachować równowagę oraz zapewniające
bezpieczeństwo ustawienie stóp. Należy
zwolnić nacisk na urządzenie startu i stopu
w przypadku przerwy w dostawie energii
zasilającej. Używać tylko środków smarnych
zalecanych przez producenta. Unikać bez-
pośredniego kontaktu z narzędziem wsta-
wianym podczas oraz po pracy, może być
gorące. Należy stosować okulary ochronne,
zalecane jest stosowanie dopasowanych rę-
kawic oraz stroju ochronnego.
Zagrożenia związane z powtarzalnymi ruchami
Podczas stosowania narzędzia pneumatycz-
nego do pracy polegającej na powtarzaniu ru-
chów, operator jest narażony na doświadcze-
nie dyskomfortu dłoni, ramion, barków, szyi
lub innych części ciała. W przypadku użyt-
kowania narzędzia pneumatycznego, ope-
rator powinien przyjąć komfortową postawę
zapewniającą właściwe ustawienie stóp oraz
unikać dziwnych lub nie zapewniających rów-
nowagi postaw. Operator powinien zmieniać
postawę podczas długiej pracy, pomoże to
uniknąć dyskomfortu oraz zmęczenia. Jeżeli
operator doświadcza symptomów takich jak:
trwały lub powtarzający się dyskomfort, ból,
pulsujący ból, mrowienie, drętwienie, piecze-
nie lub sztywność. Nie powinien ich ignoro-
wać, powinien powiedzieć o tym pracodawcy i
skonsultować się z lekarzem.
Zagrożenia związane z akcesoriami
Odłączyć narzędzie od źródła zasilania przed
zmianą narzędzia wstawionego lub akceso-
ria. Stosować akcesoria i materiały eksplo-
atacyjne tylko w rozmiarach i typach, które
są zalecane przez producenta. W przypadku
młotków, w stosownych przypadkach, nigdy
nie używać jakichkolwiek dłut jako narzędzi
ręcznych. Zostały one specjalnie zaprojekto-
wane i poddane obróbce cieplnej pod kątem
wykorzystania jedynie w nieobrotowych na-
rzędziach udarowych. W przypadku młotków i
kruszarek, w stosownych przypadkach, nigdy
nie używać tępych dłut, ponieważ są one pod-
dawane dużemu obciążeniu i może pęknąć
ze względu zmęczenia materiału. Użycie
tępego narzędzia może zwiększyć wibracje
i dlatego zawsze powinno się stosować na-
ostrzone narzędzia. W przypadku młotków, w
stosownych przypadkach, nigdy nie chłodzić
gorących narzędzi wstawianych w wodzie,
może to skutkować kruchością i przedwcze-
snym zużyciem. W przypadku młotków, w
stosownych przypadkach, uszkodzenie lub
pękniecie narzędzia może wynikać z niewła-
ściwego wykorzystania narzędzia jako dźwi-
gni, np. przy podważaniu. Lepiej pracować,
usuwając mniejsze fragmenty, co pozwoli
uniknąć zacięć. Unikać bezpośredniego kon-
taktu z narzędziem wstawianym podczas oraz
po pracy, może być gorące lub ostre.
Zagrożenia związane z miejscem pracy
Poślizgnięcia, potknięcia i upadki są głów-
nymi przyczynami obrażeń. Wystrzegać
się, śliskich powierzchni spowodowanych
użytkowaniem narzędzia, a także zagrożeń
potknięciem spowodowanym instalacją po-
wietrzną. Postępować ostrożnie w niezna-
nym otoczeniu. Mogą istnieć ukryte zagro-
żenia, takie jak elektryczność lub inne linii
użytkowe. Narzędzie pneumatyczne nie jest
przeznaczone do stosowania w strefach za-
grożonych wybuchem i nie jest izolowane od
kontaktu z energią elektryczną. Upewnić się,