Bestlink BL1000 Series User manual

BestLink2.4GHz Booster
BL1000 Series
Installation Guide
Version 1.3.0

Copyright
Copyright © 2003 all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, adapted, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any
language, or transmitted in any form or by any means without the
written permission of the supplier.
About This Manual
The purpose of this manual is for the setup of Booster & DC Injector.
This manual, revised as version 1.3.0 in 2004, includes the procedures
to assist you in avoiding unforeseen problems.
Technical Support
If you have difficulty resolving the problem while installing or using the
Booster & DC Injector, please contact the supplier for support.

FCC Notice
Reminder:
To comply with FCC part 15 rules, the Booster must only be
used as a system as FCC certified. The system must also be
professionally installed to ensure compliance with the Part 15
certification. It is the responsibility of the operator and
professional installer to ensure that only certified systems are
deployed in where FCC rules apply. Further, according to FCC
Part 15 regulations, Section 15.247(b)(3)(iii), the installer
must ensure that the high-gain directional antenna used in
this system is used exclusively for fixed, point-to-point
operations and that multiple co-located intentional radiators
transmitting the same information are not used. For further
information, please see Appendix B.
FCC Certified Declaration:
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may
not cause harmful interference and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction ..........................................................5
1-1 Product Kit.............................................................................................5
1-2 Features and Benefits........................................................................6
1-3 Specifications ........................................................................................7
1-4 Calculate Transmit Power.................................................................9
1-5 Installing the Booster Kit................................................................10
Appendix A: Channels and Cable Attenuations.............................12
Appendix B: FCC Certified Systems ...................................................13
Appendix C: Troubleshooting................................................................14

5
Chapter 1 Introduction
K-Best’s Booster, operating on the 2.4GHz ISM band, is a high
performance two-way amplifier using Time Division Duplex (TDD)
technology. It is used outdoor to extend the range of wireless radio
communication.
K-Best’s DC injector (KBDC24E) functions as a provider of DC power to
the outdoor booster or transponder through the feed cable without an
additional power cord. The DC injector comes with different types of
connector upon custom’s request . The standard product of KBDC24E-2N
is equipped with female N type at both side, and KBDC24E-AN with female
N type at one side and female SMA at another side.
1-1 Product Kit
Before installation, make sure that you the following items:
Booster
DC Injector
Jumper Cable
Power Adapter
Power Cord
Installation Guide

6
1-2 Features and Benefits
2400~2500 MHz unlicensed ISM Band
Provides DC Power to the booster without an additional Power cord
Booster has 0.5W/1W (FCC certified) output power levels.
20dB receive gain for the booster
Bi-directional TDD technology
Transmitter and receiver LED indicator
Waterproof housing
Compatible with IEEE 802.11b
Extending transmission distance
Enhance signal strength

7
1-3 Specifications
Specifications for DC Injector
Operating Frequency Range
2400~2500MHz
Bias Current / DC Voltage / Insertion Loss
1.5A (max.) / 15V (max.) / 1dB
Connector / DC Jack
N type female for both side / φ6 mm, center pin φ2.0 mm
Dimensions / Weight
99.1(H)x53.5(W)x21.2(H)mm / 165g
Specifications for Booster
Operating Frequency Range /
2400~2500MHz
Operating Mode
Bi-directional TDD
Transmitter Output Power / Transmitter Gain
30 dBm Typical / automatically adjusts to 1W power output
Transmitter Input Power
Max: 13 dBm
Min: 3 dBm
Receiver Input Power
Max: -16 dBm
Receiver Gain
20dB
Frequency Response Flatness
± 1dB over operating range
Noise Figure
< 4 dB
Switch Time
< 1.5 µs
Connector
N-type Female (50Ω);
SMA connector available for custom design
Operating Temperature
-30~60℃

8
Power Consumption
1watt, 950mA @ 9VDC
LED Indication
Transmit: Green; Receive: Red
Dimensions / Weight
120(L)x72(W)x17.5(H) mm / 380g
9
1-4 Calculate Transmit Power
In order to obtain the best performance of booster and system, user must
calculate the transmission power to meet the booster technical
requirement and FCC regulations(See Appendix B). It is advised that the
user follows the calculation below:
1. Converter power of the access point from milliwatts to dBm.
Note: dBm = 10 * Log(milliwatts)
2. Determine the attenuation of cable(please refer to manufacturer’s
specifications)
Note: Suggest the cable loss between booster and DC injector should not
exceed 10 dBm generally.
Table A – Typical Cable Attenuation Values
Cable Type Attenuation dB/100ft @2.4GHz
RG-142 21
LMR200 16.5
LMR400 6.6
LMR600 4.4
LMR900 2.92
Belden 9913 7.1
Note: Values are approximate.
3. Calculate the actual power of booster in the pole as follow:
Access point Power(dBm) – Cable Loss(dBm) – Misc. Loss = Input
Signal Level(dBm)
Note: Misc. Loss means loss of connector, adapter and DC injector and
estimates to be around 2 dB.
4. If the input signal level exceeds the max. Transmitter Input Power or
fails to meet the min. Transmitter Input Power of booster, the booster
can’t identify the input signal. Under this circumstance, user should
adjust the input signal level to fit the requirement such as using an
attenuation pad or a higher loss cable and vice versa.
10
1-5 Installing the Booster Kit
Once input signal level is determined to be in conjunction with the
technical requirement of booster, please proceed to install the booster kit
with following procedures:
1. Connect the booster RF output directly to the antenna with appropriate
cable.
2. Attach the booster RF input to the DC Injector with coaxial cable.
Note: The type and gain of antenna or type and length of cable depend
on your purpose of using booster. Please contact manufacturer for
further information.
Warning: The cable between DC injector and booster carries the DC
voltage and should not be connected to devices other than
booster.
3. Connect the coaxial cable leading from the DC Injector to the antenna
on the access point.
4. Plug the power cable leading from the DC Injector into any available
110/220 V electrical outlet.
5. Check the LED indicator of the DC injector. If the LED is on, it means
the booster kit is operating.

11
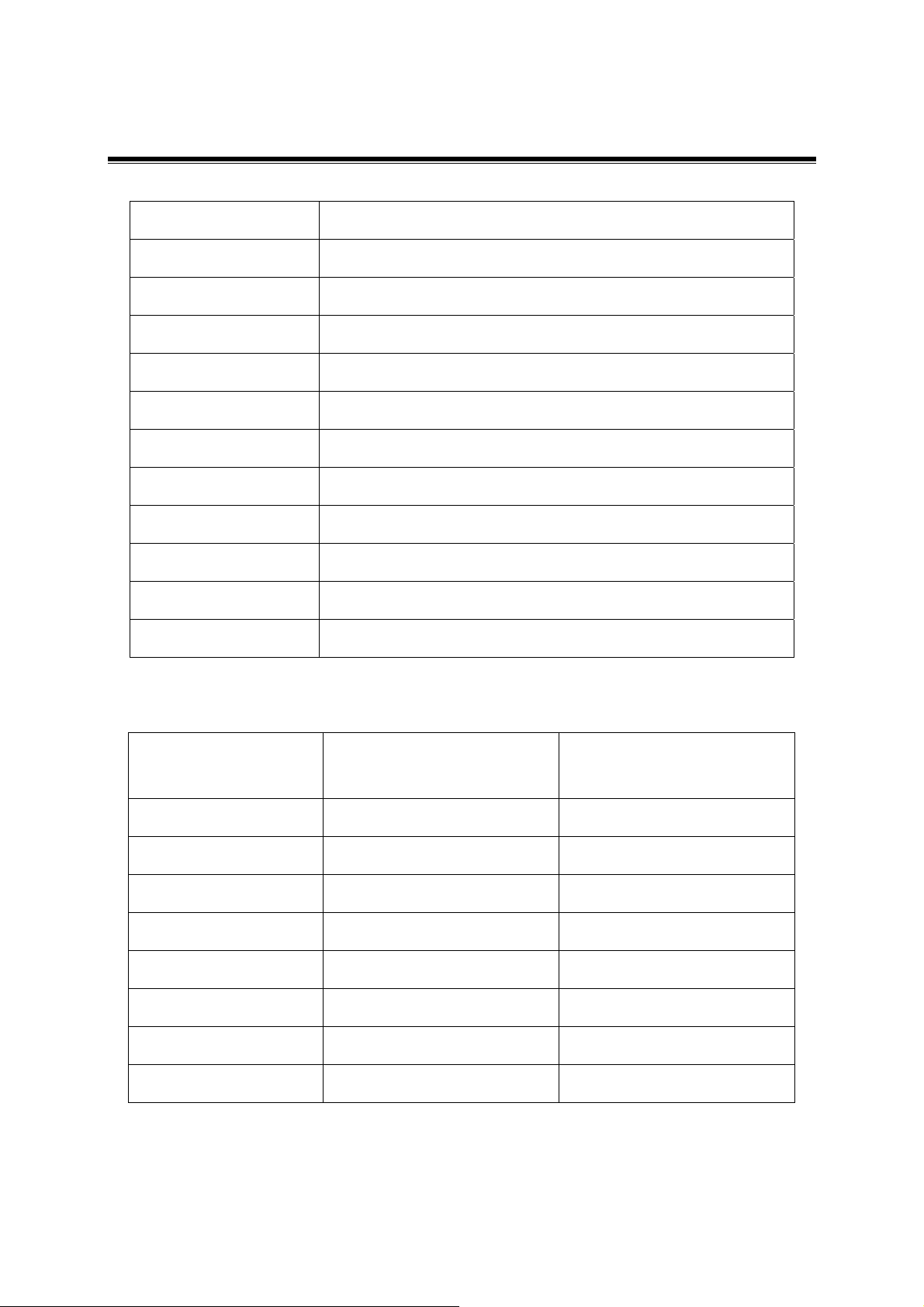
KBW24 Installation Details
To
Omni-directional,
or Grid or Panel
Antennas N-female to
N-female adapter
to attach to the
N
-
male on cable
DC Injector
Booster
110/220
VAC AC
Main Power
Cable
RF Output
interface of
Access Point
To 2.4GHz
Antenna
12
Appendix A: Channels and Cable Attenuations
Table A – Conversion Table
802.11b Channel Frequency(MHz)
1 2412
2 2417
3 2422
4 2427
5 2432
6 2437
7 2442
8 2447
9 2452
10 2457
11 2462
Table B – Authorized Cables with Minimum Length
Cable Type Minimum Length Maximum
Recommended Length
RG6/U 35 feet 75 feet
RG142 27 feet 60 feet
LMR400 100 feet 250 feet
LMR500 125 feet 300 feet
LMR600 150 feet 370 feet
LMR900 230 feet 560 feet
LMR1200 300 feet 700 feet
LMR1700 410 feet 950 feet
Note: This table is for reference only.

13
Appendix B: FCC Certified Systems
FCC ID#: QZGKBW24-001
FCC Certified Systems consist of:
¾KBW24-100 Booster,DC Injector,Power Adapter
¾NDC WLAN Access Point
¾Outdoor Antenna
¾Coaxial Cable
The Booster has passed the FCC regulations:
FCC part 15, subpart C(2002)
Table A – Authorized Antennas
Model Antenna Type Antenna
Gain(dBi)
Max
EIRP(dBm)
KBNT2406-01 Flat Panel 6 36
Note: Cable calculation must be performed using 2.4GHz attenuation
values because all signals pass between the Access point and Booster
are at a frequency of 2.4GHz.

14
Appendix C: Troubleshooting
If there is no signal output, please check the following item:
1. Check whether the LED indicator on the DC injector is on. If not, it
means there is problem with the power component.
(1) Check if the power cord is correctly connected with the power
adapter and the power outlet.
(2) Check if there is electricity on power outlet.
2. Check if the access point is working properly.
3. Check if the connection between booster and DC injector is correct, or
whether the connector is loose or not.
4. Verify if the transmit power which calculated before is correct.
5. If none of the above measures could solve troubleshooting, please
contact the supplier for further support.
Table of contents
Popular Amplifier manuals by other brands

COM-power corporation
COM-power corporation PAM-6000 instruction manual

Yaesu
Yaesu FL-2000B instruction manual

Interface
Interface BSC4 quick start guide

LightSpeed Technologies
LightSpeed Technologies Listening Enhancement System LES 600 Series user manual

Alpine
Alpine MRP-F240 Service manual

Molecular Devices
Molecular Devices Axoclamp 900A user guide











