R
Page 1
TG97A
Hazard Denitions
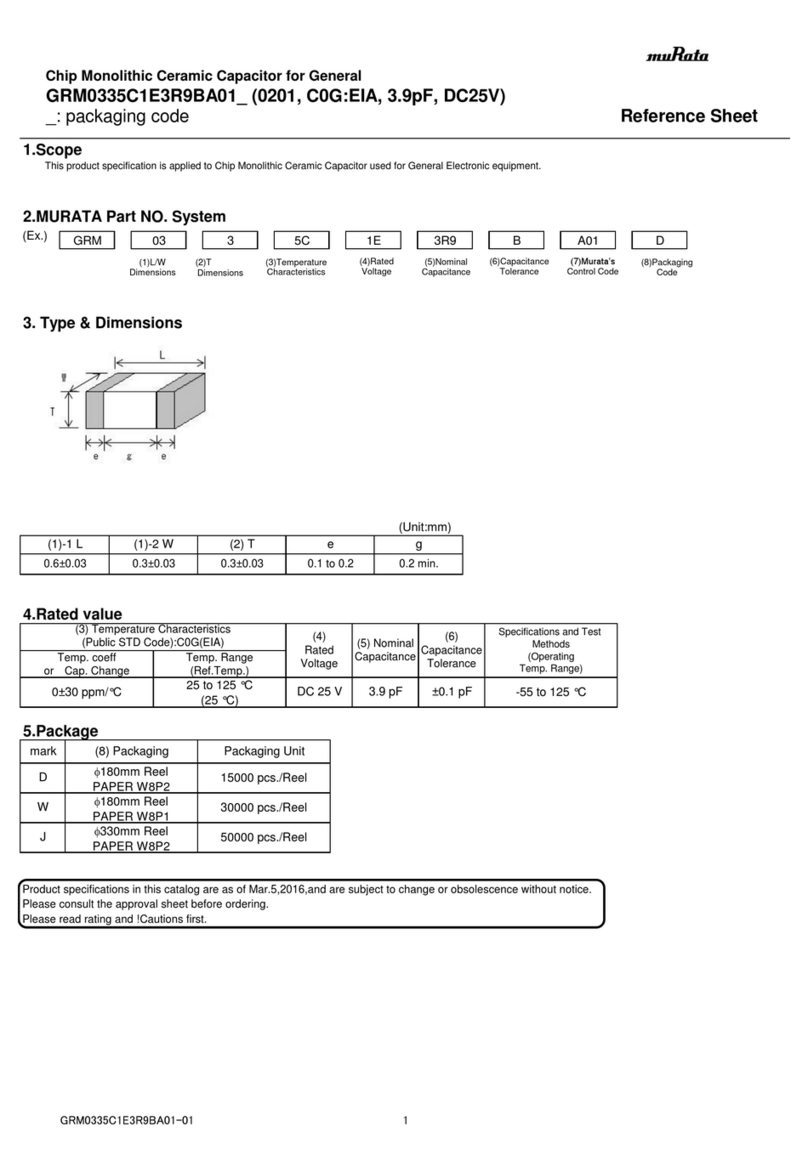
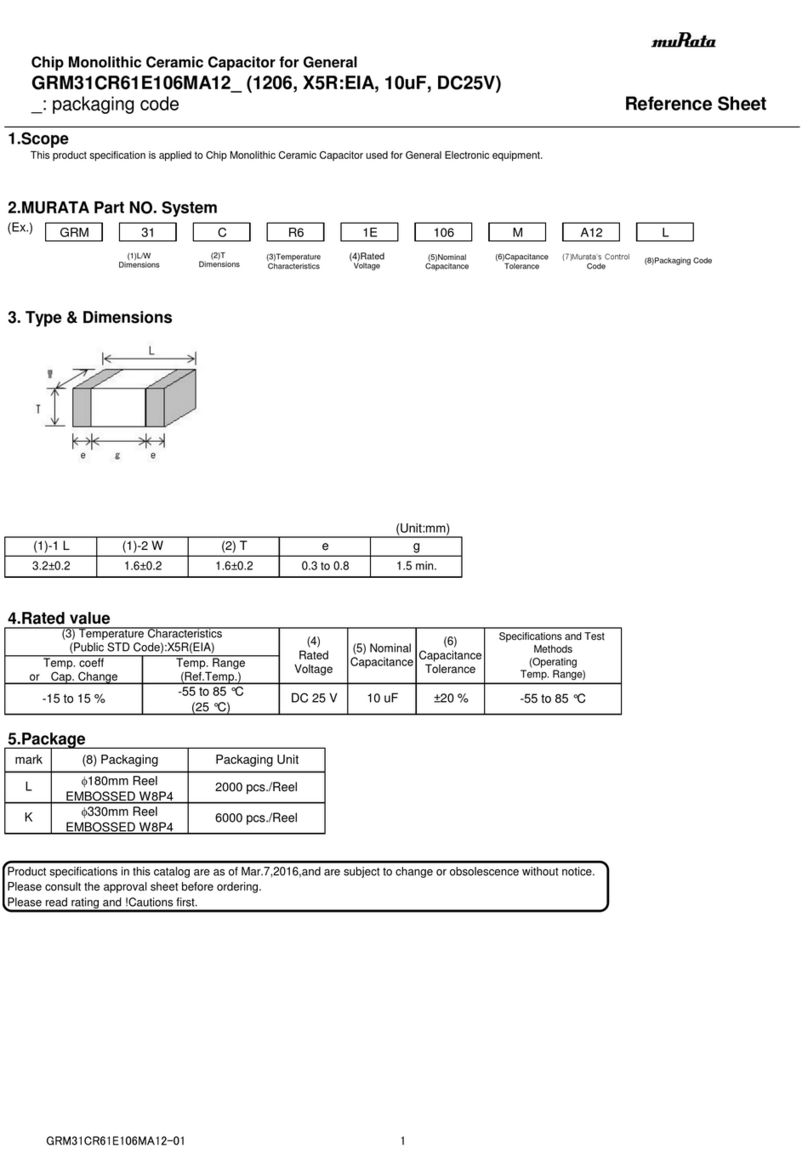
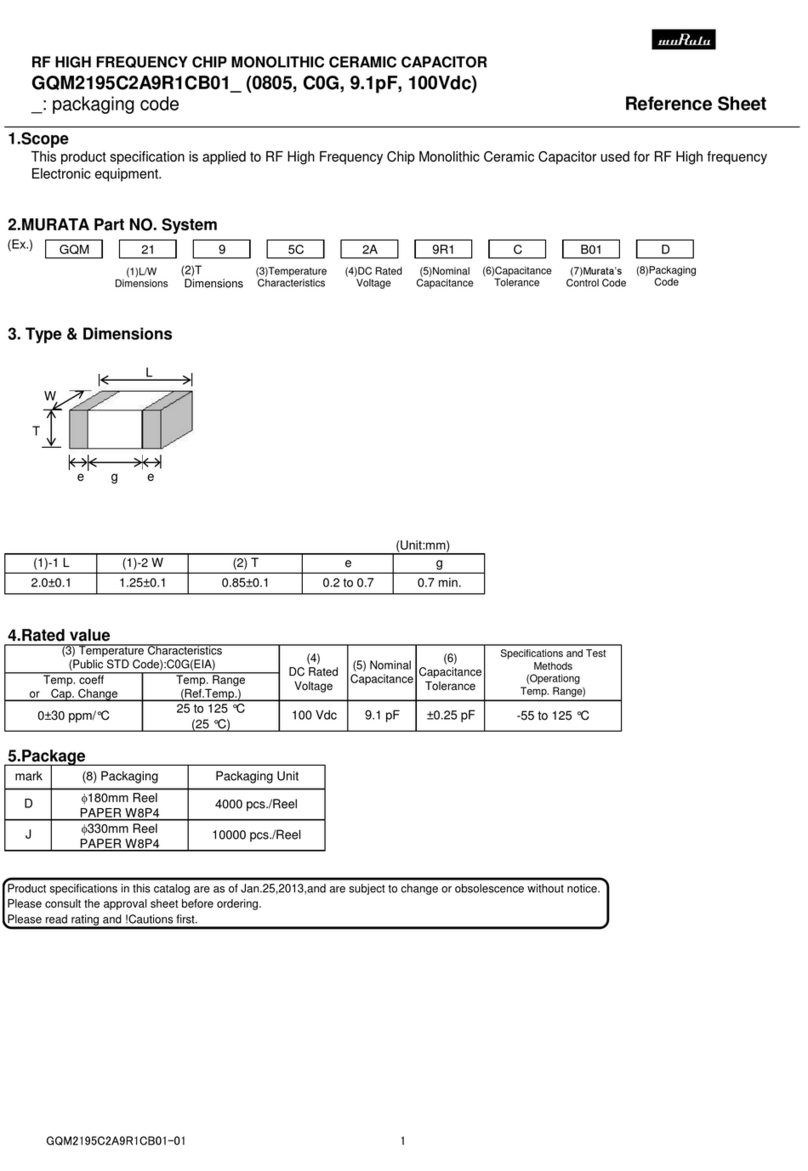
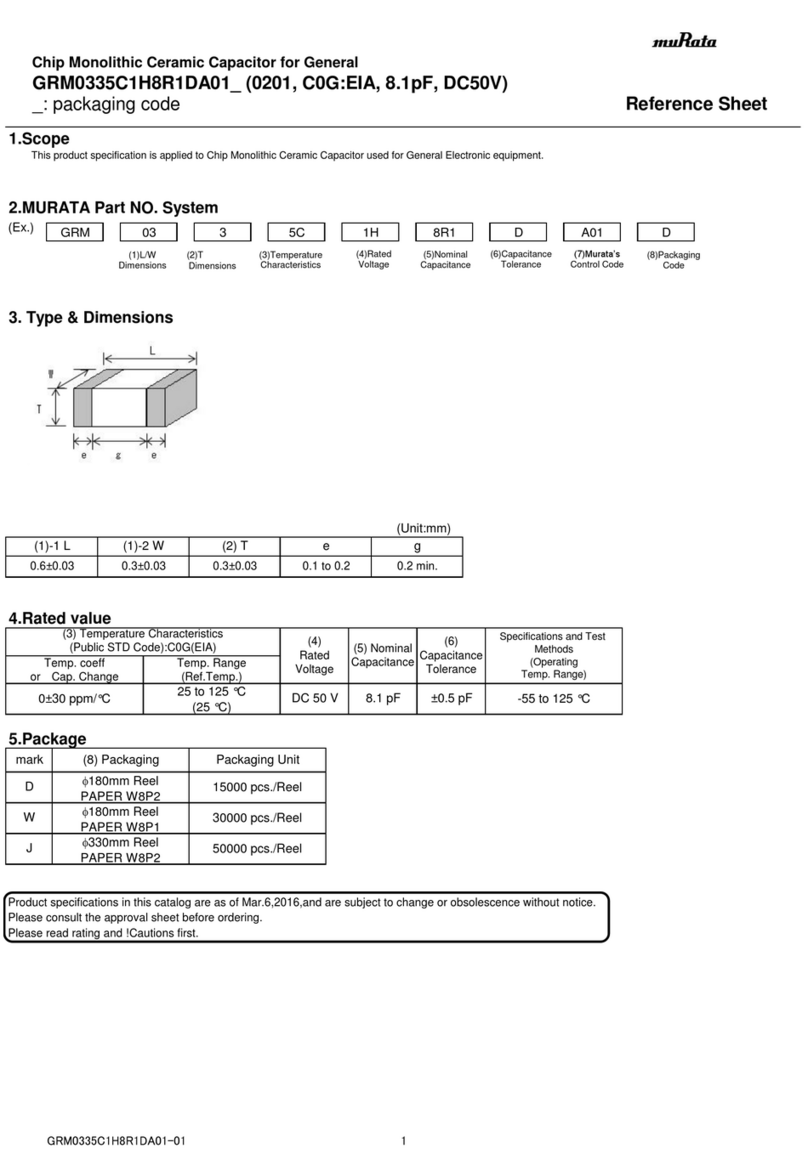
Indicates presence of hazards that will
or can cause minor personal injury or
damage to equipment.
NOTICE Indicates special instructions on installa-
tion, operation or maintenance that are
important but not related to personal injury hazards.
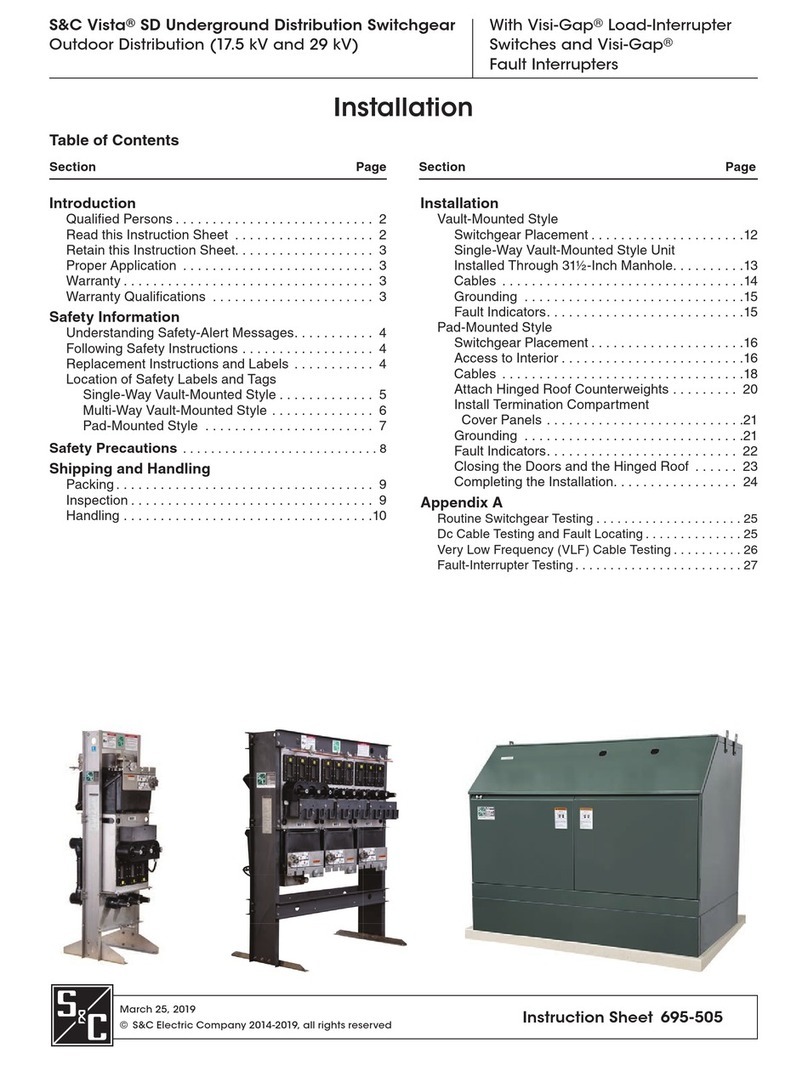
C850 Alternator
Troubleshooting Guide
C.E. Niehoff & Co.
Battery Conditions
NOTICE Battery conditions may be observed during
cold-start voltage tests until temperatures
of electrical system components stabilize.
Maintenance/Low Maintenance Battery
• Immediately after engine starts, system volts are lower
than regulator setpoint and amp output is medium.
• 3–5 minutes into charge cycle, system voltage increase
and amps decrease.
• 5–10 minutes into charge cycle, system volts increase
to or near regulator setpoint and amps decrease to a
minimum.
• Low maintenance battery has same characteristics as
maintenance battery but slightly longer recharge time.
Maintenance-free Battery
• Immediately after engine starts, system volts are lower
than regulator setpoint and charging amps are low.
• Volts and amps remain low when charge cycle begins.
• After alternator energizes, voltage increases by several
tenths. Amps increase to medium-to-high levels.
• Volts will increase to setpoint and amps will decrease.
Time required to reach optimum voltage and amps will
vary with engine speed, load, and ambient temperature.
High-cycle Maintenance-free Battery. These batter-
ies respond better than standard maintenance-free.
Charge acceptance of these batteries may display char-
acteristics similar to maintenance batteries.
AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) Maintenance-free
Battery. These dry-cell batteries respond better than
standard maintenance-free batteries. If battery state of
charge drops to 75% or less, recharge batteries to 95%
or higher separately from engine charging system to
avoid damaging charging system components and pro-
vide best overall performance. Charge acceptance may
display
characteristics similar to maintenance batteries.
Contents
Section A: Wiring Diagram ...........................................2
Section B: Basic Troubleshooting ...............................4
Section C: Advanced Troubleshooting .......................5
Required Tools and Equipment
• Digital Multimeter (DMM)
• Ammeter (digital, inductive)
• Jumper wires
Testing Guidelines
Professional service technicians rely on the following
guidelines when testing electrical components.
Voltage testing:
• Set meter to proper scale and type (AC or DC).
• Zero meter scale or identify meter burden by touching
meter leads together. Meter burden must be subtract-
edfromnalreadingobtained.
• Be sure meter leads touch power source area only.
Prevent short circuit damage to test leads or source
by not allowing meter leads to touch other pins or ex-
posed wires in test area.
• Use CEN tools designed especially for troubleshoot-
ing CEN alternators when available.
Resistance (ohms) testing:
• Set meter to proper scale.
• Zero the meter scale or identify meter burden by
touching meter leads together. Meter burden must be
subtractedfromnalreadingobtained.
• Be sure meter leads touch power source area only.
Donotallowngersorbodypartstotouchmeter
leads or power source during reading.
• Take reading when power source is at 70º F/21º C.
Readings taken at higher temperatures will increase
reading. Conversely, readings taken at lower temper-
atures will decrease reading.
• Test directly at power source. Testing through extend-
ed harnesses or cable extensions may increase read-
ing.
Voltage drop testing:
• Measure voltage between B+ on alternator or power
source and B- (ground) on alternator or source. Re-
cord reading. Move to batteries or other power source
and measure again between B+ and B- terminals on
battery or other power source. The difference be-
tween the two readings represents voltage lost within
circuit due to but is not limited to inadequate cable
gage or faulty connections.
• Voltage drop measurements must be taken with all
electrical loads or source operating.
Dynamic/Live testing: Denition:Connectingpowerand
ground to a component to test operation/function out of
circuit.
• Connect jumper leads directly and securely to
power source contacts of component being tested.
• Make any connection to power and ground at power
supply or battery source terminals. Do not make
connection at component source terminals as that
may create an arc and damage component source
terminals.