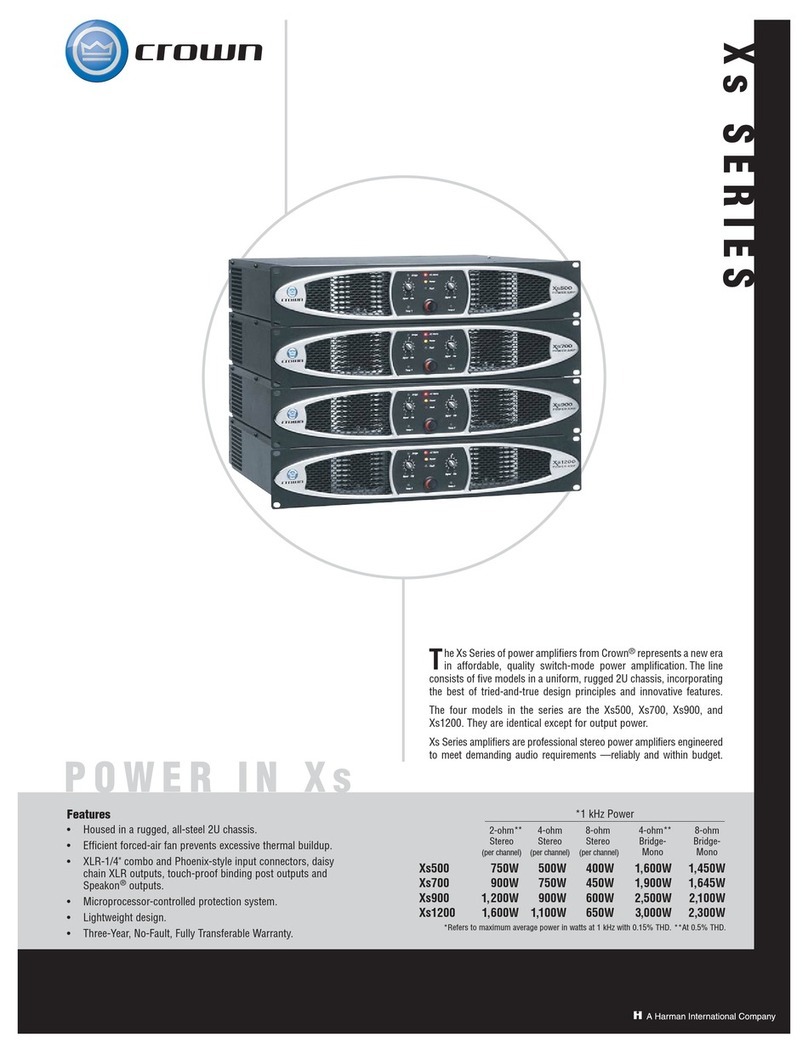
bias. The bias voltage across the Vbe multiplier should range between 2.4V (heatsink warm) and 2.5V
(heatsink cold). Bias voltages outside this range indicate a fault with the Vbe multiplier and/or a fault in the sec-
ond long-tailed pair (Q4A - Q5A, R19A, R20A, R23A, R24A). For example, too small a bias voltage could be
caused by R19A being high, R24A being high, R21A being low, Q8A being faulty etc. Too high a bias voltage is
rare, and would, most likely, be caused by a faulty transistor or resistor in the Vbe multiplier circuit.
C3A is is very important for ensuring HF Stability. A faulty capacitor in this position will usually cause
excess distortion and in the case of anything less than 330pF can reveal a very spiky instability.
Power for the class A drivers is decoupled from +HT and -HT by D17, C19 and D18, C20 respectively.
Output Stage
The output stage consists of a symmetrical Siklai follower: Q9A-Q12A, R34A, R29A, R35A, R56A and
C21A, generating the high current drive required for the parallel connected symmetrical follower output stage:
Q13A-Q20A, R44A-R51A. V-I limiting is controlled by Q21A, Q22B, R36A-R43A, C1A, C2A, R20A, R25A-R28A,
R30A, R33A, R55A, D7A-D9A, D11A, ZD3A-ZD6A.
As the output stage is symmetrical, the positive half only will be described (Q13A-Q16A, R44A-R47A,
C2A, Q22A, R36A-R39A, R25A, R26A, R30A, R55A, D8A, D11A, ZD3A, ZD5A).
Output stage protection is accomplished by a three-slope V-I limiting circuit which has limiting
characteristics chosen to emulate the Safe operating area of the output stage transistors at their maximum operat-
ing temperature.
The V-I limiting works by controlling Q22A: when the base-emitter voltage of Q22A exceeds about 0.65V then
Q22A turns on and steals current, via D8A, from the input of the output stage and thereby limiting the output. So,
V-I limiting is controlled by controlling the base-emitter voltage of Q22A.
Each output device has its own current sharing resistor -- R44A-R47A -- the voltage across which is
proportional to the current flowing in the output device. These voltages are sampled and summed by R36A-R39A.
C2A ensures stability when V-I limiting is activated.
The voltage across the output devices is sampled by R25A and R26A (R30A and ZD5A limit the voltage range to
reduce off-load distortion) and this, summed with the output current derived signals from R36-AR39A, controls
Q22A for output voltages less than about 3Vpk. Thus the amplifier is protected for short circuits because the
base-emitter voltage of Q22A increases when output current increases and when voltage across the output
devices increases.
For output voltages exceeding about 3Vpk, ZD3A conducts connecting R55A to sense the output voltage. In this
case, as output voltage increases, the base-emitter voltage of Q22A reduces, thus the current limit is increased as
the output voltage increases, defining the third slope of the limiting characteristic.
CLIP LED CIRCUIT
The clip LED (LED1A) is driven in series with the Limiter LED (LED2A) from the output of the
amplifier via D13A with its threshold controlled by ZD7A and R58A. With no signal present, ZD7A and
R58A generate a reference voltage at the anode of ZD7A which is 18V below the +HT supply rail. All the