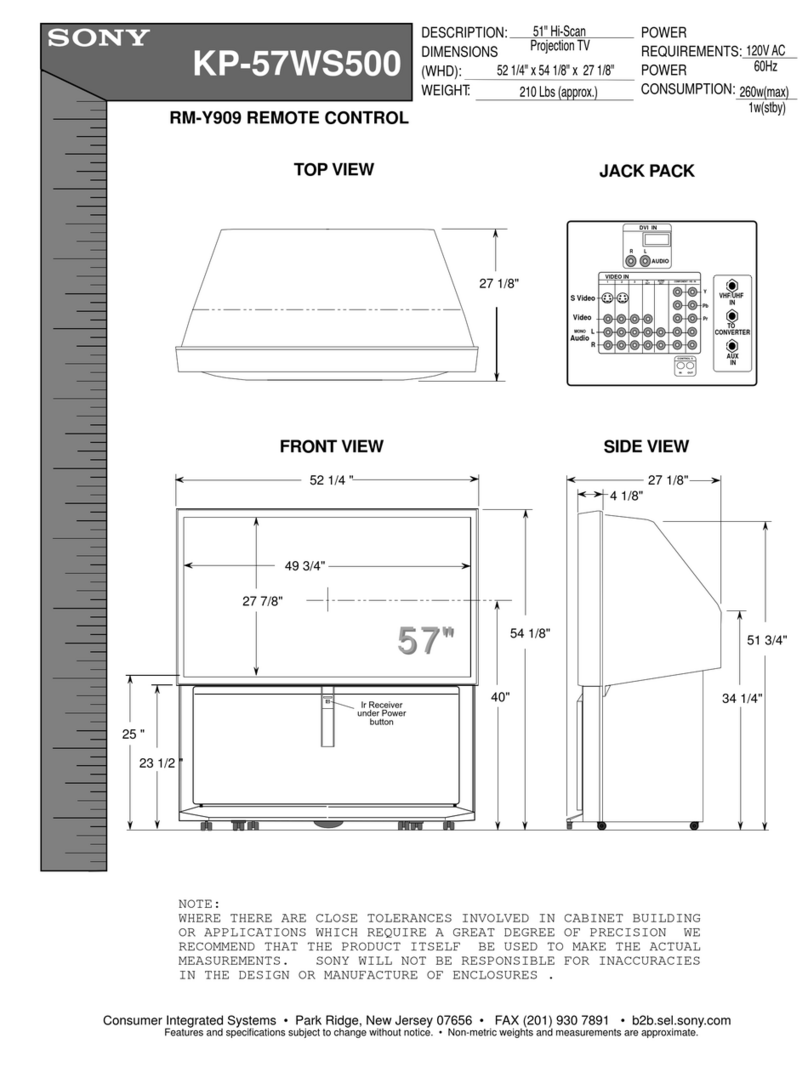
DP-2X +6V POWER SUPPLY REGULATION EXPLANATION
PAGE 01-01
+6V Power Supply Circuit Diagram explanation: The Primary Chassis Discussed is the DP-27 and DP-27D.
(See DP-26, DP-27 and DP-27D +6V Regulation Circuit Diagram for details).
(Also, see DP-23, DP-23G and DP-24 +6V Regulation Circuit Diagram for details).
Note: Items described below for the DP-23, 23G and DP-24 are shown in brackets [ ].
THIS POWER SUPPLY RUNS ALL THE TIME:
When a Projection set is plugged into an AC outlet, it must produce a power supply to energize certain circuits.
These circuits are responsible for monitoring the Infrared input or Front control Keys as well as the Auxiliary
inputs if the Auto Link feature is active.
These power supplies are generally labeled as Always power supplies or Standby power supplies. As an example
A+6V would indicate a +6V power supply that’s always present. If the power supply has an Sby prefix, (example
Sby +6V) this too is always present if the set is plugged into the AC outlet.
The DP-2X power supply Standby voltages are regulated by monitoring the Control +6V which becomes the
Sby +5V after it is regulated by I909.
The Control +6V is generated on the Secondary of T901 pin 10 [7]. The pulse is rectified by D941 and filtered
by C954 and becomes a +6V Power Supply.
REGULATION: Note: Items for the DP-23, 23G and DP-24 are shown in brackets [ ].
The primary route for the Control +6V is to pin 3of I909 and output as Sby. +5V from pin 2.
However, the regulation route is to pin 1of I904. Internally, the LED is illuminated by degrees dependant upon
the Control +6V voltage fluctuations. The internal receiver receives this light and acts as a variable resistor from
pin 4to pin 3ground. This action causes pin 6of I901 to manipulate the internal oscillator within I901. This in
turn causes the frequency of the drive pulse delivered to the Gate of the internal SMOSFET (Switch Metal Oxide
Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) to manipulate the frequency of the pulse generated on the primary of
T901. Pin 6 [3] of T901 is routed to pin 1of I901 which is the Drain of the SMOSFET. The source is connected
internally to pin 2and then to floating ground pin 9 [6] of T901. The floating ground is monitored by three [two]
low ohm resistors, R908, R909 and R910 [R908, R909] to hot ground. Here, the current drain of the internal
SMOSFET is monitored. If this current exceeds a specific value, the voltage developed by these low ohm resis-
tors is routed back into pin 5 which is the Over Current Protection circuit. This pin will inhibit the drive signal to
the gate of the SMOSFET. As soon as the excessive current situation is eliminated, the IC will recover and con-
tinue functioning.
B+ GENERATION FOR THE LOW VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY DRIVER IC:
Vcc for the Driver IC is first generated by the AC input. This voltage is called Start Up Voltage. I901 requires
16V DC to operate normal. However, it will begin operation at 6.8V DC on pin 3of I901.
When AC is applied, AC is routed through the main fuse F901 (a 6 Amp fuse), then through the Line filter L901
to prevent any internal high frequency radiation for radiating back into the AC power line. After passing the fil-
ters it arrives at the main full wave bridge rectifier D901 where it is converted to Raw 150V DC voltage to be
supplied to the power supply switching transformer T901 pin 2[1].
However, one leg of the AC is routed to a half wave rectifier D904 where it is rectified, routed through R906 and
R907 (both a 68K ohm resistor), filtered by C911, clamped by a 30V Zener D907 and made available to pin (3)
of I901 as start up voltage. When this voltage reaches 6.8Vdc, the internal Regulator of I901 is turned On and
begins the operation of I901.
When the power supply begins to operate by turning on and off the internal Switch MOS FET, the Raw 150V DC
routed through T901, to I901 in on pin 1(Drain) and out on pin 2which is the Source. The Source of the internal
Switch MOS FET is routed out of pin 2through three low ohm resistors to hot ground. When the internal Switch
MOS FET turns on, it causes the transformer to saturate building up the magnet field. When the internal Switch
MOS FET turns off, the magnet field collapses and the EMF is coupled over to the secondary windings, as well
as the drive windings. The drive windings at pin 8 [5] of T901 produce a run voltage pulse which is rectified by
D905, filtered by C911 then routed clamped by D907 and now becomes run voltage (16V) for I901 pin 3.
Note too that Hot Ground is the Negative Leg of the bridge rectifier D901 and the Floating Ground is pin 9 [6] of
T901.