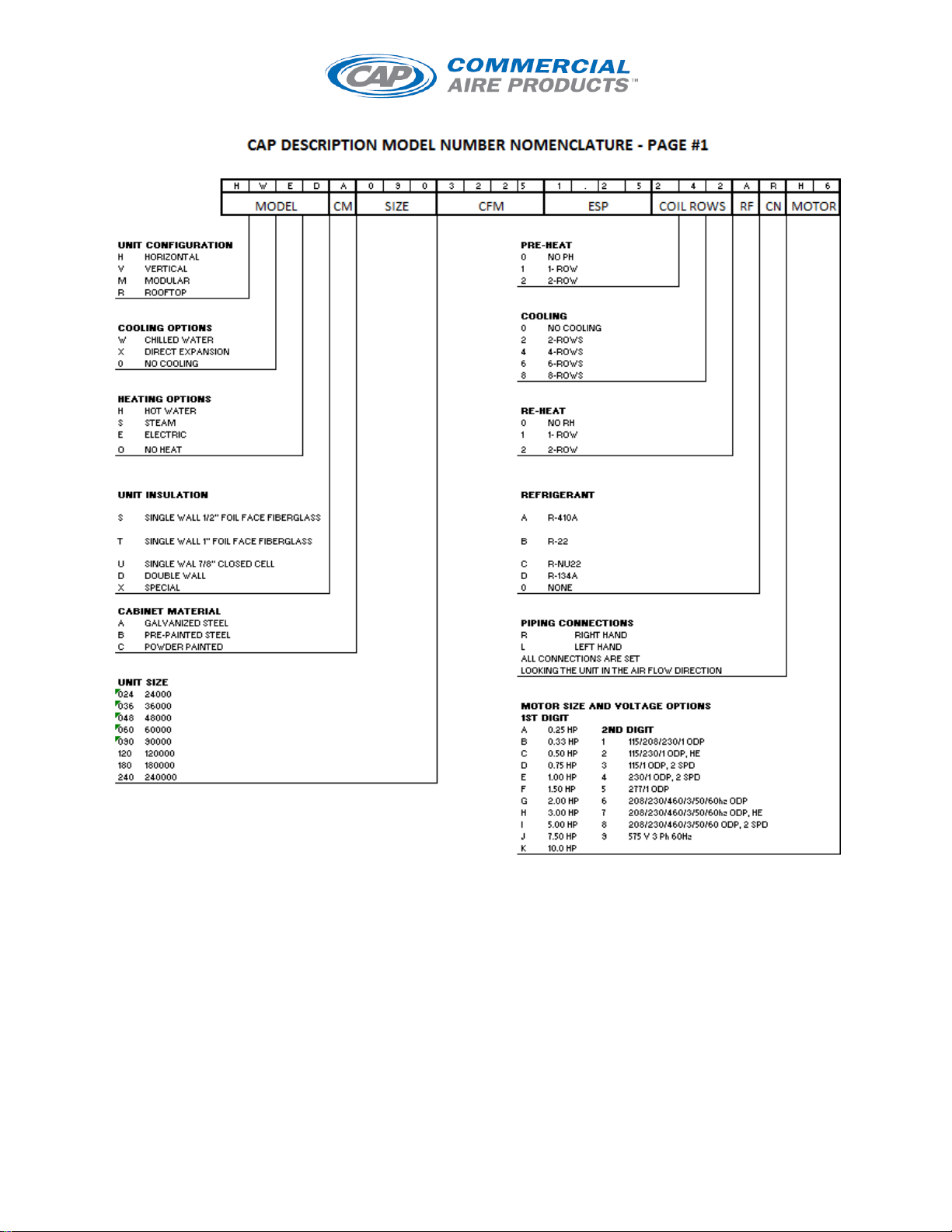
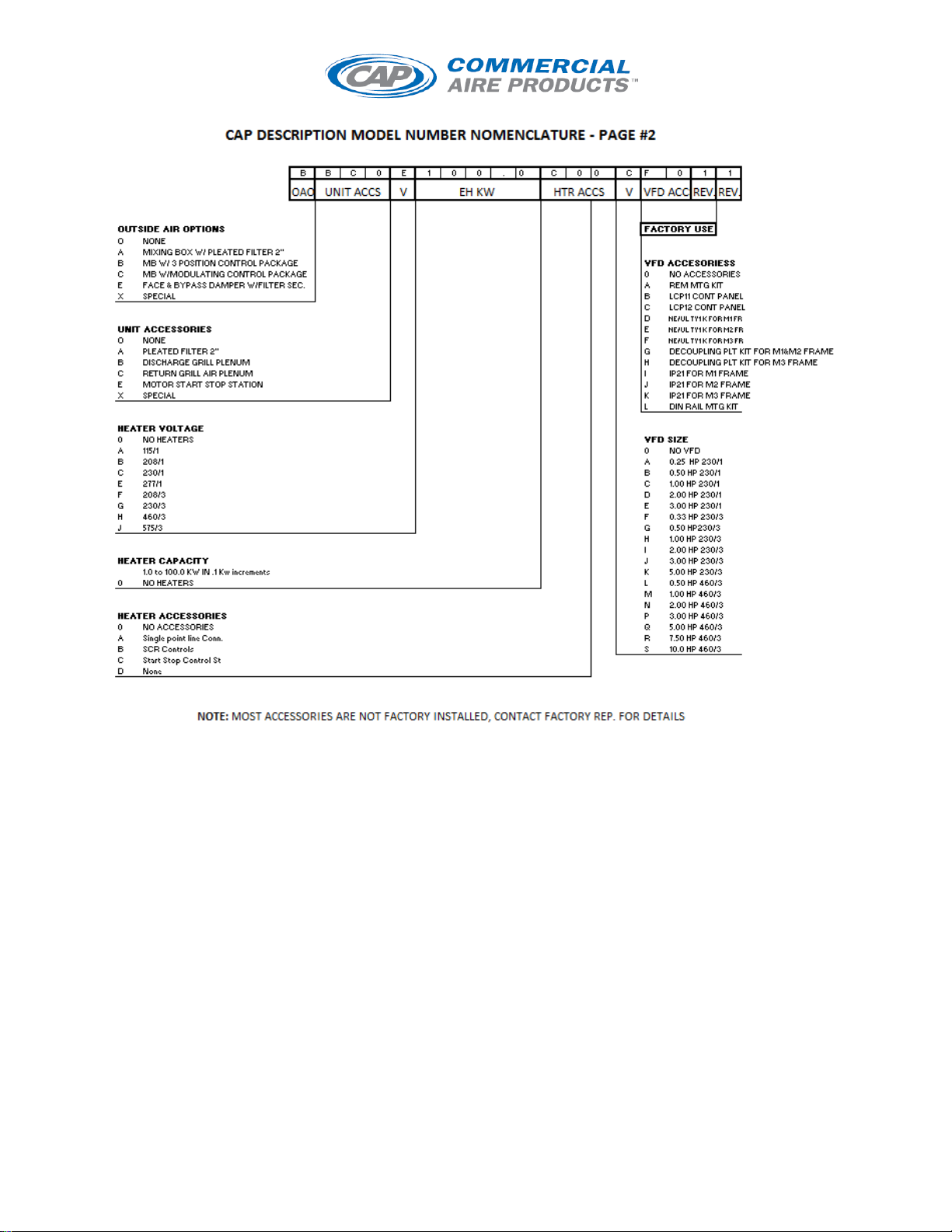
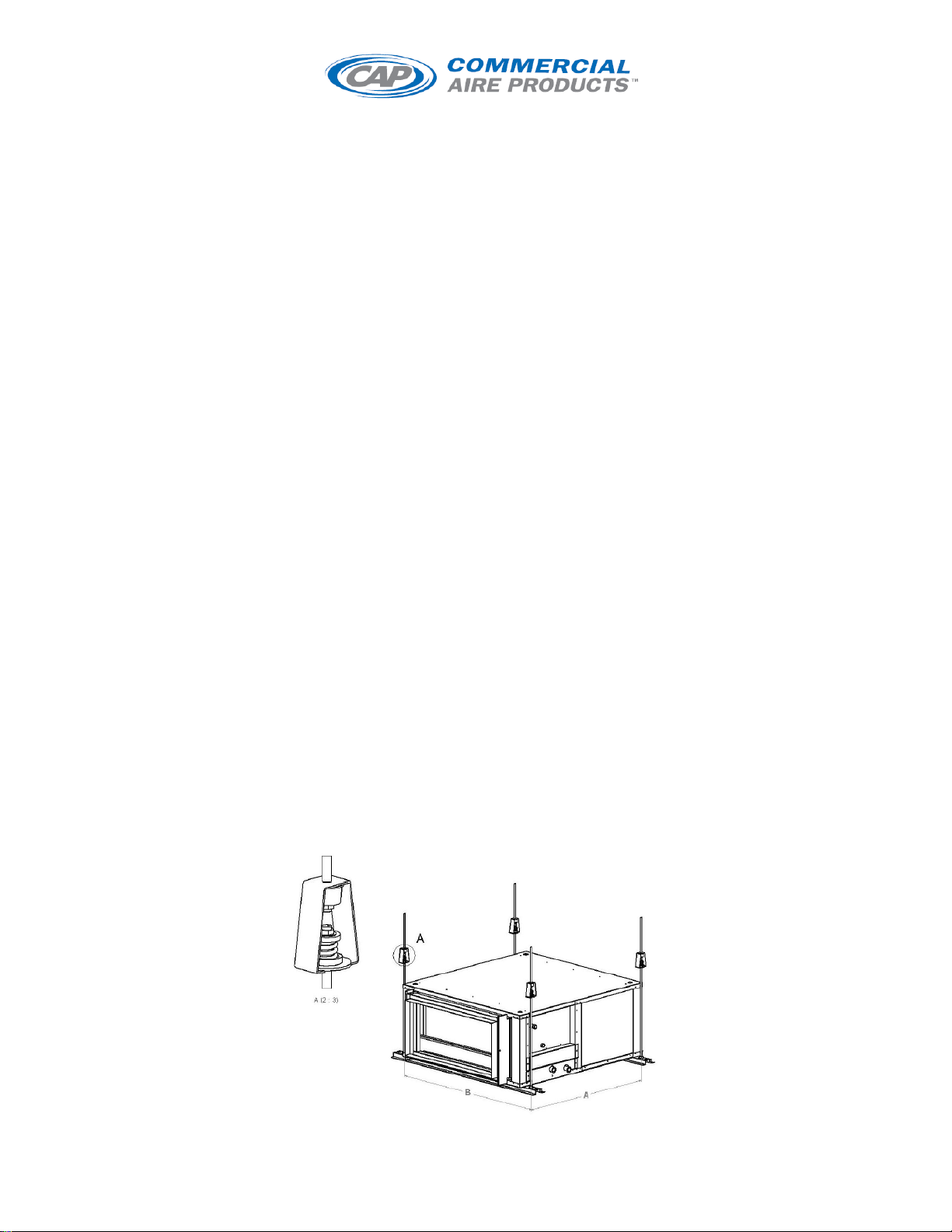
I/O MANUAL Horizontal/Modular/Vertical/Rooftop AHU 2015pg. 3
COMMERCIAL AIRE PRODUCTS 501 Terminal Road, Fort Worth TX 76106 Tel: 817-624-0820
INTRODUCTION
READ THE ENTIRE INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL. OTHER IMPORTANT
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ARE PROVIDED THROUGHOUT THIS MANUAL.
The following information is to be used by the installer as a guide. Since each installation is unique, only
general topics are covered. To order in which topics are presented may not be those required by the
actual installation.
This guide does not supersede or circumvent any applicable national, state or local code.
The installer must read the entire contents of this guide and develop a thorough understanding before
beginning installation.
Note: Due to continued product research and development, Commercial Aire Products reserves the right
to discontinue or change without notice, any or all specifications or designs without incurring
obligations.
INSPECTION
Receiving Unit
When received, the unit should be checked for damage that might have occurred in transit. If damage is
found it should be noted on the carrier’s Freight Bill. A request for inspection by carrier’s agent should
be made in writing at once. All our sales are FOB our warehouse in Fort Worth Texas and any in transit
damage is carrier responsibility.
Nameplate should be checked to ensure the correct model sizes and voltages have been received to
match the job requirements.
If repairs must be made to damaged goods, then the factory should be notified before any repair action
is taken in order to protect the warranty. Certain equipment alteration, repair, and manipulation of
equipment without the manufacturer’s consent may void the product warranty. Contact the MORTEX
MANUFACTURING Warranty Department for assistance with handling damaged goods, repairs, and
freight claims: (817) 624-0820 ext 225.
Note: Upon receipt check shipment for items that ship loose such as filters and remote sensors. Consult
order and shipment documentation to identify potential loose-shipped items. Loose-shipped items may
have been placed inside unit cabinet for security. Installers and owners should secure all doors with
locks or nuts and bolts to prevent unauthorized access
Thoroughly inspect all packages upon receipt of product. Ensure pallet(s) have not been dropped,
crushed or punctured. Inspect all contents for damage. If damage is found, immediately file a claim with
the delivering freight carrier
Storage
This equipment is not suitable for outdoor storage. If installation will not occur immediately following
delivery, store equipment in a dry protected area away from construction traffic and in the proper
orientation as marked on the packaging with all internal packaging in place. Secure all loose-shipped
items.