Preface: How to Use this Guide
This document contains recommendations and best practices for setting up a Dolby Atmos®home theater
system. The guidelines are intended to cover a typical home theater in a standard listening space. This
document does not cover all possible variables, room layouts, and factors for specific installations;
adaptations and deviations may be required in particular situations.
Dolby Atmos is a highly flexible solution, so minor variations from these recommendations are unlikely to
materially detract from the immersive Dolby Atmos experience.
1. Background on Dolby Atmos
Many leading Hollywood movies, including recent Academy Award®winning films, are presented in Dolby
Atmos, as this revolutionary sound technology allows filmmakers unprecedented realism and creative
freedom. With Dolby Atmos, content creators can precisely place and move sounds almost anywhere,
including overhead, to create an immersive listening experience.
Dolby Atmos technology is now available for the home and produces a listening experience never before
experienced in a home theater. You’ll get a great immersive experience, no matter what kind of Dolby
Atmos home theater setup you have. Dolby Atmos content is mixed as audio objects instead of traditional
channels. This means the content is not tied to any specific playback configuration. Further, the
technology automatically adapts the object audio to take full advantage of the number and placement of
your speakers, from systems with five speakers on the floor and two speakers producing overhead sound
up to a Dolby Atmos system with as many as 24 speakers on the floor and 10 overhead speakers.
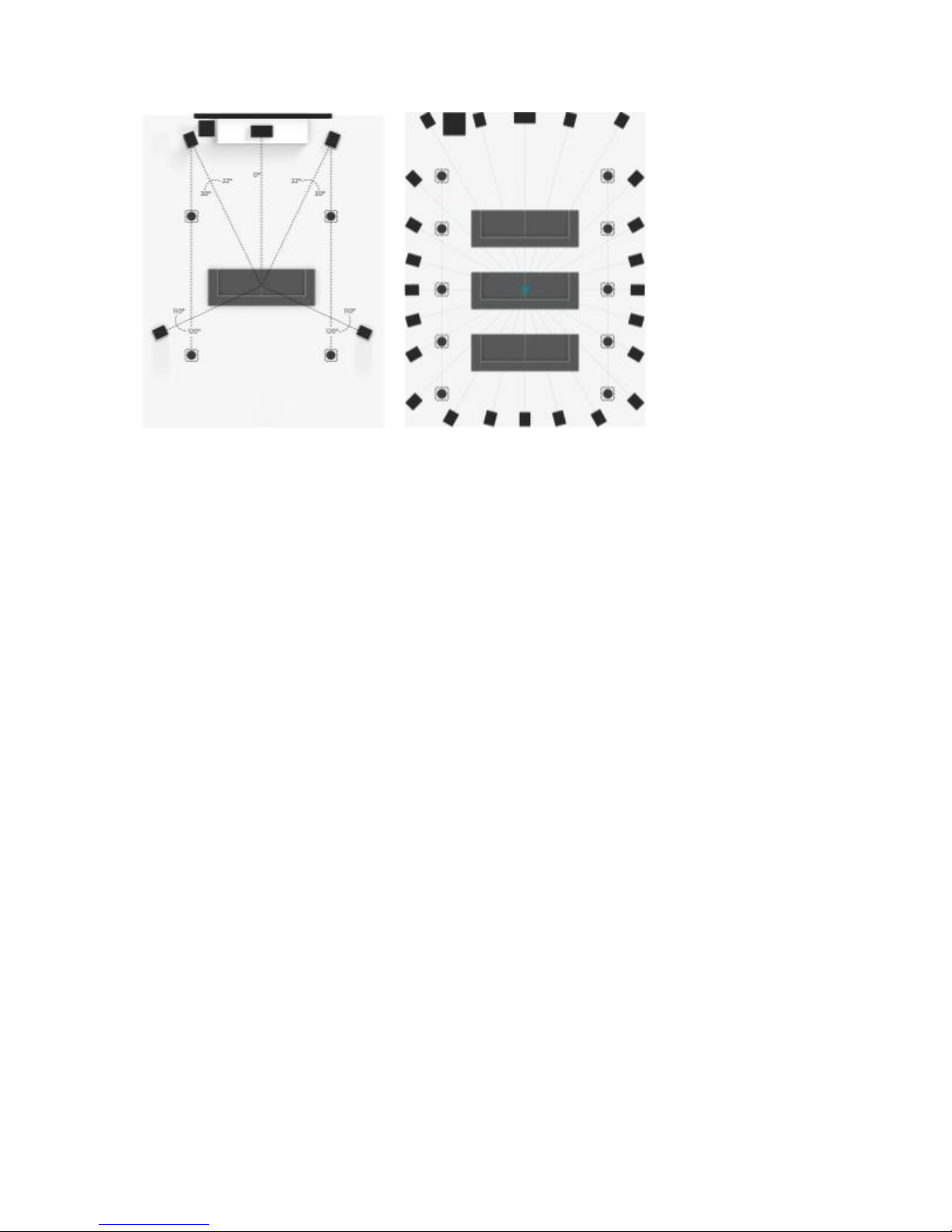
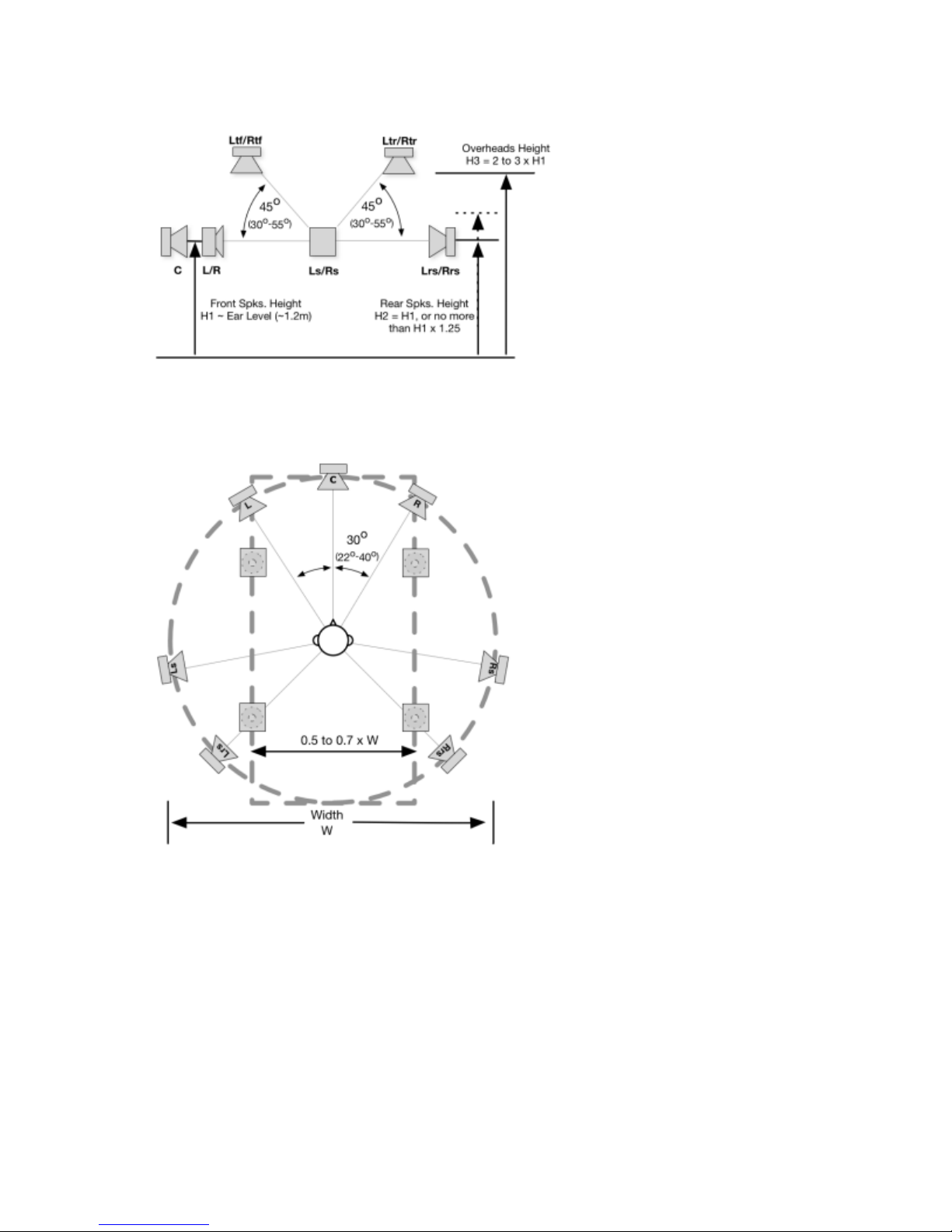
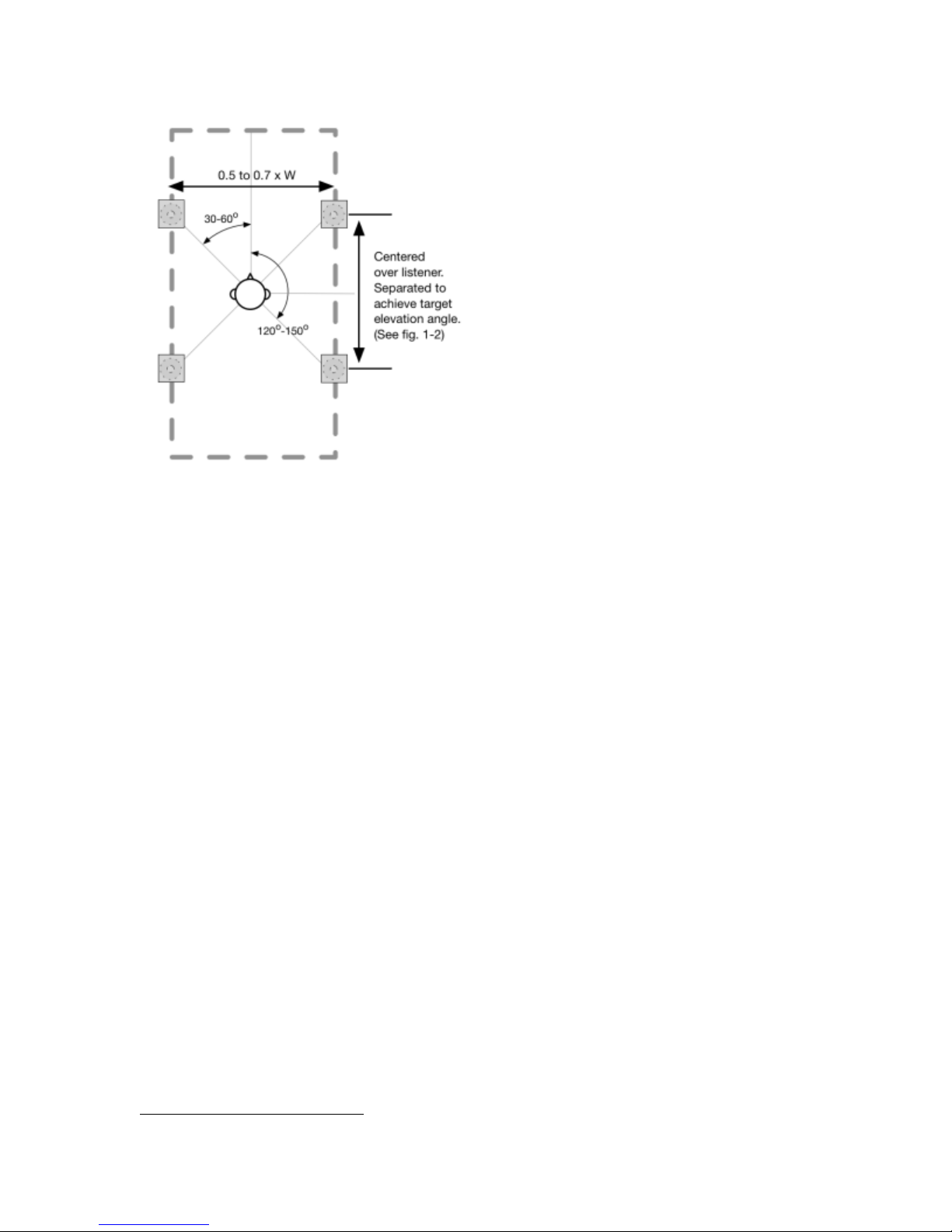
The naming of Dolby Atmos speaker configurations is based on the standard nomenclature (stereo, 5.1,
and 7.1) but adds a number at the end to specify the number of height speakers in the playback system.
For example, when we refer to a 5.1.4 setup, the 5 indicates the left, center, right, left surround, right
surround, left rear surround, and right rear surround speakers; the .1 indicates the subwoofer; and the .4
indicates the four speakers that play overhead sound (left top front, right top front, left top rear, and right
top rear).