CONTENTS
P05
P06
P07
Outline
Chapter 1 1 4-Stroke Engines
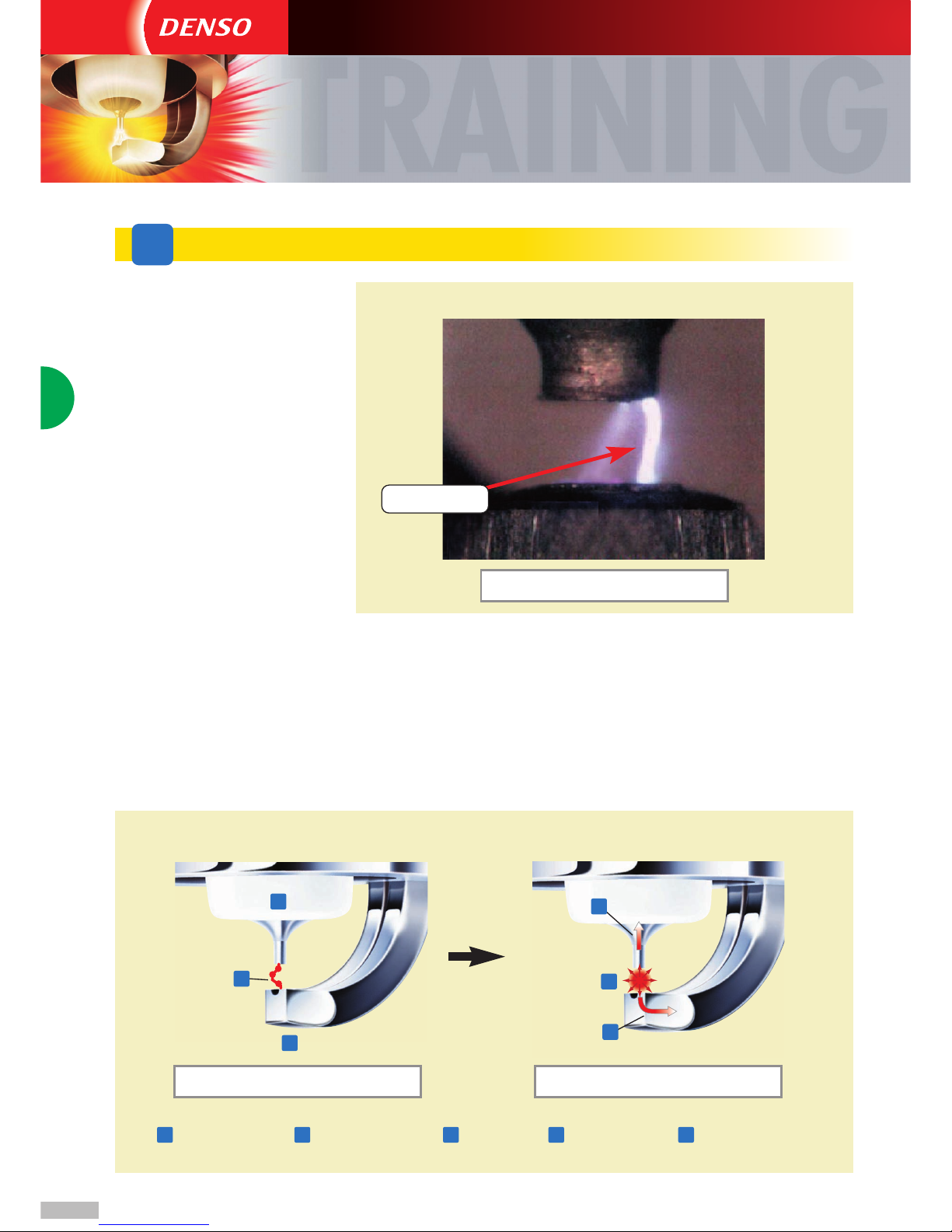
2 Role of the ignition System
3 Ignition System Configuration
P08
P08
4 Types of Ignition System
5 Comprehensive Test
P35
P38
P39
Basics of
Ignition
Chapter 3 1 High Voltage Generation
2 High Voltage Control
3 Ignition Timing
P39
P40
4 Ignition Order
5 Comprehensive Test
P09
P13
P15
P25
Spark plugs
Chapter 2
The PLUGS CONFIGURATIONS •••••••••••••••••••••••••••P41
IGNITION TECH Q&A
FAKE PLUG
LINEUP •••••••••••••••••••••••••P61
Q&A
Q&A
1 Spark and ignition
2 Structure
3 Types
4 Heat Range
P27
P29
P31
P34
5 Service Life
6 How to read Sperk Plugs
7 Troubleshooting
8 Comprehensive Test
Q1. What type of spark plug is the ? P43
Q2. Why was the center electrode of the reduced to only 0.4 mm? P44
Q3. How is the iridium tip of the welded to the electrode? P45
Q4. What advantages does the U-groove in the ground electrode have? P46
Q5. What advantages does the tapered cut in the ground electrode have? P47
Q6. What are the differences between and iridium spark plugs
offered as genuine parts by car manufacturers? P48
Q7. What type of material is used to produce the electrode employed for ? P49
Q8. Why can iridium now be used in electrodes? P50
Q9. In what other fields is iridium commonly used for? P50
Q10. Is the tip in the made of pure iridium? P51
Q11. Tell me about the firing performance of the . P52
Q12. Tell me about the required voltage in the . P53
Q13. What happens at idling when an is used? P54
Q14. What happens to fuel consumption when is used? P55
Q15. Does engine performance improve when is used? P56
Q16. Can spark plugs of other brand-names be substituted with ? P57
Q17. What type of cars can current be fitted with ? P58
Q18. Does the engine need to be specially set when fitting ? P58
Q19. How do I select the correct heat-range when fitting to my vehicle? P59
Q20. How would compare against high-performance spark plugs
offered by other spark plug manufacturers? P59
Q21. Is there anything I need to be aware of when fitting ? P60
Q22. Can the gap be adjusted?
Can I use any spark plug cleaners with the ? P60
Q1. What type of spark plug is the ? P66
Q2. What makes the ignitability of so good? P67
Q3. How does the superior ignitability of influence combustion? P68
Q4. How is the iridium tip of the welded to the electrode? P69
Q5. What is the difference between and ? P70
Q6. What patented technologies are used with ? P70
Q7.
What type of material is used to produce the electrode employed for
? P71
Q8. Why can iridium now be used in electrodes? P72
Q9. In what other fields is iridium commonly used for? P72
Q10. Is the tip in the made of pure iridium? P73
Q11. Tell me about the ignitability of the . P74
Q12. Tell me about the required voltage in the . P75
Q13. What happens at emission when an is used? P76
Q14. What happens to fuel consumption when is used? P77
Q15. Does engine performance improve when is used? P78
Q16. How does the compare to the 0.6mm iridium plugs,
platinum plugs and normal spark plugs? P79
Q17. Can spark plugs of other brand-names be substituted with ? P80
Q18. Does the engine need to be specially set when fitting ? P81
Q19. How do I select the correct heat-range when fitting to my vehicle? P81
Q20. How does the compare to iridium plugs from other makers? P82
Q21.
Can be used to replace plugs with 2, 3 or 4 ground electrodes?
P83
Q22. Is there anything I need to be aware of when fitting ? P84
Q23. Can the gap be adjusted?
Can I use any spark plug cleaners with the ? P85
Q24. What plugs are in the lineup? P86
SPECIFICATIONS ••••••••••••••••P63
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••P93
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••P97
SPECIFICATIONS •••••••••••P87
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••P88
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••P89
SPECIFICATIONS •••••••••••P91
CROSS REFERENCE ••••••••P92
DENSO Spark Plugs Package Lineup •••••••••••••••••••••P65
04