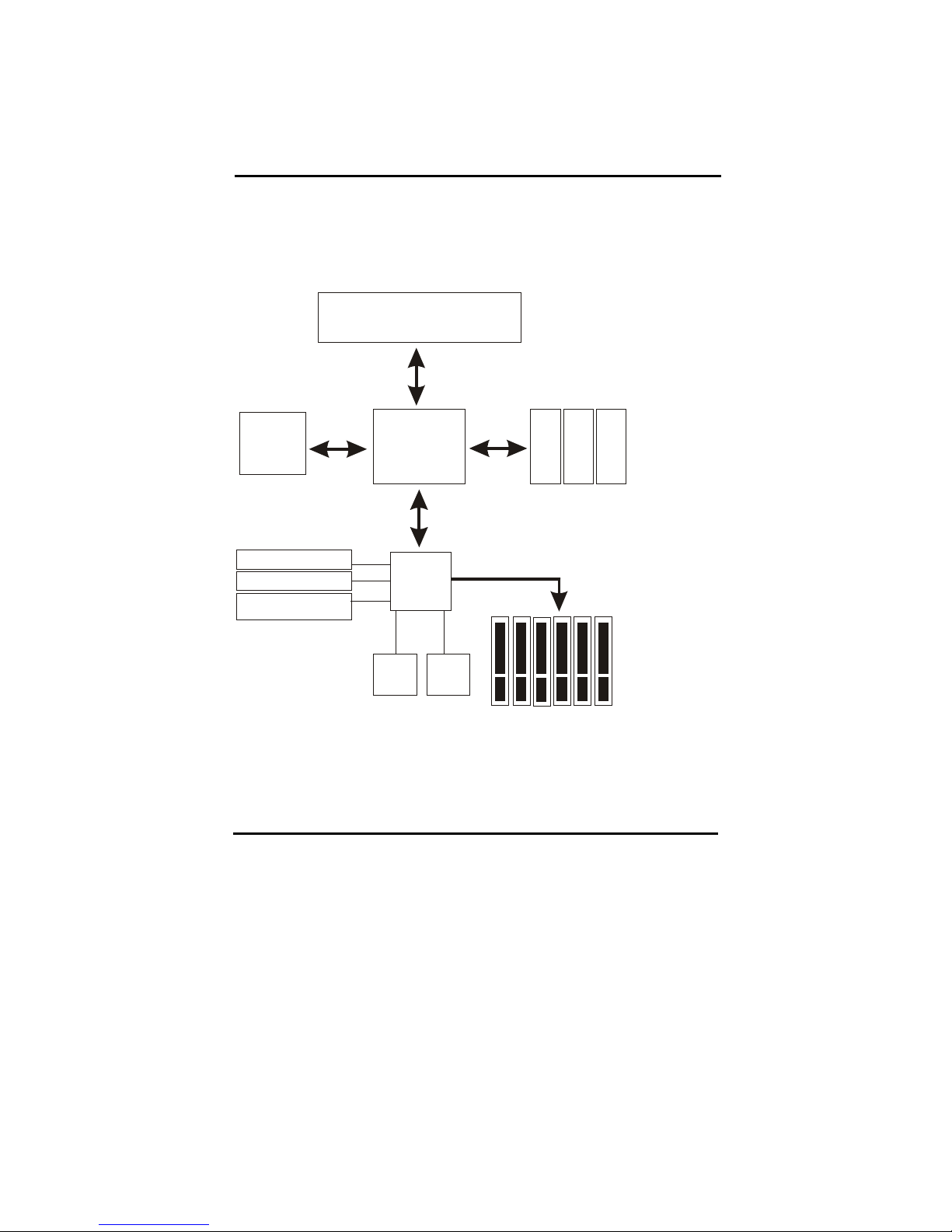
II
Chapter 4 The BIOS…..………………………………………28
4-1 Updating the BIOS……………………………………………………29
4-2 The CMOS Memory…………………………………………………30
4-3 The BIOS Setup Pages………………………………………………32
4-3-1 Standard CMOS Setup………………………………………………35
4-3-2 BIOS Features Setup…………………………………………………39
4-3-3 Chipset Features Setup………………………………………..……43
4-3-4 Integrated Peripherals………………………………………..……...48
4-3-5 Power Management Setup………………………………………….53
4-3-6 PNP/PCI Configuration Setup……………………………………….57
4-3-7 PC Health Status……………………………………………………59
4-3-8 Frequency/Voltage Control.…………………………………………60
4-3-9 Passwords Setting……………………………………………………..61
Chapter 5 Appendix………………………………….………63
5-1 Memory Map………………………………………………….………63
5-2 I/O Map………………………………...….………………………….64
5-3 Time & DMA Channels Map…………………………………………65
5-4 Interrupt Map………………………………………….……………...66
5-5 RTC & CMOS RAM Map………………………………………….67
5-6 ISA I/O Address Map……………………………………………..68
Chapter 6 Q & A…………………………………………………………………70
Important Warnings:
STOP
WARNING: NEVER run the processor without the heatsink properly and firmly
attached. This will damage the processor within SECONDS. Also do NOT try to use
Pentium Heatsinks, these will NOT fit and do NOT provide adequate cooling.
STOP
WARNING: Make sure your power supply can deliver the power your system needs.
We recommend AT LEAST a 250W power supply. Even better, get a 300W power
supply, especially when using many peripherals.