2
CONTENTS
1.0 IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION.......................................................3
2.0 GENERAL INFORMATION.....................................................................4-5
2.1 Introducon..........................................................................................4
2.2 Agency Performance Audit Tesng Noce...........................................4
2.3 Importance of a Quality Installaon.....................................................4
2.4 System Sizing and Selecon..................................................................4
2.5 Importance of Proper Indoor/Outdoor Match-Ups..............................5
2.6 Checking Product Received...................................................................5
2.7 Compressor Break-In Noce ................................................................5
3.0 UNIT SPECIFICATIONS..........................................................................5-6
3.1 Model Number Nomenclature and Available Models..........................5
3.2 Electrical and Physical Data ..................................................................6
4.0 INSTALLATION...................................................................................7-24
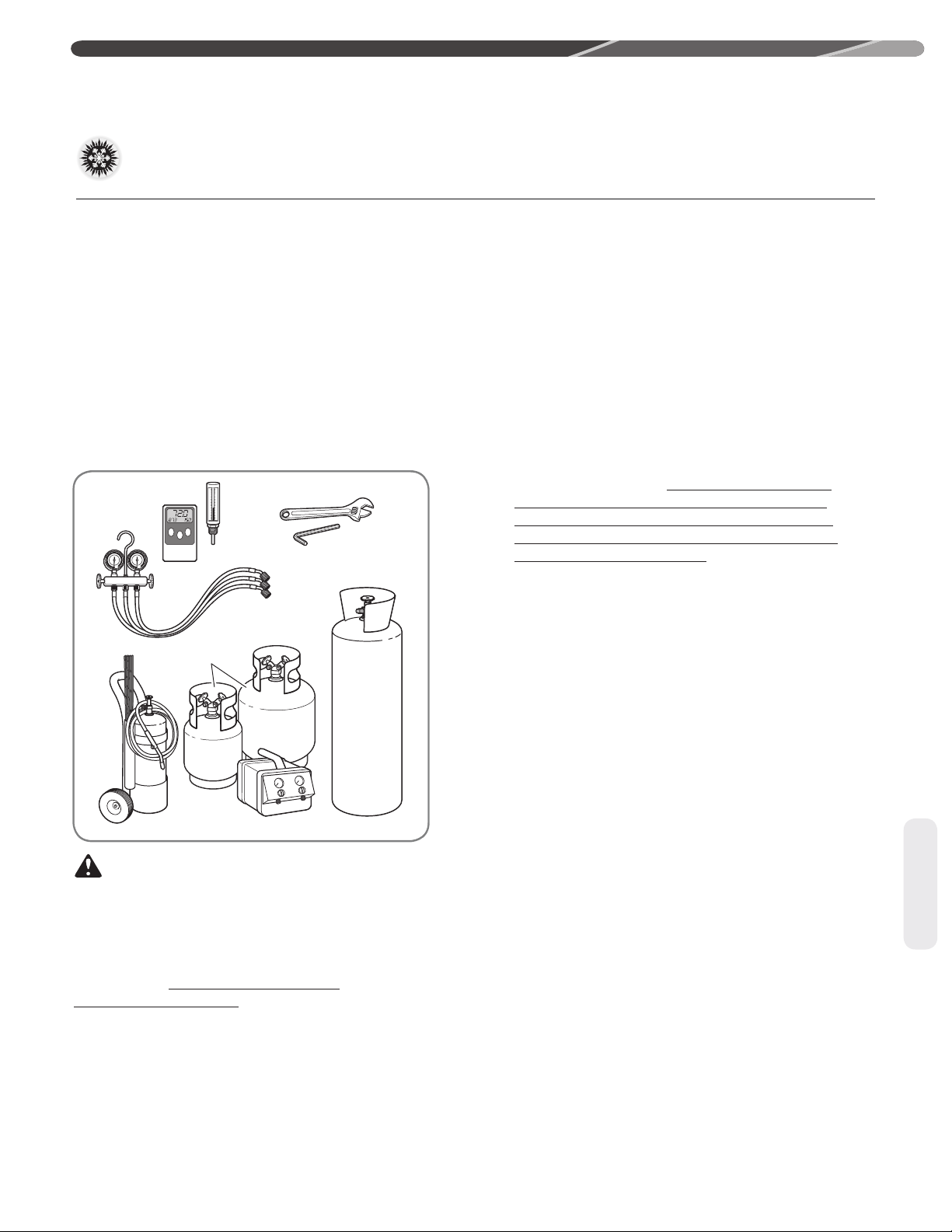
4.1 Tools & Refrigerant .............................................................................7
4.1.1 Tools Required for Installing & Servicing R-410A Models...........7
4.1.2 Specicaons of R-410A..............................................................7
4.1.3 Quick Reference Guide for R-410A..............................................7
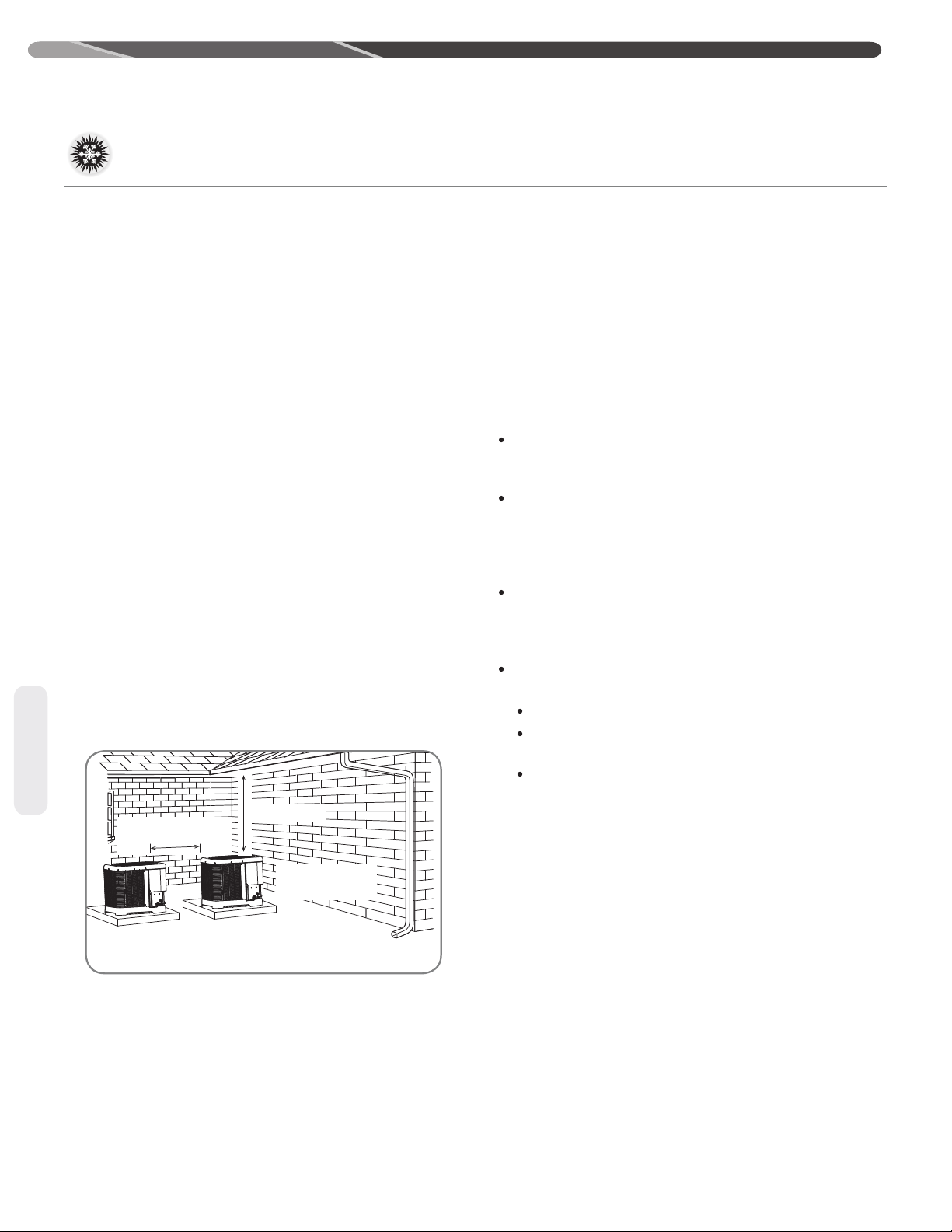
4.2 Choosing a Locaon.............................................................................8
4.2.1 Allowable Clearances..................................................................8
4.2.2 Operaonal Issues Related to Unit Locaon...............................8
4.2.3 Corrosive Environments..............................................................9
4.2.4 Customer Sasfacon Issues.......................................................9
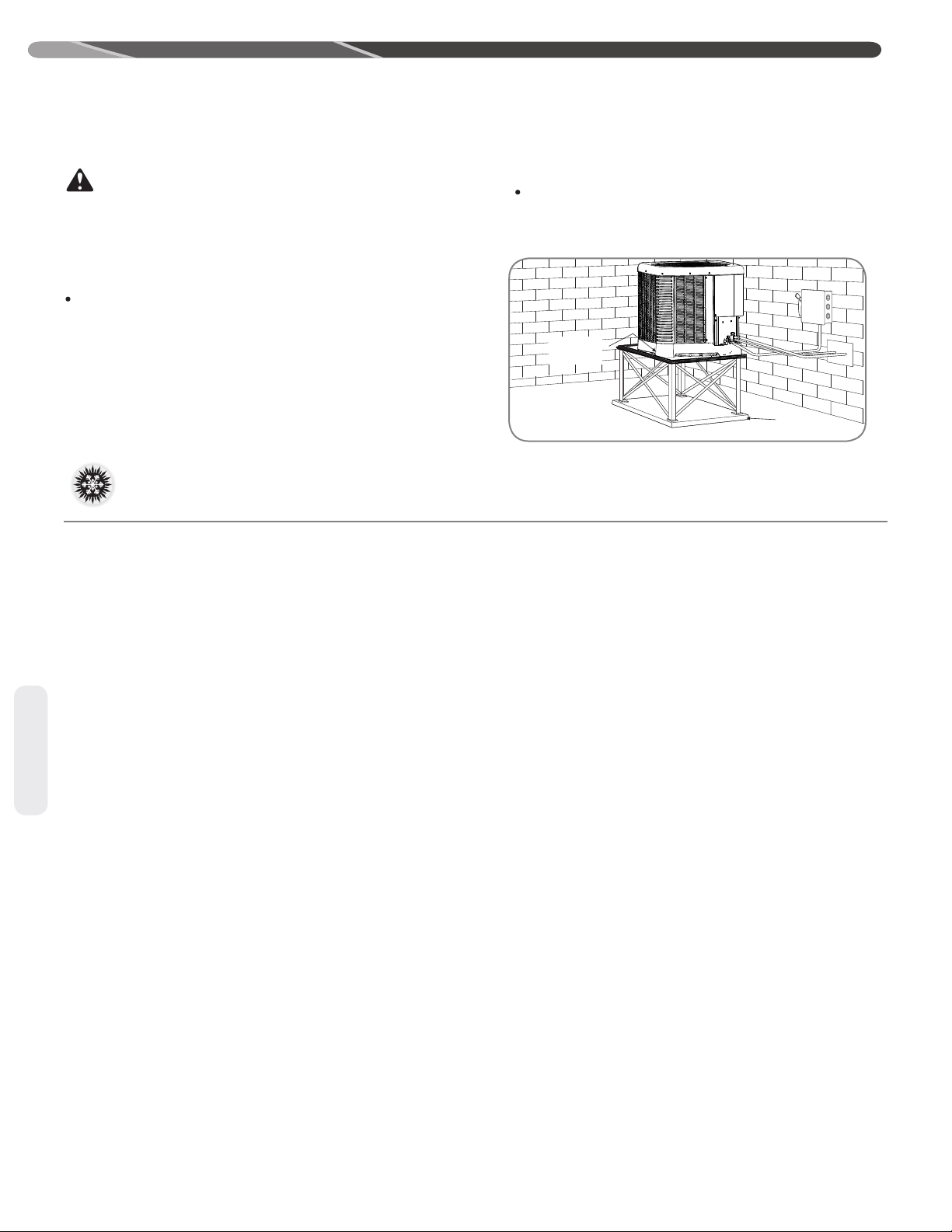
4.3 Mounng Unit......................................................................................9
4.3.1 Unit-Mounng Methods ............................................................9
4.3.2 High Wind and Seismic Tie-Down Methods ................................9
4.3.3 Elevang Unit ...........................................................................10
4.4 Refrigerant Line Set Selecon............................................................10
4.4.1 Replacing Exisng Systems.......................................................10
4.4.2 Line Set Applicaon .................................................................10
4.4.2.1 Oil Return to Compressor ...........................................10
4.4.2.2 Refrigerant Migraon During O Cycle.......................10
4.4.2.3 Maximum Liquid Pressure Drop..................................11
4.4.2.4 Liquid Line Refrigerant Flashing..................................11
4.4.2.5 Compressor Oil Level Adjustment...............................11
4.4.2.6 Capacity Losses ...........................................................11
4.4.3 Line Set Length and Fing Losses ..........................................11
4.4.4 Liquid Line Selecon ...............................................................12
4.4.5 Sucon Line Selecon.............................................................12
4.5 Line Set Installaon ...........................................................................15
4.5.1 Important Tubing Installaon Pracces...................................15
4.5.2 Relave Locaon of Indoor and Outdoor Units.......................16
4.5.2.1 Indoor and Outdoor Unit Near Same Level................16
4.5.2.2 Outdoor Unit Below Indoor Unit................................17
4.5.2.3 Outdoor Unit Above Indoor Unit ...............................18
4.5.3 Tubing Connecons ................................................................19
4.6 Inial Leak Tesng.............................................................................20
4.7 Evacuaon.........................................................................................20
4.8 Final Leak Tesng ..............................................................................21
4.9 Control Wiring...................................................................................21
4.9.1 EcoNetTM Communicaons ......................................................21
4.9.2 EcoNetTM Control Center Installaon .......................................21
4.9.3 EcoNetTM Communicaon Wiring Connecons .......................21
4.9.4
Convenonal 24VAC Thermostat Control Wiring Connecons
........22
4.10 Power Wiring.....................................................................................23
4.11 Grounding..........................................................................................24
5.0 SYSTEM START-UP AND REFRIGERANT CHARGING...........................24-28
5.1 System Start-Up Overview.................................................................24
5.2 Inial Power Up and EcoNetTM Communicaon Vericaon.............24
5.3 EcoNetTM Control Center Set-Up ........................................................24
5.4 Inial System Set-Up .........................................................................24
5.5
Entering Charging Mode Using EcoNet
TM
Control Center Service Menu
.........25
5.6
Entering Charging Mode When Using a Convenonal 24VAC Thermostat
...25
5.7 Indoor Air-Flow Vericaon ..............................................................26
5.8 Refrigerant Charging .........................................................................26
5.8.1
Measurement Device Set-Up ..................................................27
5.8.2 Preliminary Charging by Weight ..............................................27
5.8.3 Preliminary Charging by Pressures ..........................................27
5.8.4 Final Charging by Liquid Subcooling ........................................28
5.8.5 R-410A Temperature Pressure Chart .......................................28
5.9 Compleng Installaon .....................................................................28
6.0 NORMALSEQUENCEOF OPERATION..................................................29-30
6.1 Cooling Mode.....................................................................................29
6.2 On-Demand Cooling Dehumidicaon..............................................29
6.3 Low Ambient Cooling Operaon .......................................................29
6.4
Sequence of Operaon for Convenonal 24VAC Thermostat Controls
...........30
7.0 COMPONENTS AND CONTROLS......................................................30-36
7.1 Accumulator.......................................................................................30
7.2 Choke/Indoor ....................................................................................30
7.3 Coil Temperature Thermistor.............................................................30
7.4 Compressor.........................................................................................31
7.5 Compressor Sump Thermistor ..........................................................31
7.6 Discharge Line Thermistor ................................................................31
7.7 EcoNetTM Variable Speed Outdoor Control (VSODC)..........................32
7.7.1 Board Features and Connecons .............................................32
7.7.2 TEST & SW2 Buons ................................................................33
7.7.3 Memory Card ...........................................................................33
7.7.4 Menu Structure ........................................................................33
7.7.5 Replacement of the VSODC ......................................................33
7.8 Filter & Ferrite Rings ...........................................................................34
7.9 High Pressure Control .........................................................................34
7.10 Outdoor Ambient Temperature Thermistor ......................................34
7.11 Outdoor Fan Motor ............................................................................35
7.12 Outdoor Fan Blade .............................................................................35
7.13 Power Inverter Compressor Control ..................................................35
7.14 Sucon Pressure Transducer ..............................................................36
7.15 Sucon Temperature Thermistor .......................................................36
8.0 ACTIVE SYSTEM PROTECTION FEATURES..........................................37-39
8.1 Minimum Run Timer ..........................................................................37
8.2 Oil Return Cycle ..................................................................................37
8.3 Oil Diluon .........................................................................................37
8.4 O-Cycle Refrigerant Migraon – Stator Heat ..................................37
8.5 High Discharge Temperature ..............................................................37
8.6 High Discharge Pressure .....................................................................37
8.7 Low Sucon Pressure/Loss of Charge ................................................38
8.8
Compressor Shut-Down Sequence for High or Low Refrigerant Pressure Fault
....38
8.9 Overcurrent and Current Imbalance ..................................................38
8.10 Compressor Operaon Outside Envelope .........................................38
8.11 Over and Under Voltage .....................................................................39
8.12 Inverter Over Temperature ................................................................39
8.13 Controls and Communicaon Malfuncon .......................................39
8.14 Sensor Failure Default Operaon .......................................................39
8.15 Exing Acve Protecon Lock-Out Mode ..........................................39
9.0 DIAGNOSTICS AND TROUBLESHOOTING.........................................40-66
9.1 Fault Recall Procedure .......................................................................40
9.2 Compressor/Fan Motor Test Mode ...................................................40
9.3 Status and Diagnosc Codes ..............................................................41
9.4 Acve Protecon Fault Details ..........................................................50
9.5 Electrical Checks Flowchart ...............................................................56
9.6 Cooling Mechanical Checks Flowchart .............................................57
9.7 Checking Transducers and Temperature Sensors ..............................58
9.8 General Troubleshoong Guide ........................................................60
9.9 Service Analyzer Charts .....................................................................61
9.10 Troubleshoong Tips .........................................................................66
10.0 OUTDOOR UNIT MAINTENANCE .........................................................67
10.1 Outdoor Coil Cleaning .....................................................................67
10.2 Cabinet Cleaning and Care ..............................................................67
10.3 Motor Lubricaon ...........................................................................67
10.4 Replacement Parts ..........................................................................67
11.0 WIRING DIAGRAM ..............................................................................68
12.0 APPENDIX ......................................................................................69-70
12.1 Agency Performance Audit Test Instrucons ....................................69
Contents