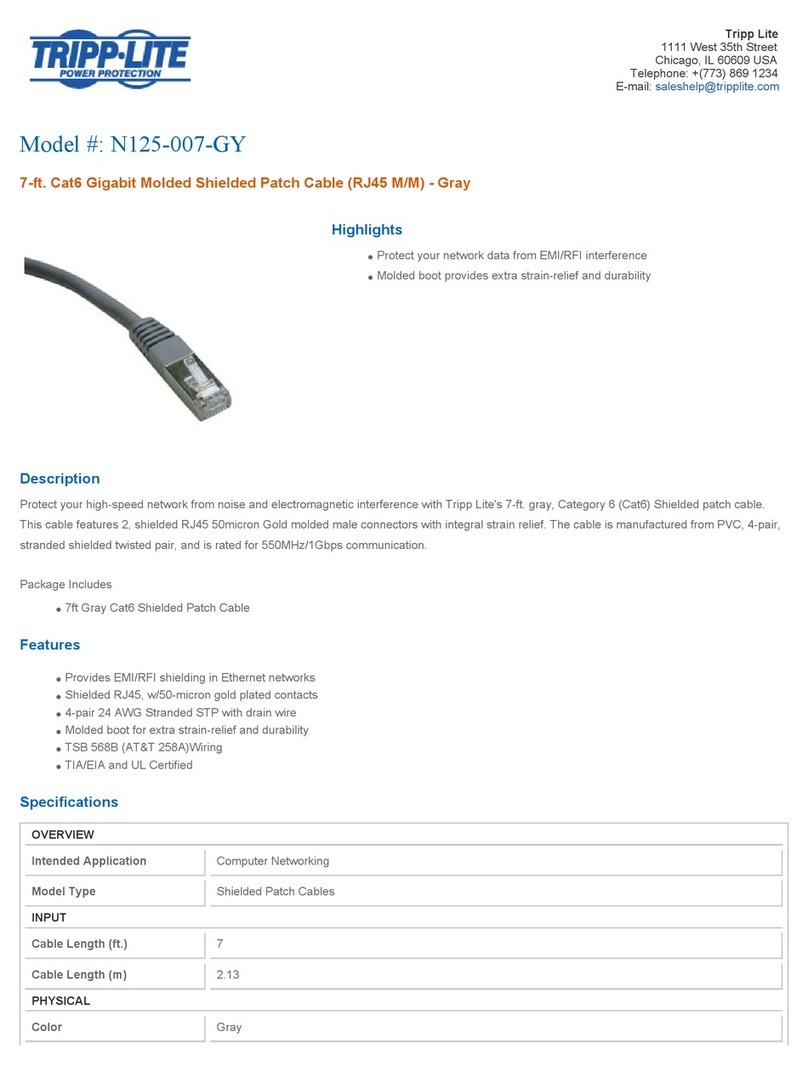
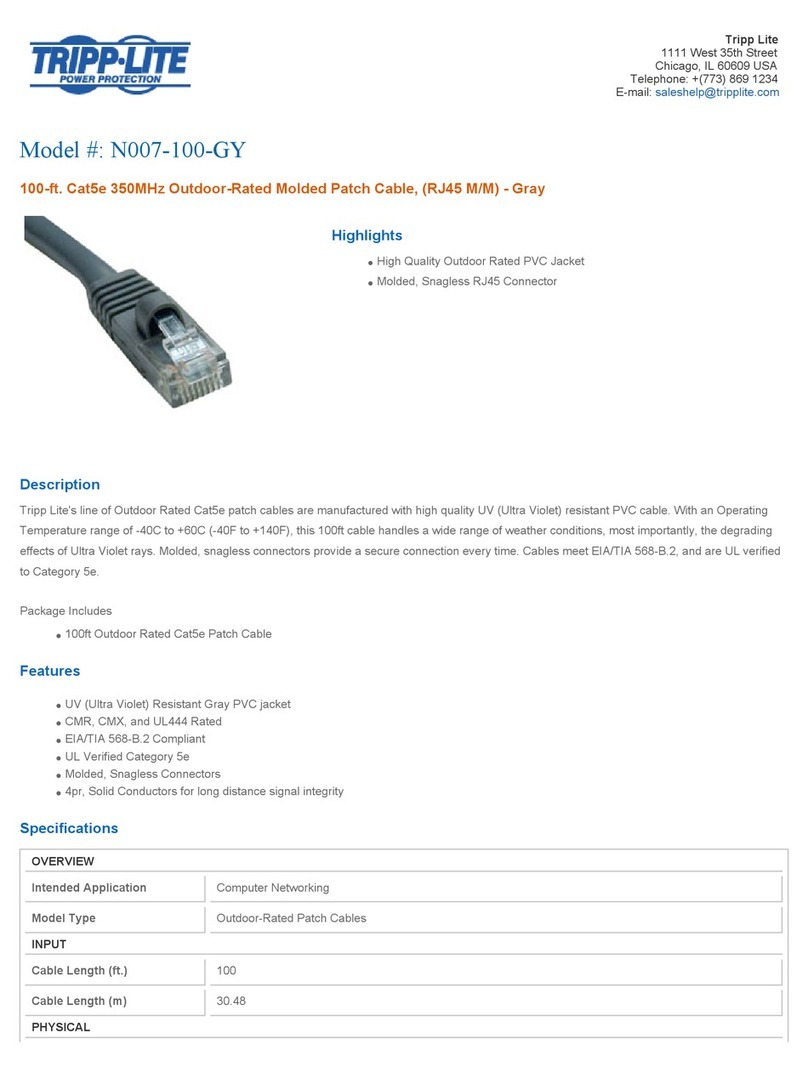
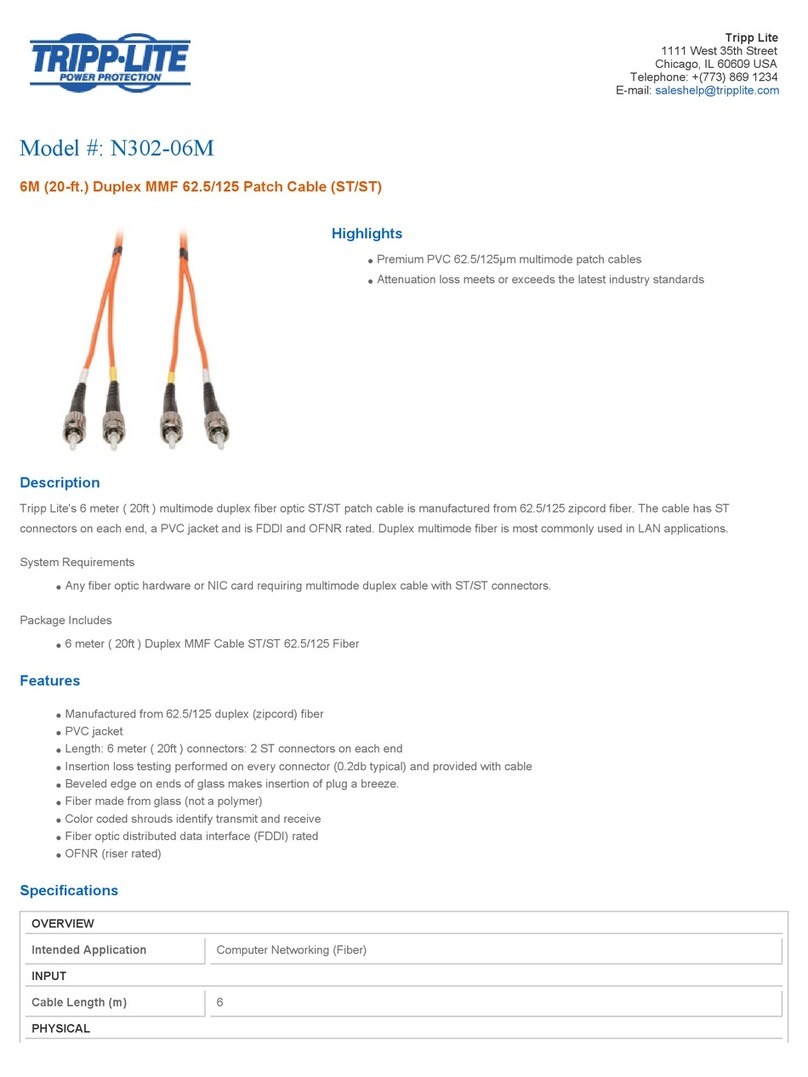
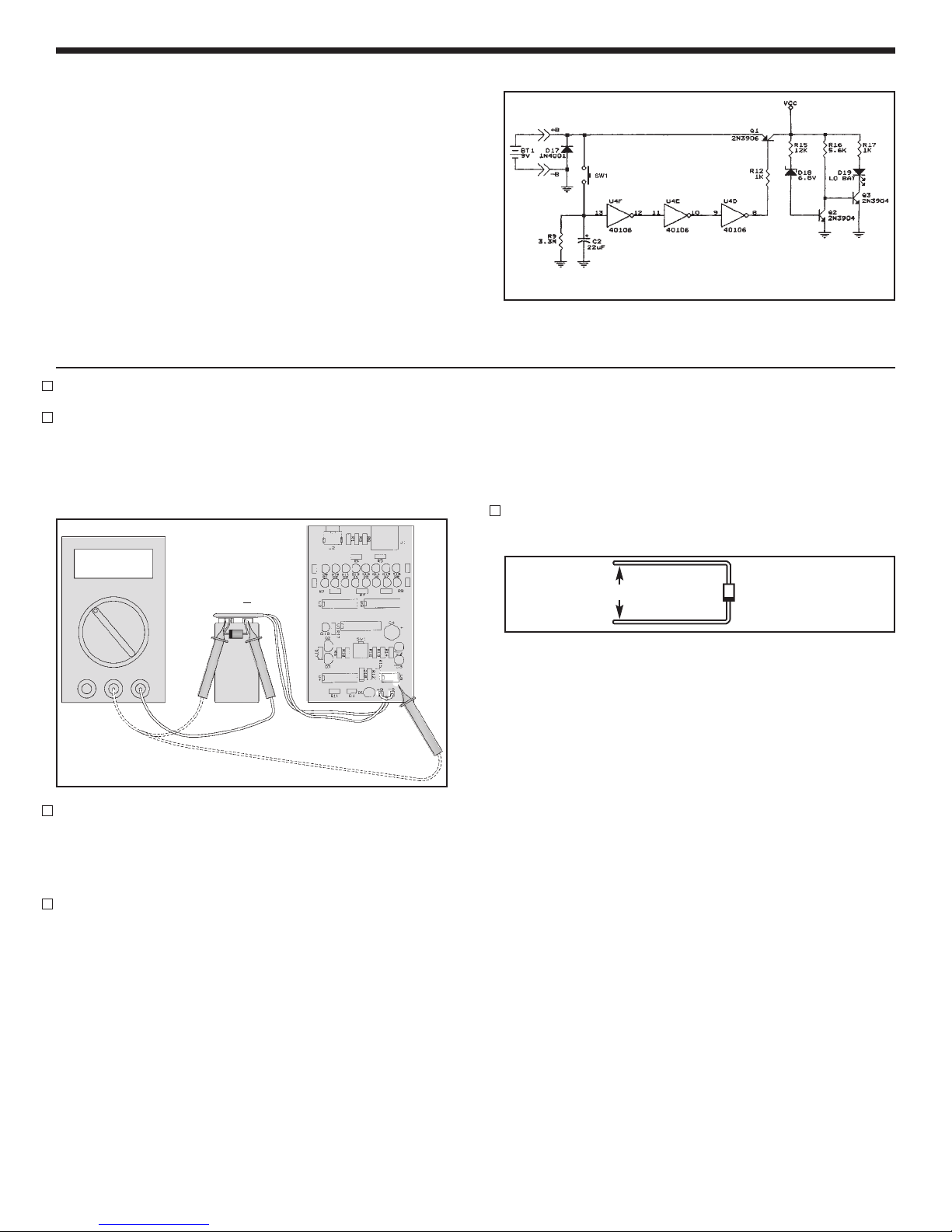
SECTION A - POWER SUPPLY
When the SW1 (test button) is pushed, capacitor C2
(see schematic diagram, Figure 1) is charged to the
battery voltage. Transistor Q1 turns on and all of the
circuits in the tester are powered. If you don’t push
SW1, capacitor C2 begins discharging. When the
voltage on C2 is less than 0.7V, transistor Q1 and
the power turn off after 30-50 seconds.
When the voltage of the battery is less than 7.5V,
transistors Q2 and Q3 turn on and LED D19 (Low
Battery) lights. The diode D17 protects the tester
from wrong polarity input voltage.
-7-
1. Connect the battery to the battery snap.
2. Set the voltmeter to read 20VDC and connect the
COM lead to the negative (--) side of the battery
and the V lead to the positive (+) side of the
battery as shown in Figure 2. The meter should
indicate 9-10VDC. Push switch SW1.
3.
Remove the V lead from the positive (+) side of the
battery and move to pad of pin 4 of IC U5. The
meter should indicate the same voltage, but after
30-50 seconds, the voltage should drop to 0V.
4. Push the switch SW1 again. The meter should
indicate the same voltage as in step 2. If not:
a) Check that the battery snap is connected
with the the right polarity as shown in the
assembly instructions.
b) Check that the transistor Q1 is 2N3906 and
mounted with the emitter, base and collector
leads as shown in the assembly instructions.
c) Check that R9, R12 and C2 are the correct
values.
d) Check that D17, D18, C2, U4 and SW1 are
installed as shown in the assembly
instructions.
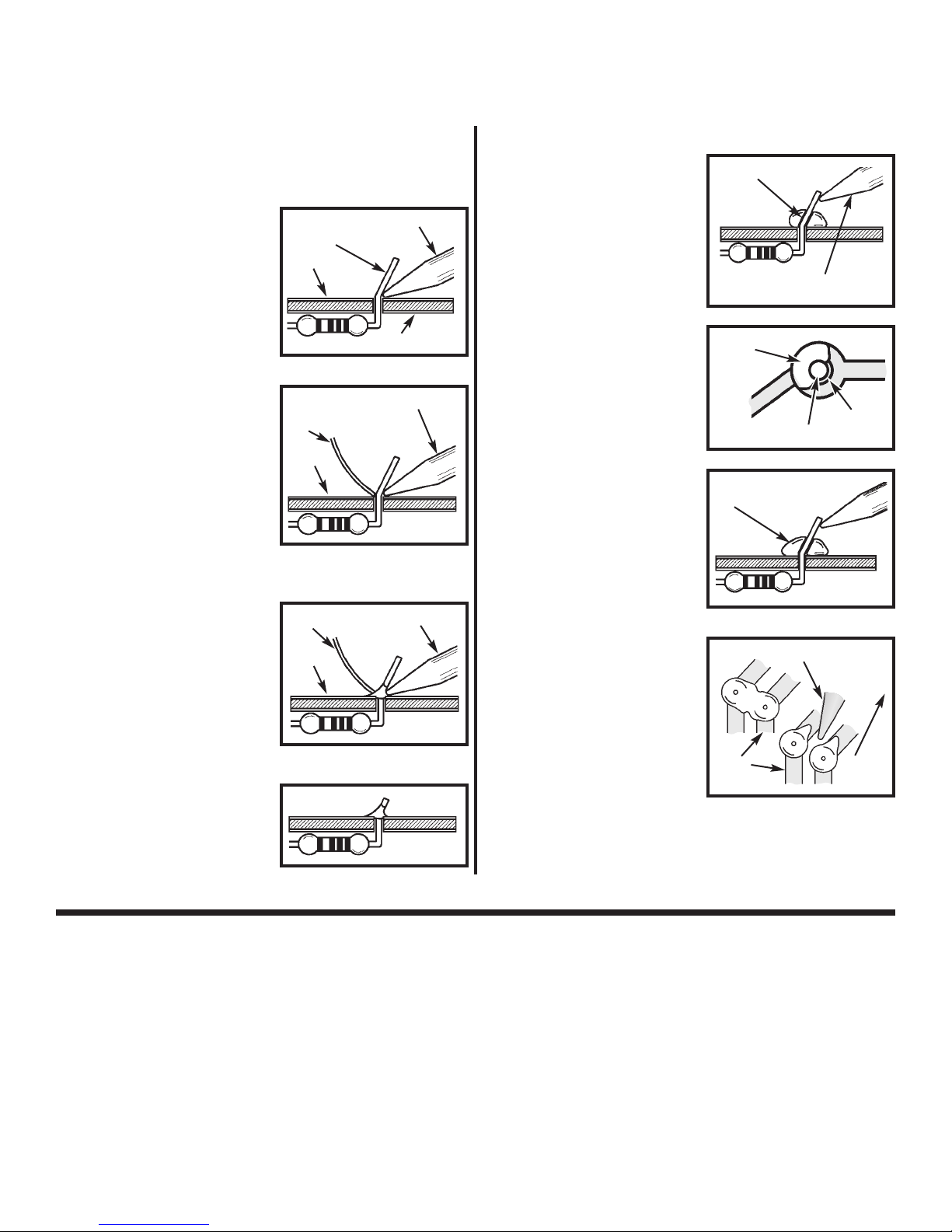
5. Bend the zener diode 1N4736 (6.8V 1W, located
in a separate bag) as shown in Figure 3.
Push the switch SW1 again and short the battery
by the zener diode for 1-2 seconds (the side with
the band should be touching the “+” terminal of the
battery, see Figure 2). LED D19 (Lo Batt.) should
be lit. Remove the zener diode and the LED should
turn off. If not:
a) Check that the transistors Q2 and Q3 are
2N3904 and mounted as shown in the
assembly instructions.
b) Check zener diode D18 and LED D19. Be
sure that they are installed as shown in the
assembly instructions.
c) Check that resistors R15, R16 and R17 are
the correct values.
Remove the battery from the battery snap and
the leads from the tester.
TESTING
Figure 1
Figure 3
0.5” - 0.6”
VCOM
VDC +
9V
Figure 2
1
8