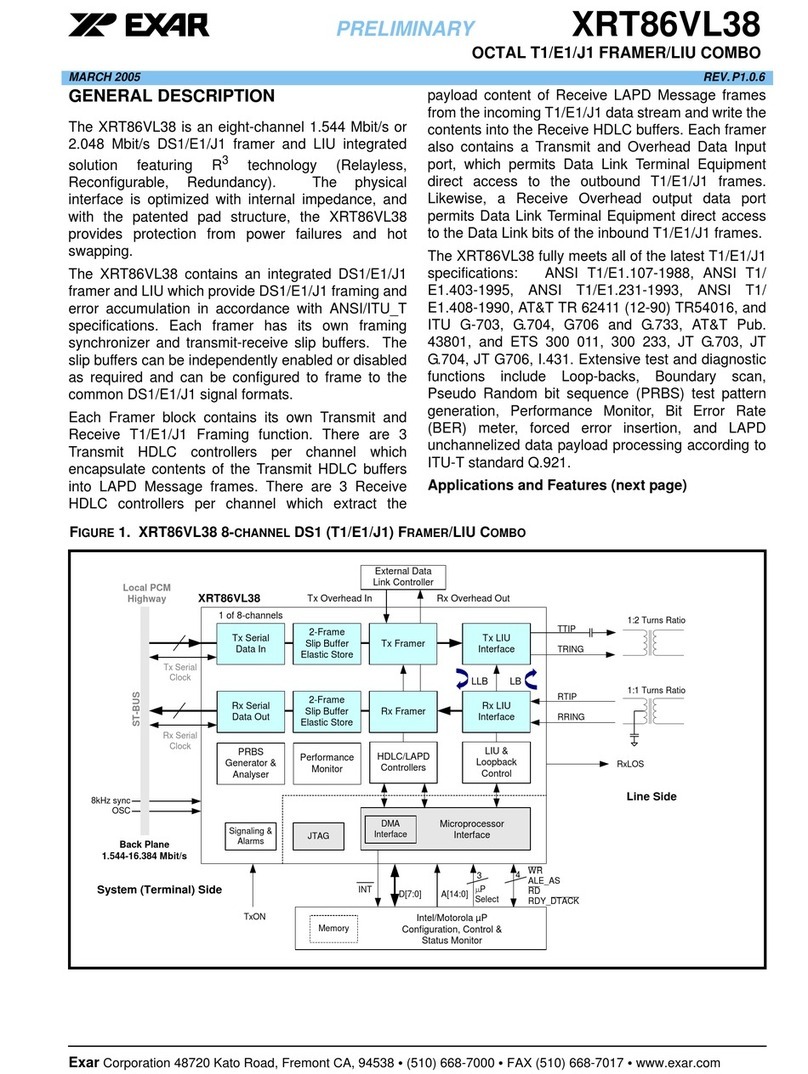
Exar XRT71D00 User manual

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
1
DESIGNING THE XRT71D00 AND THE XRT73L00
DEVICES TO OPERATE IN THE HOST MODE, AND TO
BE ACCESSED VIA A SINGLE CHIP SELECT PIN

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
2
DESIGNING THE XRT71D00 AND THE XRT73L00
DEVICES TO OPERATE IN THE HOST MODE, AND TO
BE ACCESSED VIA A SINGLE CHIP SELECT PIN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS............................................................................................................................... 2
1.0 INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................................. 3
2.0 BACKGROUND INFORMATION ON THE XRT73L00 AND XRT71D00 DEVICES...................... 4
2.1 BACKGROUND INFORMATION – THE XRT73L00 1-CHANNEL DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC ...... 4
2.2 BACKGROUND INFORMATION – THE XRT71D00 1-CHANNEL DS3/E3/STS-1 JITTER
ATTENUATOR IC ................................................................................................................................... 7
3.0 THE CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT FEATURE OF THE XRT71D00 DEVICE................................... 9
4.0 HARDWARE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS .................................................................................... 12
4.1 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS WHEN THE JITTER ATTENUATOR IS DESIGNED IN THE
RECEIVE PATH.................................................................................................................................... 15
4.2 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS WHEN THE JITTER ATTENUATOR IS DESIGNED IN THE
TRANSMIT PATH................................................................................................................................. 18
5.0 POWER CONDITION CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE XRT73L00 AND THE XRT71D00
DEVICES..................................................................................................................................................... 21
6.0 THE BNC CONNECTOR SHIELDS.................................................................................................. 27
APPENDIX A – REGISTER DESCRIPTION FOR THE XRT73L00 DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC ............... 28
APPENDIX B – REGISTER DESCRIPTION FOR THE XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1 JITTER
ATTENUATOR IC...................................................................................................................................... 39
APPENDIX C – DESCRIPTION OF MICROPROCESSOR SERIAL INTERFACE PINS................... 44
C.1 A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE MICROPROCESSOR SERIAL INTERFACE PINS........ 45
C.2 USING THE MICROPROCESSOR SERIAL INTERFACE........................................................ 47
APPENDIX D - CONTACT INFORMATION FOR API-DELEVAN: .................................................... 50
APPENDIX E – REVISION CHANGE HISTORY ................................................................................... 51

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
3
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The purpose of this Applications Note is two-fold.
a. To describe a possible approach that one can use to interface the XRT71D00
DS3/E3/STS-1 Jitter Attenuator to the XRT73L00 DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC, while
operating each device in the “Host” Mode. In particular, this Applications Note
describes how to design a system, such that a Microprocessor can perform
READ/WRITE access to both the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 device with a
single Chip-Select (CS) signal.
b. To provide some “Power Conditioning” recommendations for designs using the
XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 devices.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
4
2.0 BACKGROUND INFORMATION ON THE XRT73L00
AND XRT71D00 DEVICES
The next couple of sections present a detailed description of both the XRT73L00 and the
XRT71D00 devices.
2.1 BACKGROUND INFORMATION – THE XRT73L00 1-
CHANNEL DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC
The XRT73L00 device is a single Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC that was designed to
operate at 3.3V. Further this device can be configured via two possible approaches.
a. The Hardware Mode
b. The Host Mode.
If the XRT73L00 device has been configured to operate in the “Hardware” Mode, then
all Mode/Configuration selection is achieved by setting certain input pins either “HIGH”
or “LOW”. If the user configures the XRT73L00 device to operate in the “Hardware”
Mode, then the user can configure the XRT73L00 device into a wide variety of modes,
via the following external input pins.
•REQDIS – Receive Equalizer Enable/Disable Input pin
•TXLEV – Transmit Line Build-Out Circuit Enable/Disable Input pin.
•LLB & RLB – Loop Mode Select input pins.
•STS-1/DS3* & E3 – Data Rate Select Input pins.
•ENDECDIS – B3ZS/HDB3 Encoder & Decoder Block Enable/Disable Input pin.
•DR/SR* - Dual-Rail/Single-Rail Select Input pin.
•TxOFF – Transmit Shut Off Input pin.
•TAOS – Transmit All Ones Enable Input pin
•RCLK2INV – RCLK2 Invert/Non-Invert Select Input pin.
Therefore, for Hardware Mode operation, the XRT73L00 device provides the user with
11 input pins that can be used to control various operational aspects of the XRT73L00
device.
If the XRT73L00 device has been configured to operate in the Host Mode, then all
Mode/Configuration selection is achieved by writing data into the on-chip Command
Registers (via the Microprocessor Serial Interface block). The Microprocessor Serial
Interface block consists of the following pins.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
5
•SDI – Serial Data In
•SDO – Serial Data Out
•SCLK – Serial Clock In
•CS* - Chip Select Input
•REG_RESET* - Register Reset Input.
A more detailed description of each of these pins is presented in Appendix C.
Therefore, for Host Mode operation, the XRT73L00 device provides the user with 5 pins
(4 input and 1 output) that can be used to control various operational aspects of the
XRT73L00 device.
The bit-format of the Command Register set, within the XRT73L00 LIU device is
presented below in Figure 1.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
6
Register Bit-Format
Address Command
Register Type D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0x00 CR0 RO RLOL RLOS ALOS DLOS DMO
0x01 CR1 R/W TXOFF TAOS TXCLKINV TXLEV TXBIN
0x02 CR2 R/W Reserved ENDECDIS ALOSDIS DLOSDIS REQDIS
0x03 CR3 R/W RNRZ LOSMUT RCLK2/
LCV* RCLK2INV RCLK1INV
0x04 CR4 R/W Reserved STS-1/
DS3* E3 LLB RLB
0x05 CR5 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0x06 CR6 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0x07 CR7 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
0x08 CR8 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Figure 1, The Bit Format of the Command Registers, within the XRT73L00 Device.
A detailed discussion of each of these command register bits is presented in Appendix A.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
7
2.2 BACKGROUND INFORMATION – THE XRT71D00 1-
CHANNEL DS3/E3/STS-1 JITTER ATTENUATOR IC
The XRT71D00 device is a single-channel DS3/E3/STS-1 Jitter Attenuator IC that was
designed to operate at either 3.3V or 5V. Further, this device can be configured via two
possible approaches.
a. The Hardware Mode
b. The Host Mode
If the XRT71D00 device has been configured to operate in the “Hardware” Mode, then
all Mode/Configuration selection is achieved by setting certain input pins either “HIGH”
or “LOW”. If the user configures the XRT71D00 device to operate in the “Hardware”
Mode, the user can configure the XRT71D00 device into a wide variety of modes, via the
following external input pins.
•FSS – FIFO Size Select
•DJA – Disable (Jitter Attenuator PLL) Select
•CLKES – Clock Edge Select
•BWS – (Jitter Attenuator PLL) Bandwidth Select
•DS3*/E3 – Data Rate Select Input pin
•STS-1 – Data Rate Select Input pin.
Therefore, for Hardware Mode operation, the XRT71D00 device provides the user with 6
input pins that can be used to control various operational aspects of the XRT71D00
device.
If the XRT71D00 device has been configured to operate in the “Host” Mode, then all
Mode/Configuration is achieved by writing data into the on-chip Command Registers
(via the Microprocessor Serial Interface block). The Microprocessor Serial Interface
block consists of the following pins.
•SDI – Serial Data In
•SDO – Serial Data Out
•SCLK – Serial Clock Input
•CS* - Chip Select Input
•RST* - Reset Input
A more detailed description of each of these pins is presented in Appendix C.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
8
Therefore, for Host Mode Operation, the XRT71D00 device provides the user with five
(5) pins (4 inputs and 1 output) that can be used to control various aspects of the
XRT71D00 device.
The bit-format of the Command Register set, within the XRT71D00 Jitter Attenuator
device is presented below in Figure 2.
Register Bit-Format
Addr. Command
Register Type D6 D5 D4
D3 D2 D1 D0
Channel 0 Registers
0x06 CR6 R/W STS-1 0 E3/DS3* DJA BWS CLKES FSS
0x07 CR7 R/O Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved FL
Channel 1 Registers
0x0E CR14 R/W STS-1 0 E3/DS3* DJA BWS CLKES FSS
0x0F CR15 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved FL
Channel 2 Registers
0x16 CR22 R/W STS-1 0 E3/DS3* DJA BWS CLKES FSS
0x17 CR23 R/W Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved FL
Figure 2, The Bit Format of the Command Registers, within the XRT71D00 Device.
A detailed discussion of each of these Command Register bits are presented in Appendix
B.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
9
3.0 THE CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT FEATURE OF THE
XRT71D00 DEVICE
The “Channel Assignment” feature, within the XRT71D00 device, permits the user to
perform “READ/WRITE” access to the following sets of devices, with only one Chip
Select pin.
•1- XRT73L00 1-Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC and 1-XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1
Jitter Attenuator IC.
•1-XRT7300 1-Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC and 1-XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1 Jitter
Attenuator IC.
•1- XRT73L02 2-Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC and 2-XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1
Jitter Attenuator Devices.
•1-XRT7302 2-Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC and 2-XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1 Jitter
Attenuator Devices.
•1-XRT73L03 3-Channel DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU IC and 3-XRT71D00 DS3/E3/STS-1
Jitter Attenuator Devices.
Figure 2 presents the bit format of the Command Registers, within the XRT71D00
device. In this figure, the Command Register set is sub-divided into “Channels”.
Command Registers CR6 and CR7 are allocated to “Channel 0”; Command Registers
CR14 and CR15 are allocated to “Channel 1”; and finally, Command Registers CR22 and
CR23 have been allocated to “Channel 2”. The XRT71D00 device contains two external
input pins, which are relevant to this discussion.
•Ch_Addr_0 (Pin 28)
•Ch_Addr_1 (Pin 15)
A XRT71D00 device (within a given system) can be assigned a “Channel Number” by
setting the “Ch_Addr_0” and “Ch_Addr_1” input pins either high or low. The
relationship between the states of the “Ch_Addr_0” and the “Ch_Addr_1” input pins, and
the “Assigned Channel” is presented below in Table 1.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
10
Table 1, The Relationship between the Logic States of the “Ch_Addr_0” and
“Ch_Addr_1” input pins, and the “Assigned Channel”
Ch_Addr_1 Ch_Addr_0 Assigned Channel
0 0 Channel 0
0 1 Channel 1
1 0 Channel 2
1 1 Not Valid
If a given XRT71D00 device is assigned to “Channel 0” then it will only respond to
READ/WRITE operations to Address locations 0x06 and 0x07 (within the device). If the
Microprocessor attempts to perform write operations to address locations “0x0E” and
“0x16”, then the XRT71D00 device will ignore this particular operation. Further, if the
Microprocessor attempts to perform read operations to address locations “0x0E”, “0x0F”,
“0x16” and “0x17”, then the XRT71D00 device will simply ignore these particular
operations and will continue to tri-state its “SDO” output pin.
Similarly, if a given XRT71D00 device is assigned to “Channel 1” then it will only
respond to READ/WRITE operations to Address locations 0x0E and 0x0F (within the
device). If the Microprocessor attempts to perform write operations to address locations
“0x06” and “0x16”, then the XRT71D00 device will ignore this particular operation.
Further, if the Microprocessor attempts to perform read operations to address locations
“0x06”, “0x07”, “0x16” and “0x17”, then the XRT71D00 device will simply ignore these
particular operations and will continue to tri-state its “SDO” output pin.
This Applications Note discusses how to interface a single XRT71D00 device to the
XRT73L00 device. Therefore, the Jitter Attenuator IC (within this Applications Note)
will be assigned to “Channel 0”.
When the XRT71D00 device has been assigned to “Channel 0” and has been interfaced
with the XRT73L00 device (as shown in Figure 3); then the resulting composite
Command Register Address Map is as presented below.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
11
Register Bit-Format
Addr. Command
Register Type D6 D5 D4
D3 D2 D1 D0
0x00 CR0 R/O Res. Res. RLOL RLOS ALOS DLOS DMO
0x01 CR1 R/W Res. Res. TXOFF TAOS TXCLK
INV TXLEV TXBIN
0x02 CR2 R/W Res. Res. Res. ENDECDIS ALOSDIS DLOSDIS REQDIS
0x03 CR3 R/W Res. Res. RNRZ LOSMUT RCLK2/
LCV* RCLK2
INV RCLK1
INV
0x04 CR4 R/W Res. Res. Res. STS-1/
DS3* E3 LLB RLB
0x05 CR5 R/W Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res.
0x06 CR6 R/W STS-1 0 E3/DS3* DJA BWS CLKES FSS
0x07 CR7 R/O Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. FL
Figure 3, The Bit-Format of the “Composite Set” of Command Registers (from the
XRT73L00 and the XRT71D00 Device).
NOTE: The “shaded” register bits (within Figure 4) actually reside within the
XRT71D00 device. Conversely, the “un-shaded” register bits actually reside within the
XRT73L00 device.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
12
4.0 HARDWARE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Figures 4 and 6 each presents a schematic design of the XRT71D00 device being
interfaced to the XRT73L00 device. In these schematics, both the XRT73L00 and the
XRT71D00 devices have been configured to operate in the “Host” Mode. In the case of
Figure 4, the XRT71D00 device has been designed to operate in the Receive Path.
Additionally, in the case of Figure 6, the XRT71D00 device has been designed to operate
in the Transmit Path.
There are numerous other things to note about Figures 4 and 6.
1. The XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 devices are each connected to the following
signals.
a. HW_RESET*
This signal is tied to the “RST*” input pin of the XRT71D00 device and the
“REG_RESET*” input pin of the XRT73L00 device. Therefore, pulsing the
“HW_RESET*” input signal “low” will command a “Hardware RESET” to both the
Jitter Attenuator and the LIU IC.
b. JA_LIU_CS*
This signal is tied to the CS* (Chip-Select) input pins of both the XRT71D00 and the
XRT73L00 devices. Therefore, pulsing the “JA_LIU_CS*” input signal “low”
asserts Chip Select for both of these devices, simultaneously.
c. JA_LIU_SCLK_IN
This input signal is tied to the “SCLK” input pins of both the XRT71D00 and the
XRT73L00 devices. Hence, applying a clock signal to this input signal permits the
clock signal to be applied to the “SCLK” input pins of both devices, simultaneously.
d. JA_LIU_SDI_IN
This input signal is tied to the “SDI” input pins of both the XRT71D00 and the
XRT73L00 devices. Hence, applying data (via this signal) permits this signal to be
applied to the “SDI” input pins of both devices, simultaneously.
e. JA_LIU_SDO_OUT
This output signal is tied to the “SDO” output pins of both the XRT71D00 and the
XRT73L00 device. Therefore, either the “SDO” output pin of the XRT73L00 device,
or that of the XRT71D00 device can drive this output signal.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
13
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT THE SDO OUTPUT PINS
OF THE XRT71D00 AND THE XRT73L00 DEVICE
Earlier, this Applications Note states that since the XRT71D00 device has been
assigned to “Channel 0”, then it will only respond to READ operations to address
locations “0x06” and “0x07”. Additionally, the XRT71D00 device will also tri-state
its SDO output pin during READ operations to any other address location. The
purpose behind this feature is to prevent the XRT71D00 device from contending with
the XRT73L00 device over the JA_LIU_SDO_OUT” line, by pulling its SDO output
pin to GND. By designing the XRT71D00 device to tri-state its SDO output,
whenever the Microprocessor performs a READ operation to other address locations
(e.g., within the XRT73L00 Command Register); this prevents the XRT71D00 device
from pulling the entire “JA_LIU_SDO_OUT” line to GND, and corrupting the data
that needs to be read via from the XRT73L00 LIU Device.
Unfortunately, the XRT73L00 LIU IC does not have this same “tri-stating of the SDO
output pin” feature. Further, the content of any Command Register bit (within the
XRT73L00 device) other than those at address locations “0x00” through “0x04”; are
set to “0”. Therefore, whenever the Microprocessor performs a READ operation to
any address location, other than locations “0x00” through “0x04”, then the
XRT73L00 LIU IC will automatically pull its SDO output pin to GND.
HOW TO SOLVE THIS PROBLEM
This issue with the SDO output pins means that simply tying the SDO output pins, of
the two devices together, is not a prudent thing to do. Instead, we recommend that
the user route the SDO output (of the XRT73L00 LIU device) through a 475 Ω
resistor, prior to being connected to the trace carrying the SDO output of the
XRT71D00 device. This 475 Ωresistor serves to isolate the data, being output via
the SDO output pin, of the XRT71D00 device; from the SDO output pin of the
XRT73L00 device.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
14
2. The XRT71D00 device has been designed to operate in the Receive Path (Figure
4)
Figure 4 presents a schematic design in which the Jitter Attenuator is placed in the
“Receive Path” such that the “RPOS”, “RNEG” and “RCLK” output signals (from the
XRT73L00 LIU IC) are being routed to the “RPOS”, “RNEG” and “RCLK” input signals
of the XRT71D00 Jitter Attenuator IC.
3. The XRT71D00 device has been designed to operate in the Transmit Path (Figure
6).
It should be noted that it is entirely acceptable to design a board such that the Jitter
Attenuator is placed in the “Transmit Path”; as is shown in Figure 6. Please note that in
this case, the “RRPOS”, “RRNEG” and “RRCLK” outputs (from the XRT71D00 Jitter
Attenuator IC) are being routed to the “TPDATA”, “TNDATA” and “TCLK” input
signals of the LIU IC.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
15
4.1 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS WHEN THE JITTER
ATTENUATOR IS DESIGNED IN THE RECEIVE PATH
If the user has designed his/her board such that the XRT71D00 device is operating in the
“Receive Path” (as illustrated in Figure 4), then it is imperative that the two devices be
configured such that the “set-up” and “hold” time requirements (of the RPOS/RNEG
inputs of the XRT71D00 device) are met.
By default, the XRT73L00 device will update its “recovered” data, via the “RPOS” and
“RNEG” output pins, upon the rising edge of “RCLK1” and “RCLK2”. According to the
XRT73L00 Data Sheet, the “RCLK to RPOS/RNEG” output delay is about 4ns
(maximum). Therefore, the user is advised to configure the XRT71D00 device to sample
the data, via its “RPOS” and “RNEG” input pins, upon the falling edge of the “RCLK”
input signal. According to the XRT71D00 Data Sheet, the “RPOS/RNEG” to “RCLK”
set-up and hold time requirements are each 3ns (maximum).
In order to achieve this configuration, the user must insure that the “RCLK1” or
“RCLK2” bit-fields (within the XRT73L00 device) are set to “0”, and that the “CLKES”
bit-field (within the XRT71D00 device) is set to “1”; as illustrated below.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
16
FIGURE 4, SCHEMATIC DESIGN OF XRT71D00 DEVICE BEING
INTERFACED TO THE XRT73L00 DEVICE (IN THE RECEIVE
PATH)

5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
Install Close to the
DC-DC Converter or
Switching Regulator
NOTE: BNC Connector on
Transmit Side is sometimes
AC coupled to Chassis
GND
NOTE: External Input
Control pins should be
pulled to GND, when the
LIU is configured in
HOST Mode.
NOTE: In this Configuration,
the XRT71D00 device should
be assigned a "Channel
Address" of 00.
(3.6V)
XRT71D00_XRT73L00_HOST.sch 1.01
Schematic Design for TAN_042
B
1 1Thursday, June 07, 2001
Title
Size Document Number Rev
Date: Sheet of
JITTERY RECOVERED CLOCK SIGNALSMOOTHED RECOVERED CLOCK SIGNAL
3.3V
JP2
JUMPER
1 2
R1
100
C10
0.1uF
R11
4.7K
U3
XRT71D00
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
14
15
18
19
20
21
22
23
26
27
28
29
30
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
GNDD
MCLK
GNDA
VDDA
STS-1
SDI
SCLK
HOST/HW
FL
Ch_Addr_1
SDO
RST
ICT
GNDD
RRCLK
RRNEG
RRPOS
VDDD
Ch_Addr_0
CS
VDDD
C8
0.1uF
C9
0.1uF
J1
BNC
1
2
J2
BNC
1
2
R4
37.4
R5
37.4
JP1
JUMPER
1 2
T1
T3001
1 6
3 4
L1
15uH
T2
T3001
16
34
C11
1000pF
L2
6.8uH
L3
6.8uH
D1
D1N5914
U10
XRT73L00
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 40
41
42
43
4420
11
39
TxLEV
TAOS
TxAVDD
DMO
TxAGND
AGND
RxAGND
RRTIP
RRING
RxAVDD
REQDIS
LOSTHR
LLB
RLB
STS-1/DS3
E3
HOST/HW
SDI
SCLK
CS
RLOL
RLOS
DGND
DVDD
EXCLK
RxDGND
RxDVDD
LCV
RCLK1
RNEG
RPOS
ICT
TxOFF
TCLK
TPDATA
TNDATA TRING
TTIP
TxAVDD
MRING
MTIPSDO
REG_RESET
TxAGND
C15
1000pF
R6
31.6
C14
0.1uF
C3
2.2uF
R3
475
R7
31.6
C4
2.2uF
C1
0.01uF
R8
274
C5
33uF
R9
274
R10
4.7K
R2
100
C13
0.1uF
C6
0.1uF
C7
0.1uF
C12
0.1uF
HW_RESET*
JA_LIU_CS*
JA_LIU_SCLK_IN
RxLOS
RxLOL
XMIT_FAIL
LINE_CODE_VIOL
RxPOS_De_Jittered
RxNEG_De_Jittered
RCLK_De_Jittered
44.736MHz
44.736MHz
TxPOS
TxNEG
JA_LIU_SDO_OUT
JA_LIU_SDI_IN
JA_FIFO_ALARM
TxAVDD
RxAVDD
DVDD
DVDD RxAVDD
DVDD
DVDD
TxAVDD
RxAVDD

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
17
Register Bit-Format
Addr. Command
Register Type D6 D5 D4
D3 D2 D1 D0
0x00 CR0 R/O Res. Res. RLOL RLOS ALOS DLOS DMO
0x01 CR1 R/W Res. Res. TXOFF TAOS TXCLK
INV TXLEV TXBIN
0x02 CR2 R/W Res. Res. Res. ENDECDIS ALOSDIS DLOSDIS REQDIS
0x03 CR3 R/W Res. Res. RNRZ LOSMUT RCLK2/
LCV* RCLK2
INV
0
RCLK1
INV
0
0x04 CR4 R/W Res. Res. Res. STS-1/
DS3* E3 LLB RLB
0x05 CR5 R/W Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res.
0x06 CR6 R/W STS-1 0 E3/DS3* DJA BWS CLKES
0 FSS
0x07 CR7 R/O Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. FL
Figure 5, The Recommended Bit-Format of the “Composite Set” of Command
Registers (from the XRT73L00 and the XRT71D00 Device), when the XRT71D00
device is configured to operate in the “Receive Path”.
If the above-mentioned configuration is implemented, then the XRT71D00 device will be
provided with the following set-up and hold times, for each of the three (3) data rates.
Table 2, The “RPOS/RNEG” to “RCLK” Set-up and Hold Times provided to the
XRT71D00 Device, when configured as presented in Figure 4.
Data Rate RPOS/RNEG to RCLK Set-up
Time Provided RCLK to RPOS/RNEG Hold Time
Provided
E3 10.5ns 18.5ns
DS3 7ns 15ns
STS-1 5.5ns 13.5ns
NOTES:
1. Minimum “RPOS/RNEG to RCLK Set-up Time” Requirements of XRT71D00 Device
= 3ns.
2. Minimum “RCLK to RPOS/RNEG Hold-Time Requirements of the XRT71D00
Device = 3ns.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
18
4.2 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS WHEN THE JITTER
ATTENUATOR IS DESIGNED IN THE TRANSMIT PATH
If the user has designed his/her board such that the XRT71D00 device is operating in the
“Transmit Path” (as illustrated in Figure 6), then it is imperative that the two devices be
configured such that the “set-up” and “hold” time requirements (of the
TPDATA/TNDATA inputs of the XRT73L00 device) are met.
By default, the XRT73L00 device will sample the data, input at the
“TPDATA/TNDATA” pins, upon the falling edge of “TCLK”. According to the
XRT73L00 Data Sheet, the “TPDATA/TNDATA to TCLK” set-up time requirements are
3ns (minimum). Additionally, the “TCLK to TPDATA/TNDATA” hold time
requirements are also 3ns (minimum). According to the XT71D00 Data Sheet, the
“RRPOS/RRNEG to RRCLK” output delay is 5ns (maximum). Therefore, the user is
advised to configure the XRT71D00 device to output the “RRPOS/RRNEG” data upon
the rising edge of “RRCLK”.
In order to achieve this configuration, the user must insure that the “TXCLK INV” bit-
field (within the XRT73L00 device) is set to “0”, and that the “CLKES” bit-field (within
the XRT71D00 device) is set to “1”; as illustrated below.

TAN-042
Designing the XRT71D00 and the XRT73L00 Devices to
operate in the Host Mode, and to be accessed via a single Chip
Select pin.
Preliminary July 19, 2001
Revision 1.03
19
FIGURE 6, SCHEMATIC DESIGN OF XRT71D00 DEVICE BEING
INTERFACED TO THE XRT73L00 DEVICE (IN THE TRANSMIT
PATH)
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Exar PCI Card manuals
Popular PCI Card manuals by other brands

Airlink101
Airlink101 AWLH6045 user manual
Teledyne Lecroy
Teledyne Lecroy Express Gen3 x4 User manual and quick start guide

StarTech.com
StarTech.com ST1000SPEX user guide

National Instruments
National Instruments IMAQ PCI-1424 Getting started

TeVii
TeVii D622 Quick start up guide

StarTech.com
StarTech.com PEXUSB3S24 instruction manual