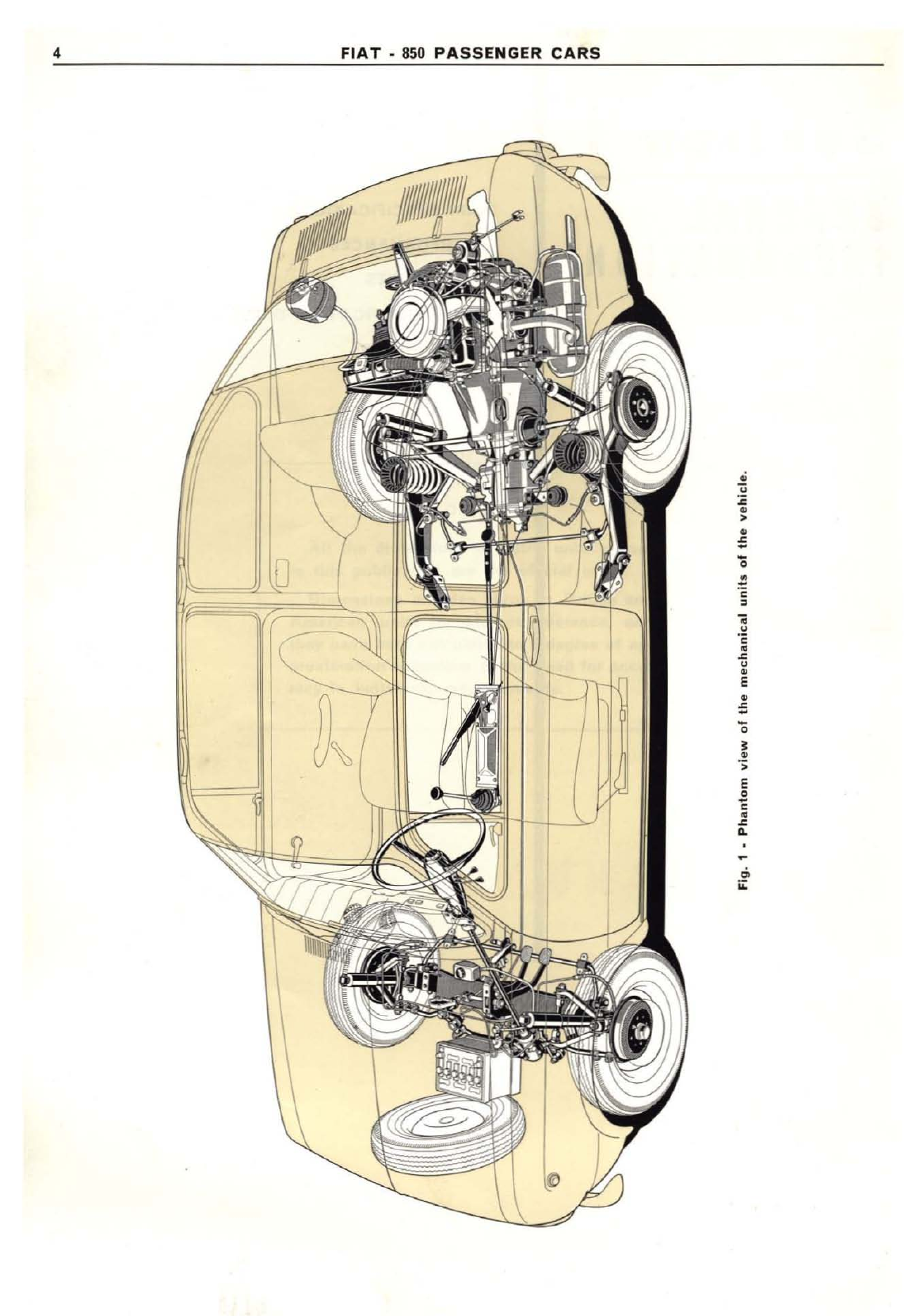
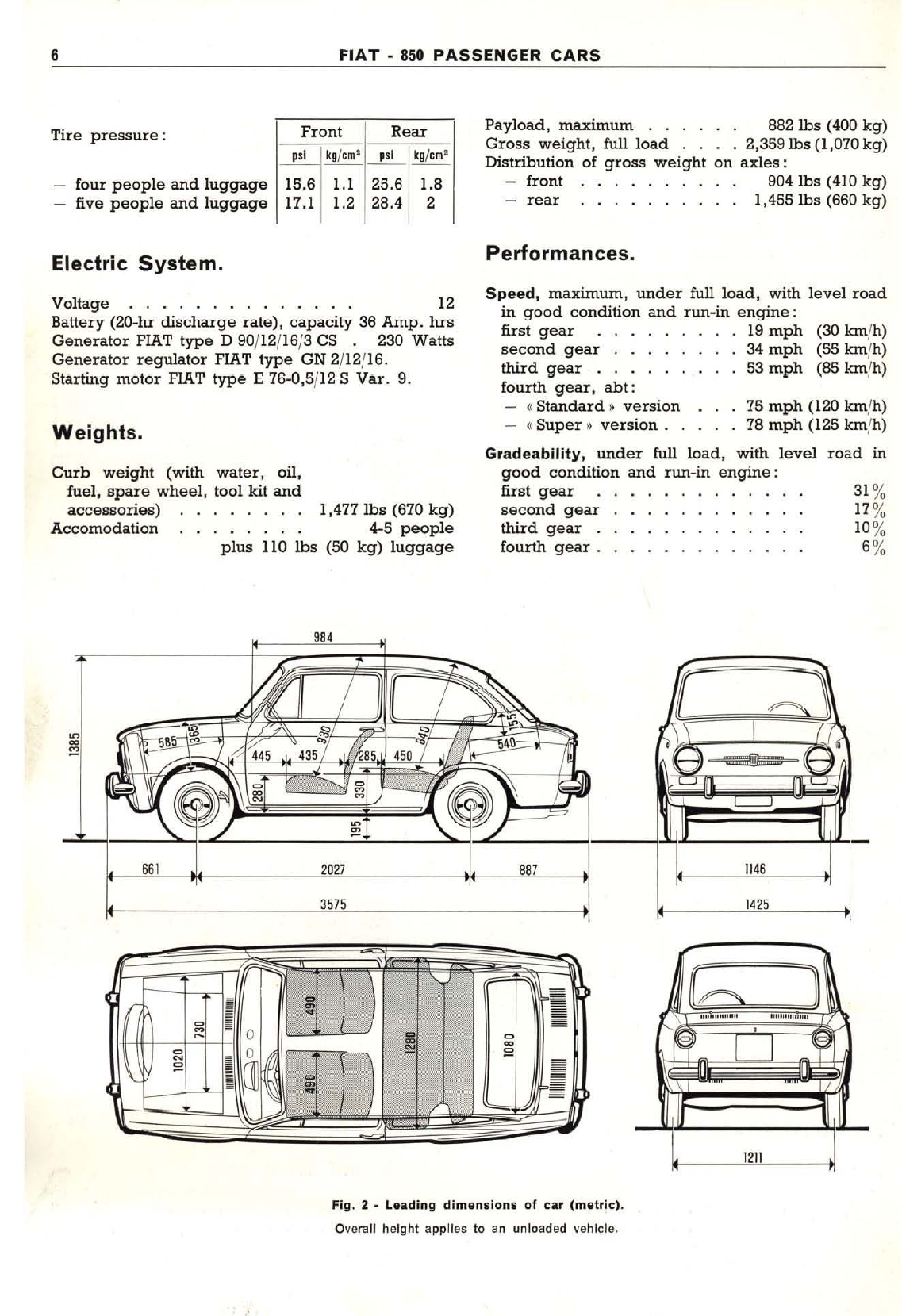
Fiat 850 Sedan 1968 Install guide
Other Fiat Automobile manuals

Fiat
Fiat 124 Spider 2019 User manual

Fiat
Fiat 500L User manual

Fiat
Fiat PANDA User guide
Fiat
Fiat 1998 Marea Weekend User manual

Fiat
Fiat 500e User manual

Fiat
Fiat 1986 Panda Van User manual

Fiat
Fiat 1995 Bravo User manual

Fiat
Fiat 500 ABARTH 2017 User manual

Fiat
Fiat Marea Weekend Instruction manual

Fiat
Fiat 124 SPIDER 2020 User manual

Fiat
Fiat 500 Abarth User guide

Fiat
Fiat 1995 Bravo User guide

Fiat
Fiat 500L 2018 User manual

Fiat
Fiat 2015 500e User manual

Fiat
Fiat Spider 124 1975 User manual

Fiat
Fiat 479 cc Instruction manual

Fiat
Fiat 1986 Panda Van Product guide

Fiat
Fiat Barchetta 2000 User manual

Fiat
Fiat Spider-2000 User manual

Fiat
Fiat PUNTO User guide