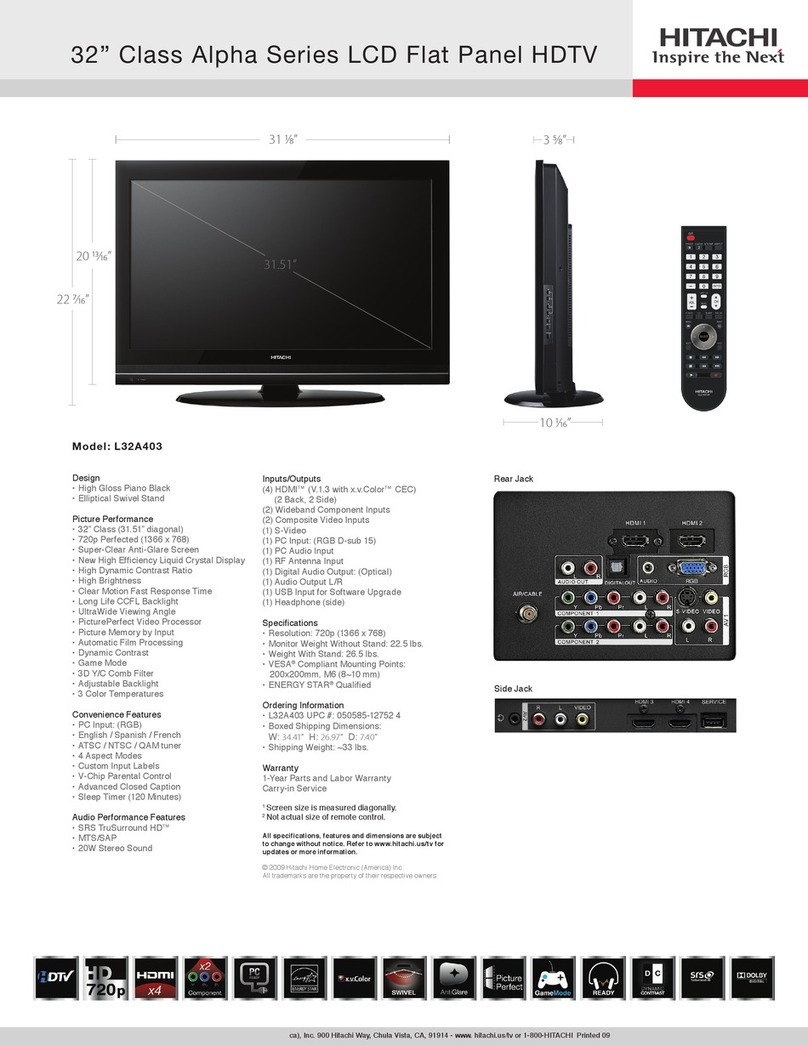
Page 01-03
The 61HDX98B utilizes a non-repairable Front End
Assembly called the DM-1 Module. This module con-
tains the main System control center, NTSC Front
End, Direct TV Receiver and ATSC Tuner. The block
diagram indicates the internal blocks contained within
the Front End Assembly, hear after called the DM-1.
Starting counterclockwise from the upper left.
SATELLITE:
This represents the Direct TV satellite dish connection
to the back of the set.
SATELLITE TUNER/IF:
This is the internal IRD, (Integrated Receiver and De-
coder). This receives the satellite signal from the LNB
(Low Noise Block) located on the Dish. This block
converts the signal to a usable signal for decoding.
SATELLITE CARD and SATELLITE LINK
BLOCK:
To receive Direct TV signals, the customer is required
to insert an active Security Card into the back of the
set. This care contains a programmable chip that con-
tains the consumer’s information and the channels that
the consumer is allowed to receive. Also, this card is
used when billing information is retrieved by Direct
TV.
LINK/MIX:
This block passes the particular signal that the cus-
tomer has decided to view on screen. Either the Direct
TV signal or the ATSC tuner.
TERRESTRIAL:
This indicates the outside antenna the consumer has
erected to receive NTSC signals as well as ATSC sig-
nals.
CABLE:
This is the input from the consumer’s cable signal.
HD/NTSC TUNER/IF SPLITTER:
This block receives the Terrestrial signal and depend-
ant upon which source the consumer has decided to
view, processes the signal through the appropriate
tuner.
•HD: Receives the Terrestrial Signal and routes it
to the ATSC tuner. This tuner is capable of re-
ceiving all 18 ATSC formats.
•NTSC: Receives the Terrestrial Signal and route
it to the NTSC Tuner.
•The NTSC signal is routed out of this block on the
line labeled Composite Video to the Signal Selec-
tor IC which selects the appropriate signal accord-
ing to the consumer’s choice. Either Tuner,
AVX1, 2 or 3 and/or S-In 1,2 or 3.
•The NTSC audio IF signal is routed to the MTS
STEREO DECODER.
•SPLITTER:
•The splitter routes the NTSC signal out to the RF
Out PinP Tuner path to the PinP Tuner.
MTS STEREO DECODER:
Decodes the NTSC Audio IF signal an decodes it into
Left Total and Right Total. This signal is routed to the
Dolby®Pro-Logic decoder.
HDTV LINK:
This block routs the ATSC signal received by the
ATSC tuner to the Link Mix.
NTSC YUV A/D:
This block receives the NTSC luminance and chroma
signals and converters them to a digital signal to be
utilized by the MPEG VIDEO decoder.
FROM MAIN MICRO:
This is communication in and out for the Sub-
Microprocessor. Information such as the Selector IC
selection, power on/off commands, etc.., are routed
from the ARM/Transport or Main Microprocessor sec-
tion.
SD-A/V:
This is the output of the AC-3 digital audio to be used
by an off board AC-3 decoder.
MODEM:
Direct TV polls the Direct TV receiver section through
the customer’s phone lines and determines such things
as Pay for View authorization, customer’s informa-
tion, Card authorization and billing information.
ARM/TRANSPORT:
The Arm/Transport block receives all signals from Di-
rect TV, ATSC. It also receives the Infrared remote con-
trol signals, Front panel Key data, and Slave Microproc-
essor information. This is the Main Microprocessor sec-
tion of the DM-1 module. Dynamic RAM and ROM in-
formation is processed from Soft ward load into ROM
and determines the state of the Television. Information
from ATSC and/or Direct TV is routed to the MPEG
VIDEO DECODER.
BLOCK DIAGRAM EXPLANATION FRONT END