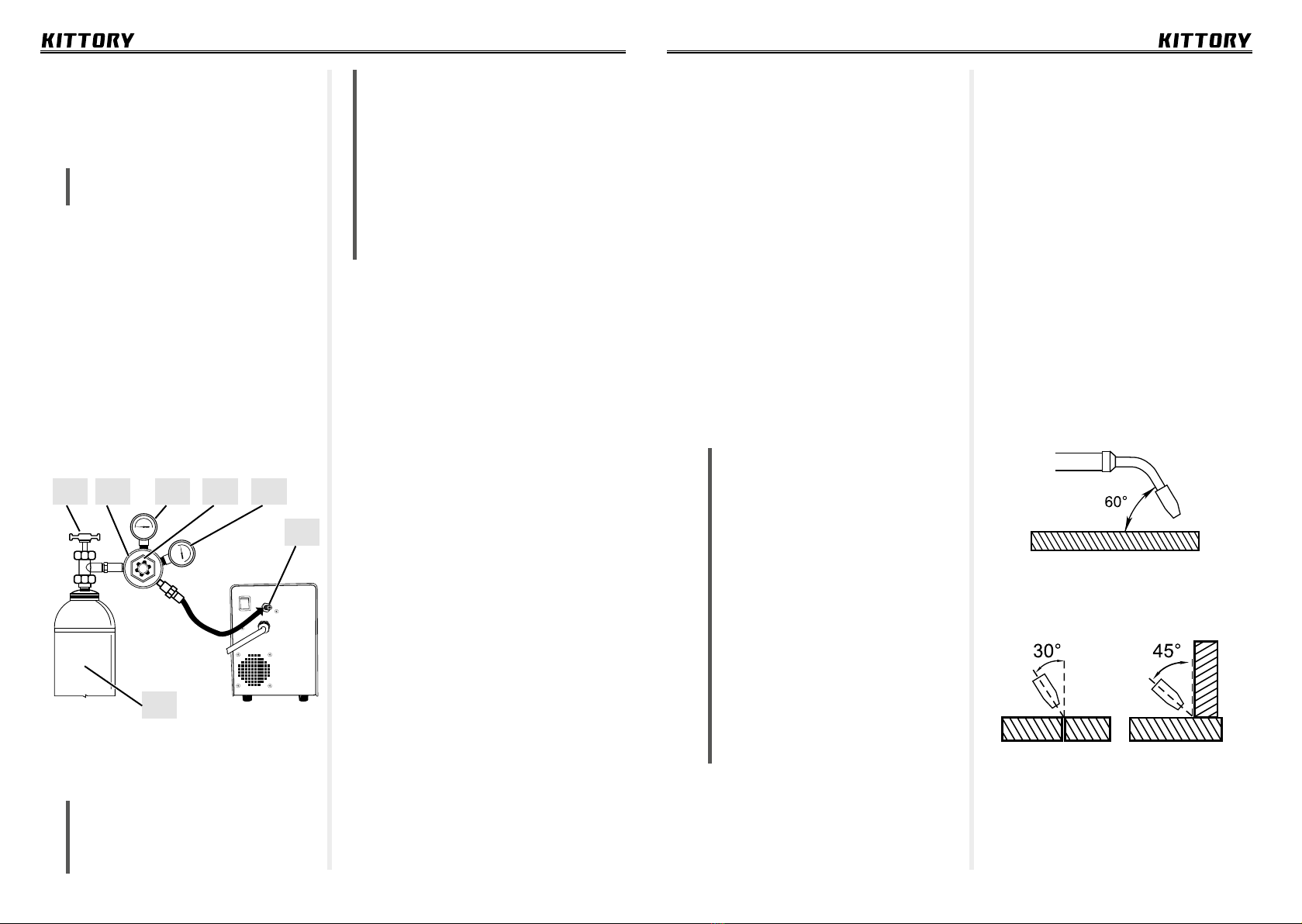
-4- -5-
Safety instructions
damage gloves.
• Provide safe insulation of your body
from the workpiece. Isolate bare parts
of you body from both the workpiece
and the ground.
• When performing automatic or
semi-automatic welding, the welding
wire, reel, welding head, contact tip or
semi-automatic welding torch are also
live.
• Do not attempt to repair or service the
welding machine connected to the
power supply.
• Make sure that all electrical cables are
properly insulated. If damage is found,
repair the insulation or replace the
damaged cable.
• Use only recommended cables and
extension cords.
• Never immerse the welding electrode
into water for cooling.
• Always attach a negative clamp to the
workpiece or a working table as close
as possible to the welding area.
• Do not touch simultaneously the weld-
ing wire and ground, grounded parts or
equipment.
• Do not use a welding machine to
defrost a frozen pipeline.
• When working at height, use a safety
belt or other safety equipment that
can prevent a fall in case of an electric
shock.
Gases andn fumes
• Gases and aerosols that pose a health
hazard are formed in the process of
welding. Do not inhale these gases and
aerosols.
• Work in well-ventilated areas or use a
ventilation system that safely removes
harmful gases from the working area.
• When welding with electrodes requir-
ing special ventilation, for example,
electrodes for welding stainless steels,
cast iron and the like (see Material
Safety Data Sheet - MSDS, or data
on the original electrode package),
for welding of galvanized steels, lead
and cadmium-coated steels or others
metals, or coatings that produce highly
toxic gases, use local air extraction
systems or mechanical ventilation sys-
tems. If possible, remove coatings that
emit harmful gases from the welding
zone.
• When working in confined spaces
or under other circumstances, wear
a respirator while performing work.
Additional precautions are also neces-
sary when welding galvanized steel.
• Do not weld next to materials that
release toxic fumes when heated.
Vapors of cleaning agents, degreasing
compounds, paintwork and similar
materials can be very toxic when
heated.
• Protective gases used in welding, can
force air out of the breath zone of the
welder and cause serious breathing
disorders. Always provide sufficient
ventilation of the working area, espe-
cially in confined areas, to ensure
sufficient oxygen in the working area.
UV and IR rays
• The welding arc produces ultraviolet
(UV) and infrared (IR) rays, which can
Safety instructions
Safety instructions
Workplace
• Welding works must be performed
away from flammable materials.
• Always keep fire extinguishing
equipment at a handy location in the
workshop.
• Make sure that the surrounding
surface is clean, dry, and the room is
well ventilated. Do not use the welding
machine in damp areas.
• Welding works should be carried out
in well-ventilated places or in places
where you can provide safe disposal of
gases generated during welding.
• Allow only qualified personnel and
authorized service center specialists
to service and repair the welding
machine.
• Keep an eye on the people around
the workplace, do not allow strangers
and especially children to the place of
welding.
• When working in a crowded place, pro-
tect others from dangerous reflecting
arc flash.
• Safely place the welding machine to
prevent it from turning over.
Safety guide
• Prior to initial operation, make sure
that all electrical cables are properly
insulated. If damaged, repair the insu-
lation or replace the cable.
• Prior to operation of the machine,
make sure all machine components are
clean and in good working condition.
• Do not use the welding machine if the
output cable, electrode holder, torch,
cables or wire feeder are wet. Do not
expose these parts to water. These
components and the welding machine
must be completely dry.
• Follow the recommendations of this
user’s manual.
• Turn off the machine, when not in use.
• Connect the negative terminal to the
welding area as close as possible to
welding area and provide for a stable
contact.
• Do not allow any part of the body to
come in contact with the welding wire
and the workpiece, negative termi-
nal or electrode of another welding
machine.
• To ensure safe work, take a comfort-
able and stable position. Use safety
belt for work at height.
• Do not coil cables around your body.
• A welding helmet or welding goggles
(TIG) with correct shade of filter must
be worn at all times.
• Wear protective clothing and dry insu-
lated gloves to protect your skin from
hot materials, UV and IR rays.
• Do not allow the welding machine
to overheat. Let the machine have
enough time to cool down between the
operating cycles. Strictly observe the
operating mode specified on the case
of the device and in this user’s manual.
• Do not point the torch at yourself or at
anyone else.
Safety precautions
• While the welding machine is in use,
welding cables, the electrode holder,
the negative electrode terminal and
connectors are live. Do not touch live
cables or connected to them parts of
the welding circuit with bare skin or
wet clothing. Work only in dry, free of