M Pumps SCE Series User manual

ISM0034 CT MAG-MS series instruction manual. Issue of 2012 rev.03- do not destroy, do not modify
Setting Innovative
Standards
M PUMPS PROCESS SRL
Via dell’artigianato, 120
45015 Corbola (RO) – Italia
Tel. +39 0426 346304 Fax + 39 0426 349126
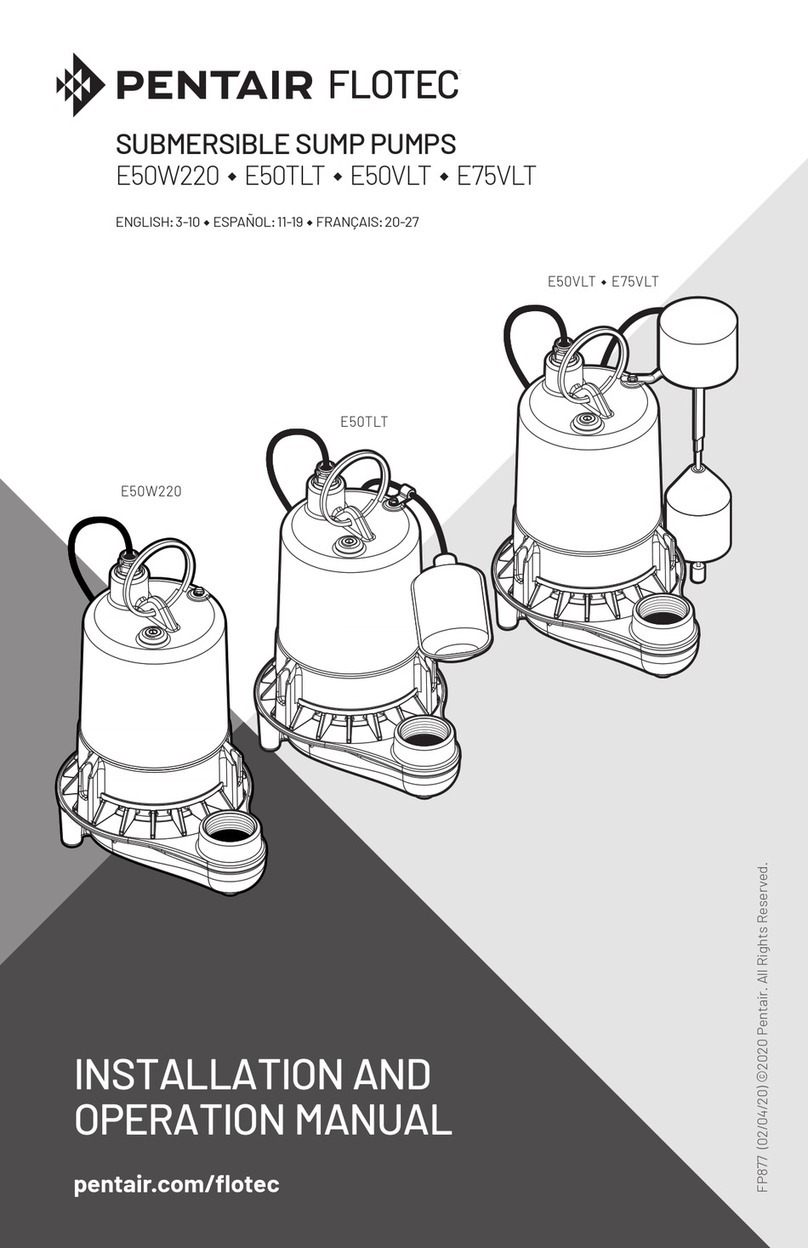
MAGNETIC DRIVE PUMPS
Centrifugal, Horizonthal, Top-Top,
Side Channel, Metallic
•SCE series
User Manual
This copy of the manual is a translation of the Italian version
and both manuals must be always furnished together
MODEL: pump only
MODEL: pump and motor assembly (Close Coupled version)
CAUTION
These instructions are intended for operators:
- Pump installation by qualified personnel;
- Use the pump, by staff
- Carry out maintenance / repair of the pump.
Read this instruction manual before using the pump.

Pag. 2/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
THIS INSTRUCTION MANUAL is intended to guide those responsible for the installation,
operation and maintenance of M PUMPS PROCESS SCE series seal-less magnetic drive
pumps. Please read it carefully, before you install and operate your M PUMPS PROCESS
pump. Useful information can also be obtained from: - Hydraulic Institute Standards (USA)
regarding pump installation.

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 3/33
CONTENTS
GENERAL WARNINGS AND SAFETY.....................................................................................................................................4
Symbols used in the manual......................................................................................................................................................... 4
WARRANTY..........................................................................................................................................................................4
NAMEPLATE ........................................................................................................................................................................5
1. 7
2. Key feature of magnetic drive pumps is that the fluid that have to be moved never comes into direct contact with
engine parts, ensuring the physical separation between the motor and the pump and the transmission is delivered via a
coaxial magnetic coupling...................................................................................................................................................7
Applications.................................................................................................................................................................................. 8
TECHNICAL DATA................................................................................................................................................................9
3. 10
4. 10
NOISE AND VIBRATION ....................................................................................................................................................11
RADIATION IONISING......................................................................................................................................................11
CHECKS TO PUMP DELIVERY, STORAGE............................................................................................................................11
SHIPPING AND HANDLING ...............................................................................................................................................11
ASSEMBLY, INSTALLATION, CONNECTIONS, COMMISSIONING AND SETTING................................................................12
Assembly ................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Connection of the pump to suction and discharge pipes................................................................................................................ 12
Checks for the proper operation .................................................................................................................................................. 13
Commissioning and operator training........................................................................................................................................... 13
Self-priming pumps and non self-priming pumps..........................................................................................................................14
INTENDED USE OF THE PUMP. IMPROPER USE. DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTIONING.PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
DURING USE......................................................................................................................................................................14
Intended use of the pump........................................................................................................................................................... 14
Instructions for proper use reasonably foreseeable....................................................................................................................... 14
Not permitted use....................................................................................................................................................................... 14
RESIDUAL RISKS AND PROTECTION MEASURES TO BE TAKEN........................................................................................15
Description of the residual risks that remain................................................................................................................................. 15
Protection measures to be taken by the user and instructions ....................................................................................................... 15
Personal protective equipment to wear ........................................................................................................................................ 15
OPERATIONAL LIMITS, DESCRIPTION OF HAZARDS NOT EXCLUDED FROM THE SECURITY MEASURES TAKEN............15
Safety information present on the pump ...................................................................................................................................... 16
INSTRUCTIONS AND PROCEDURES FOR THE TRAINING OF THE PERSONNEL AND FOR EMERGENCIES.........................16
Recovery mode .......................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Fire-fighting equipment to be used:............................................................................................................................................. 17
Emission / dispersion of harmful substances................................................................................................................................. 17
MALFUNCTIONING, FAILURE, BREAKDOWN, ACCIDENT. MOST FREQUENT PROBLEMS: CAUSES AND REMEDIES..........17
Malfunctioning and Failure .......................................................................................................................................................... 17
Breakdown................................................................................................................................................................................. 17
Accident..................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Most frequent drawbacks: problems, causes, remedies, residual risks............................................................................................ 17
PERIODIC AND EXTRAORDINARY MAINTENANCE............................................................................................................20
Cleaning components and magnet............................................................................................................................................... 20
Periodic preventive maintenance ................................................................................................................................................. 20
Emptying of the fluid contained in the pump................................................................................................................................21
Draining the oil contained in the pump ........................................................................................................................................21
Extraordinary maintenance.......................................................................................................................................................... 21
Pump reassembling .................................................................................................................................................................... 23
DECOMMISSIONING, DISMANTLING AND DISPOSAL OF MATERIALS..............................................................................24
Decommissioning........................................................................................................................................................................ 24
Demolition and dismantling......................................................................................................................................................... 24
EXPLODED VIEW PART LIST..............................................................................................................................................25
NOTES ...............................................................................................................................................................................27
APPENDIX A – Register of maintenance and periodic checks of the pump.......................................................................28
APPENDIX B – Startup check list.......................................................................................................................................29

Pag. 4/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
GENERAL WARNINGS AND SAFETY
This manual was prepared by M PUMPS PROCESS pump to provide the buyer all necessary information for its
proper use and regular maintenance. In this manual is also contained the manual of the electric motor when the
pump is supplied with this.
For safety and hygiene of the workplace and to ensure a fair and sustainable use of the pump, the manual should
be kept for any consultation.
As part of the pump, this manual must go with it.
For any given non-deductible or not included in this manual is recommended that you contact M PUMPS
PROCESS.
Do not use the pump before you have read and assimilated all safety rules and instructions in this
manual.
In case of damage or loss of the manual, ask for a copy to M PUMPS PROCESS promptly.
The failure to follow instructions in this manual, exempt M PUMPS PROCESS from any liability.
The pump and the instructions are intended for operators who make professional use and should be used by
qualified personnel adequately trained, aware of uses, operation and risk that the pump generates during its use,
the user with experience is the best form of qualification.
M PUMPS PROCESS reserves at any time the right to make changes deemed necessary to improve the pump,
taking care to update this manual as soon as possible. This reflects the state of the art at the marketing pump. In
case of transfer of the pump, the user is encouraged to report to M PUMPS PROCESS the address of the new
owner to facilitate the transmission of any additions to the manual to the new user.
M PUMPS PROCESS reserves all rights to this manual, no total or partial reproduction is allowed without written
permission.
Symbols used in the manual
In the text to indicate the risk of maneuvers or possible dangerous situations, warnings have been included, each
of which consists of a symbol followed by a warning.
MAGNETIC
Persistence of a magnetic field. This field may represent an immediate danger to
individuals who have electronic medical devices, metal heart valves, metal or any other
metal objects, impairing its functionality.
M PUMPS PROCESS declines any responsibility for any damages to people who did not
keep a safe distance of at least 1metre, where it is shown that symbol
DANGER
Indicates a potential risk to operators who are using the pump and / or the integrity of the
pump, which could result in damaging itself and / or serious injury to people concerned.
CAUTION
Calls attention to important details that the staff must know and keep in mind for the
proper use and operation of the pump.
PROHIBITION
Calls attention to transactions that are absolutely prohibited, not respecting the prohibition
you may damage the pump and / or operators.
M PUMPS PROCESS declines responsibility for damages to things or people for not
having complied with the prohibitions set.
WARRANTY
Valid for one year from the date of the pump sale. M PUMPS PROCESS do not assume any liability for any
warranties explicit or implied, nor as regards the possibility to sell or the suitability of the items supplied.
The warranty will not be applied if:

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 5/33
−the repair and / or maintenance was not carried out strictly in accordance with the instructions;
−the pump has not been installed and put into service as instructed;
−the repairs were not made by staff M PUMPS PROCESS or were made without consulting M PUMPS
PROCESS;
−spare parts are not original were used;
−lubricants were used different from those recommended;
−the parts supplied were not used according to their nature and / or destination;
−the parts supplied were used carelessly, negligently, improperly;
−the parts supplied were damaged due to external circumstances.
All wear parts are excluded from warranty.
NAMEPLATE
The pump for installation in ordinary environments has the nameplate on the side of the support as shown: only
the fields are compiled must be considered relevant and therefore valid for identification.
-PUMP UNIT SUPPLIED WITH ELECTRICAL MOTOR:
-PUMP UNIT SUPPLIED WITHOUT ELECTRICAL MOTOR:

Pag. 6/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
The serial number of the pump, here called serial number (s.nr) defines the type of components installed in the
pump:

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 7/33
PUMP DESCRIPTION AND OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF SIDE CHANNEL PUMPS
1.
2. Key feature of magnetic drive pumps is that the fluid that have to be moved never comes into
direct contact with engine parts, ensuring the physical separation between the motor and the
pump and the transmission is delivered via a coaxial magnetic coupling.
The pump consists of a part (outer rotor) that is coupled to an electric motor through elastic coupling (bare shaft
version) or directly (close couple) and a part (internal rotor integral with the pump impeller) that allows the
pumping fluid. The outer rotor is composed of a series of magnetic elements with features and size variations to
the torque to be transmitted. The inner and outer rotor magnets generate a magnetic field. At the start of the
electric motor the outer rotor rotating synchronously with the internal rotor, thus the power is transmitted to the
impeller pump, which acts as the pumping of liquid in the pump body itself. A static containment can, called rear
casing, located between the two rotors, separates the liquid from the atmosphere, making the pump seal.
The design of the side channel pump allows for the transfer of liquid-gas mixtures with up to 50% vapor;
therefore eliminating possible air or vapor locking that can occur in other pump designs.
This pump series is provided of a special centrifugal impeller that lowers NPSH requirement for the pump.
The side-channel pump design is similar to a regenerative turbine in that the impeller makes regenerative passes
through the liquid. However, side channel impeller design and casing as well as the principles of operation differ
greatly.
The side-channel pump has a channel only in the discharge stage casing (A) and a flat surface which is flush with
the impeller on the suction stage casing (B). A star-shaped impeller (C) is keyed to the shaft and is axially
balanced through equalization holes (C1) in the hub of the impeller. The liquid or liquid/vapor mixture incomes
each stage of the pump through the inlet (B1). Once the pump is initially filled with liquid, the pump will provide
a siphoning effect at the inlet port similar to what happens in water ring pumps. The water remaining in the
pump casing forms a type of water ring with a free surface. A venturi effect is created by the rotation of the
impeller and the free surface of the water, thus pulling the liquid into the casing. After the liquid is pulled through
the inlet port, it is forced to the outer periphery of the impeller blade by centrifugal action.
It is through this centrifugal action that the liquid is accelerated and forced into the side channel. The liquid then
flows along the semicircular contour of the side channel from the outermost point to the innermost point until
once again it is accelerated by the impeller blade. The liquid moves several times between the impeller and the
side channel. Thus the rotating impeller makes several regenerative passes until the liquid reaches the outlet
port. The speed of the impeller along with the centrifugal action impart energy to the liquid through the
exchange of momentum, thus allowing the pump to build pressure.
The side channel leads directly to the outlet (A1). At the outlet port, the main channel ends and a smaller
minichannel (A2) begins. At the point where the mini-channel ends, there is a small secondary discharge port
(A3) level with the base of the impeller blades.
As the liquid is forced to the periphery through centrifugal action due to its density, the vapor within the liquid
stream tends to remain at the base of the impeller blades since it has a much lower density. The main portion of
liquid and possibly some vapor, depending on the mix, is discharged through the outlet port. A small portion of
the liquid flow follows the mini-channel and eventually is forced into the area between the impeller blades. The
remaining vapor which was not drawn through the outlet port resides at the
base of the impeller blades. At the end of the minichannel, as the liquid is forced into the area between the
blades, the area between and around the impeller blade is reduced.
The liquid between the blades displaces and thus compresses the remaining vapor at the base of the impeller
blades. The compressed vapor is then forced through the secondary discharge port where it combines with the
liquid discharged through the outlet port as it is pulled into the next stage or discharged from the pump. Thus
entrained vapor is moved through each stage of the pump.
Each subsequent stage operates under the same principle.
The number of stages can be varied to meet the required discharge head. When multiple stages are required, the
relative positions of the stage outlet ports are radially staggered to balance shaft loads.

Pag. 8/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
ITEM
DESCRIPTION
A
Discharge Stage
A1
Outlet
A2
Mini channel
A3
Secondary gas discharge
B
Suction Stage
B1
Inlet
C
Impeller
C1
Equalization Holes
Applications
−pumps in general, this model is ideal for clean liquids slightly contaminated, no particles that may become
magnetized;
−the maximum working pressure of the plant,the temperature suitable and the maximum rotation speed
depends on the type of pump and it is specified in the "TECHNICAL DATA".
Other uses are not permitted because you must comply with the conditions of use in "TECHNICAL DATA": the
use of a pump in a plant or in fluid conditions different from those for which the pump was designed, can lead to
dangerous situations for the user.
ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 9/33
TECHNICAL DATA
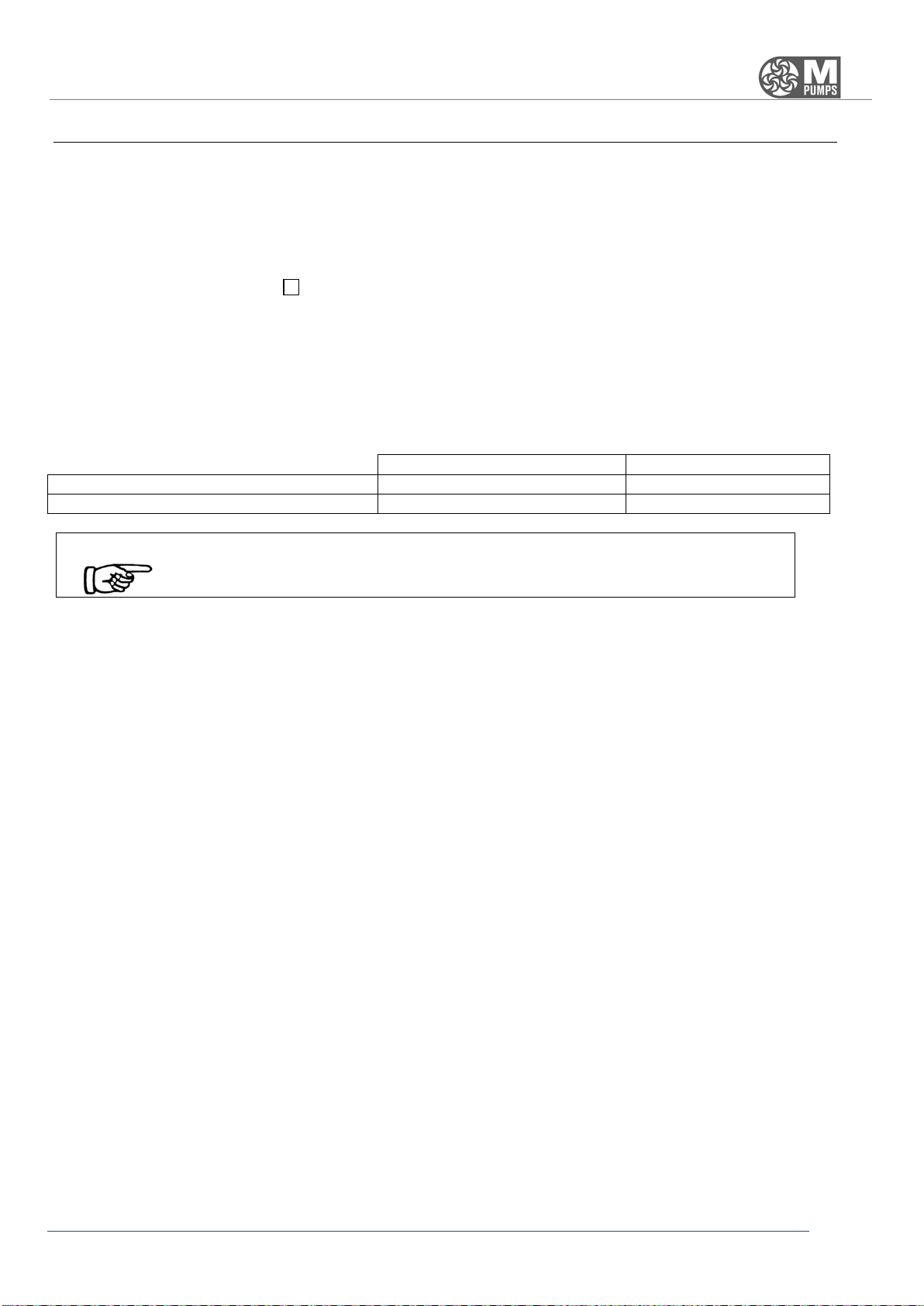
The pumps described in this manual have the following characteristics:
Available in bare shaft configuration or close couple, with the engine directly keyed to the pump support.
SCE
•Nozzle: DIN PN16 flanged;
•Max viscosity: 200 cps;
•Max system pressure: 16 BAR (standard)
•Flow up to 12 m³/h;
•Head up to 110 m;
•Working temperature from -50°C to +120 °C (std. Version)
•Installable motor power: from 0.75KW to 7.5KW;
•Speed: up to 2000 rpm;
•Weight (pump only): from 19 to 59 kg;
Electric Motor characteristics:
Supply frequency: 50 Hz
Supply frequency: 60 Hz
4 poles
1450 rpm
1750 rpm
6 poles
950 rpm
1150 rpm
CAUTION
−CAUTION: If the pump is driven by inverter, remain within the recommended limits
of rotation
Pag. 10/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
3

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 11/33
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
See specific documentation provided with this manual.
NOISE AND VIBRATION
The pump noise depends primarily on the operating conditions. The operating condition of the pump during the
measurements is: the coupling of the pump with the electric motor on the bench with pumping fluids.
The A-weighted sound pressure level to front and side of the pump is below 85 dB (A).
RADIATION IONISING
The pump does not emit any kind of ionising radiation that could endanger persons.
CHECKS TO PUMP DELIVERY, STORAGE
All
M PUMPS PROCESS
pumps are tested before shipment and carefully packed for transport: at the reception of
the pump make sure that the pump has not been damaged during the transport. If there are problems, contact
immediately the carrier and inform
M PUMPS PROCESS
about what happened.
So that the pump is preserved over time as best as possible, we recommend storing it away from the sun, bad
weather and dust, if not immediately installed or used for long periods.
Stoppers closing the input and output connections of the fluid must not be removed until installation. If provided
with electric motor, observe also the motor manufacturer’s storage formality.
The maximum allowable temperature range during storage, preservation and use must be between -15 e +40 °C
with humidity between 10 e 90%.
SHIPPING AND HANDLING
You should carry out a precautionary check of the pump at the receiving to detect and report any damage in the
transport and handling operations. In case of breakages contact immediately
M PUMPS PROCESS
.
The precautions to ensure the stability of the pump concern the possible slips and overturning caused by
handling and transport, which must be prevented by setting the pump casing of the pump with ropes to the
vehicle frame.
Pump and motor assembly cannot be moved manually due to its high weight.
To move a pump positioned on a pallet, enlarge as maximum as possible the forks and then operate.
For a stable lifting the pump can be lift as indicated in the figures:
close couple pump without motor
Bare frame pump without motor
close couple pump with motor
Centre of gravity approximately in
the middle
Centre of gravity approximately in
the middle
Centre of gravity approximately in
the middle
Pag. 12/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
These operations must be performed by a trained staff who is informed of the risk of these proceedings.
PROHIBITION
−It is forbidden to lift the pump using different lugs from the ones specially designed and
reported, as points of anchorage.
−You cannot lift a pump and motor assembly using the eye-bolt of the electric motor
only.
−During the lifting the entire surrounding area is considered as a danger zone and must
be cleared by personnel not engaged in those operations.
It is indicated the possibility of transporting and handling the pump using the lugs designed for that use: you
must ensure that chains and shackles are able to withstand the weight of the pump (as shown in "TECHNICAL
DATA").
ASSEMBLY, INSTALLATION, CONNECTIONS, COMMISSIONING AND SETTING
Assembly
Install the pump on a solid foundation as close as possible to the liquid to be pumped, below the level, in a
position to facilitate maintenance and inspection.
Ensure that the pump doesn’t take rough shacks as this may damage the magnets of the internal and external
rotor or the silicon carbide bearings.
Ensure that the heated air from other units does not affect the pump; the air temperature must not exceed
40 °C, for higher temperatures contact your distributor
M PUMPS PROCESS
; ensure also the free circulation of air
cooling of at least ¼ the engine diameter, because either the pump or the motor should be able to dissipate the
heat by natural air convection. Insufficient cooling could lead to high surface temperatures of the bearings seat,
poor lubrication and premature failure of bearings. Useful is the monitoring of the surface bearings’ temperature.
It is always responsibility of the operator to keep low the temperature of the liquid so that not to superheat the
pump: in case of irregular pressure fluctuations and flow drop turn off the pump.
CAUTION
−Normally you should mount the pump horizontally. If mounted vertically or inclined,
the pump, or rather the suction flange shall be placed in the lowest point. Leave a
space of at least 50 cm between the pump and any walls or pipes.
−When pumping liquid can reach high temperatures: form 60 °C upwards you must
install protections to prevent contact with hot pump parts;
−Connect to the ground the entire pump casing to prevent accumulation of static
electricity;
−If the pumped liquid can be dangerous to people and environment, the user must take
precautions for a simple and quick block in case of leakage for breakage/ replacement/
pump maintenance.
Connection of the pump to suction and discharge pipes
For a proper assembly aimed at an optimal use of the pump, you must follow these requirements:
−pipes must be supported and kept in line regardless of the pump, until its connections, so that not to
impose on it;
−links must not be subjected to stresses during the job ;
−the maximum permissible forces and moments on flanges shall not exceed those listed in “technical
data”;
−inlet pipes should be constructed with as few restrictions as possible in order to have the highest
available NPSH;
−the length of pipes , particularly that of the inlet pipe must be minimized;
−the pipe must be placed so that it is not possible the formation of air; if this is not possible, it should be
calculated the possibility of bleeding the air from the highest point ;
−during suction use full section valves only;
ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 13/33
if the suction tube was larger than the suction flange, you will use an eccentric reduction, in order to prevent
formation of air and turbulence;
if there is a possibility that the maximum working pressure can be overcome, for example due to excessive
suction pressure, you should take appropriate measures by including a safety valve in the pipe;
Avoid using quick-closing valves, because sudden changes of pressure cause water hammer very dangerous for
the pump and the pipes;
Before installing the pump, make sure the suction line is clean and/or provided with a filter to protect the
impeller and the stationary bearings from damages incurred by slag, or other foreign particles , especially when
you start the installation for the first time.
Electrical connections:
DANGER
The pump is provided with or without electric motor: only qualified personnel
should carry out mechanical connection of the pump to the motor (for the model without
motor) and the electrical connections of the motor to the electrical system. Please read
carefully the instructions of the manufacturer of the motor
or the manual before you
complete the installation.
Make sure that the motor doesn’t start during maintenance jobs.
Checks for the proper operation
We recommend installing a pressure gauge on both inlet and outlet pipes to allow the operator to easily control
the proper pump functioning in relation to the required operating point: in case of cavitation or other
malfunctions, there will be obvious pressure fluctuations.
Check the differential pressure of the pump between the suction and discharge connections to verify that it works
in the point of work provided.
Check that the absolute pressure at suction is not so low to cause the cavitation.
CAUTION
The absolute pressure at pump suction (m) must be at least 0,5 to 1 m, the vapour
pressure of the pumped liquid, in order to avoid cavitation.
Cavitation should always be avoided as it is very dangerous for the structure of the pump.
Do not dry run the pump!
Commissioning and operator training
−Fully open the inlet valve and fill the pump and suction line;
−Ensure there are no obstacles to the free rotation of the pump impeller.
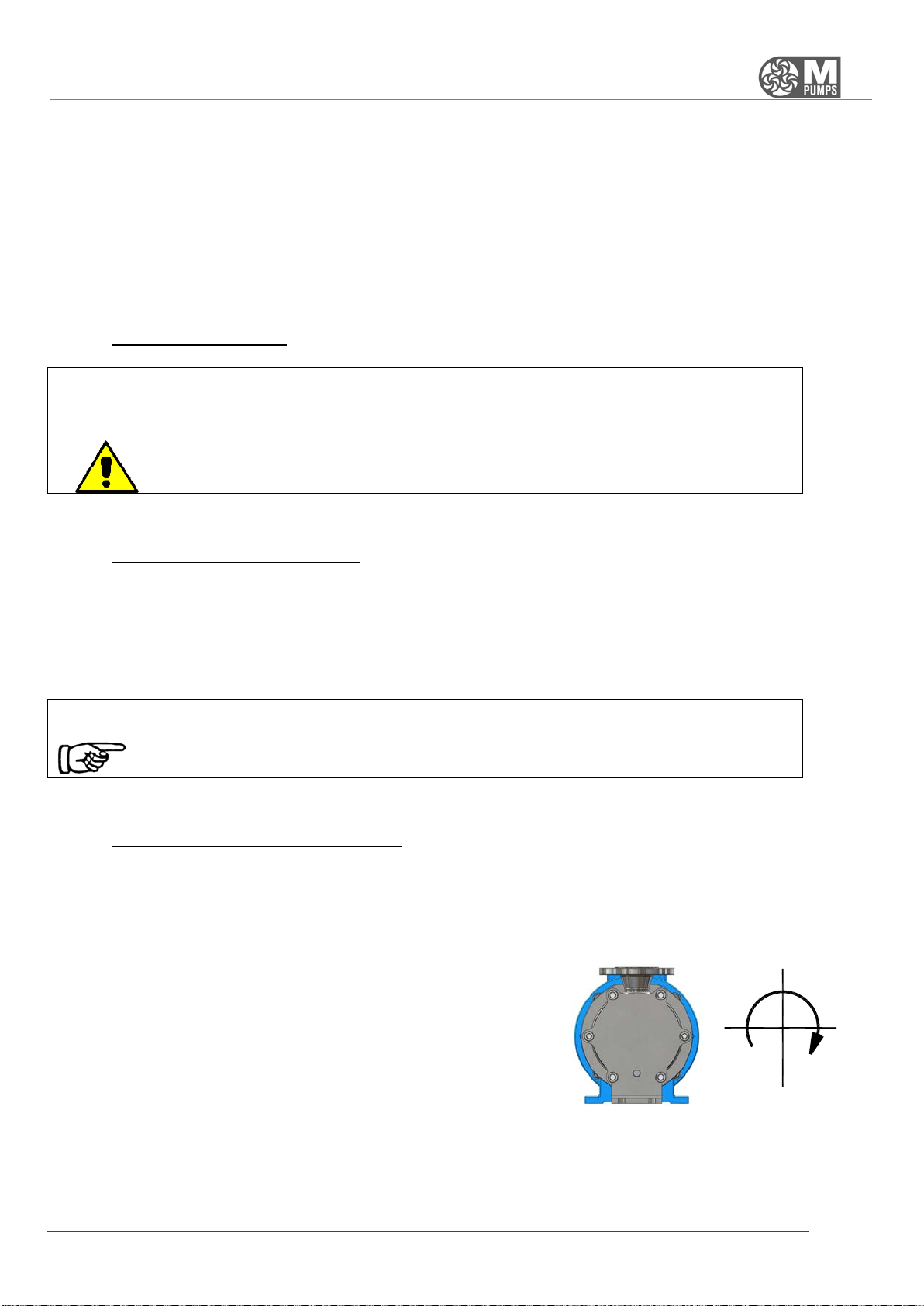
The
M PUMPS PROCESS
series SCE are not reversible so the rotation
cannot be reversed.
The proper direction is clockwise.
If you put in front of the pump casing, an arrow indicates the correct
direction of rotation; to reverse the direction of rotation may cause
damages to the pump.
To control the direction of
rotation, give and immediately remove
voltage, then observe the direction of rotation.
ROTATION SENSE:
Make sure that rotating parts, such as flexible coupling or other related organs, are always protected when the
pump is running.
Operators using the pump must have read this manual in the sections committed to the functioning, use and
maintenance, as well as being qualified to fully understand the features and to be able to identify the problems of
the pump.

Pag. 14/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
By carrying out the functions mentioned in the previous section and all controls listed in the register
maintenance, the pump is ready for use.
Self-priming pumps and non self-priming pumps
SCE pumps are self-priming: Make sure the pump is always filled with the pumping liquid to maintain the self-
priming feature. Use a back flow check valve to stop reverse flow when operating with suction lift, dry run shall
be avoided.
INTENDED USE OF THE PUMP. IMPROPER USE. DESCRIPTION OF
FUNCTIONING.PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT DURING USE.
Intended use of the pump
The magnetic drive pump, thanks to its decoupling between the pump and the motor, never enters into direct
contact with motor parts, providing a friction effect on the impeller of the pump. The pump works correctly if the
parameters specified in the paragraph “TECHNICAL DATA” are followed.
Instructions for proper use reasonably foreseeable
Before starting work you must check that:
−All maintenance actions were properly carried out according to the time intervals set by
M PUMPS
;
−There are no damaged parts of the pump;
−All the warning stickers and safety licence plates are present and in good condition and are operating the
emergency stop buttons (check through a test).
CAUTION
Do not dry run the pump!
At the start, immediately check the pressure gauge placed in the discharge: if the
discharge pressure reaches the nominal value quickly, stop the pump and try staring.
Check the pump and piping to make sure that there is no leakage of liquid from the plant.
A noisy pump is a symptom of a malfunction that represent a failure in the short term. A
very low frequency and with a rumbling can indicate the state of cavitation; an excessive
noise of the motor can be caused by a wear of a bearing.
Not permitted use
While maintaining the conditions of use indicated in the paragraph “TECHNICAL DATA”, the ways in which the
pump should not be used are given here. To avoid damaging the pump, it is forbidden to use it in the following
conditions:
PROHIBITION
−Start the pump dry: the pump casing must be full of liquid.
−Run the pump dry for more than 1 minute;
−
Mare the pump work with inlet valve and /or outlet closed: the heat generated by the
impeller, by magnetic coupling and bearings will boil the liquid, which will cause pump
cavitation/vibration, the impeller damaging and the bearings collapse;
−
The pump flow should never be adjusted by the valve located in the suction pipe,
which must be kept fully open, start and or make the pump work if there are losses;
−Start the pump if there are losses;
−Change working condition of the pump without having consulted the
M PUMPS
PROCESS
technical office;
−loosen the pump connections while under pressure;
−try to clean the pump while it is running;
ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 15/33
−run the pump in the opposite direction to that shown in the pump casing;
−run the pump over nominal temperature and pressure;
−pumping liquids containing ferromagnetic particles of any size, or substances that can
attack chemically or erode the inside of the pump;
−remove guards and shelters while the pump is running;
−act on electrical parts installed without first removing the tension, not to alter the
safety devices installed, do not activate repeatedly the command buttons.
DANGER
It is incorrect any use of the pump other
than that mentioned in the paragraph
“Instructions for a proper use reasonably foreseeable”.
M PUMPS PROCESS
disclaims any liability damages to things and people related to uses for
which the pump was not specifically designed and constructed.
Also the ways in which certain situations of danger might present as a result of improper use, are prohibited.
RESIDUAL RISKS AND PROTECTION MEASURES TO BE TAKEN
Description of the residual risks that remain
Despite adopted measures incorporated in the pump, the main dangers associated with the use of the pump and
the solutions identified are the followings:
Danger of sketches projection of process fluid that can be corrosive or burning, as a result of improper
installation and sudden ruptures of the pump casing and hydraulic lines;
Danger of cuts to the hands due to the presence of smears on the pump casing;
Explosion of the pump is due to a formation of explosive mixture inside the pump casing as a result of an
improper use.
Protection measures to be taken by the user and instructions
PROHIBITION
It is absolutely forbidden to the user to tamper with safety devices. Before using
the pump check the proper couplings mechanical protection. Any tampering nullifies the
warranty and liability of
M PUMPS PROCESS
towards the pump users.
Only maintenance personnel can perform maintenance operation affecting safety devices.
Personal protective equipment to wear
Protection measures that have to be taken during this phase are adopting antacid and antistatic coverall,
chemical-resistant glasses, gloves to protect from mechanical and chemical agents and safety shoes.
Avoid the use of accessories (necklaces, bracelets, etc.) and clothes unshackled; torn or dangling that could get
entangled in parts of the structure.
OPERATIONAL LIMITS, DESCRIPTION OF HAZARDS NOT EXCLUDED FROM THE
SECURITY MEASURES TAKEN
Dangers that have not been reduced/ eliminated with the security measures adopted on the pump can be
reduced/eliminated if operators apply measures on management as a result of having to:
−Keep all the safety warnings of and all plaques and labels intact and replace them when necessary,
periodically checking their good condition;
−Don’t employ substances which may affect the physical ability or the mental faculty (alcoholic
beverages, medicines, drugs, etc);
−Don’t use without permission spare parts not identical to the originals or components not approved by
M PUMPS PROCESS
;
−Don’t perform any modification or structural intervention without the approval of
M PUMPS PROCESS
;

Pag. 16/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
−After shocks accidentally suffered by the pump, check the pump integrity and perform a check to
M PUMPS PROCESS
;
−After a long period of pump detention check the pump integrity and functionality of stakeholders to
wear. If necessary perform the replacement with identical spare parts to the originals.
CAUTION
Each of the misuse or negligence listed here causes:
−immediate cancellation of
M PUMPS PROCESS
assistance.
−cancellation of
M PUMPS PROCESS
responsibility for damage to property, animals or
people.
Safety information present on the pump
Safety warnings applied to the pump must be respected and restored in case of illegibility, and are as follow:
Warning Description signs applied Symbol/indication Quantity Notes
1.
Marking plate
M PUMPS
PROCESS
.
As described in paragraph
“PLATE”
1 1
2. Label rotation and not run dry
indication
1 2
3. Hydro-test label
1 3
4. Label quality control assembly
1 Internal use
INSTRUCTIONS AND PROCEDURES FOR THE TRAINING OF THE PERSONNEL AND
FOR EMERGENCIES
Operators responsible for the various life stages of the pump must be:
- for assemblers: staff formed and trained on good practices for handling of goods with the use of tools and
lifting equipment;
- for installers of pipes and electrical connections: qualified and trained staff to operate on electrical plants, staff
with experience in hydraulic installations;
-f or users: professional staff trained in the instruction for use of this pump.
In case of emergency:
- alert who is close to the situation of danger, even waving his arms;
- stop the pump by pressing the nearest emergency stop button;
Recovery mode
To return to normal operating conditions, you must delete all the causes that have generated the emergency,
possibly repairing or replacing the components that caused the failure.
CAUTION
After the intervention of security devices, you must find the cause of action
before continuing operations.

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 17/33
Fire-fighting equipment to be used:
In case of fire involving the pump, you can use water or foam liquid only after removing the voltage, or a powder
type fire extinguisher with extinguishing agent. Do not use CO2 as being launched at -79 ° C may react violently
with the hot parts.
Emission / dispersion of harmful substances
The fluid in the plant might be released in the atmosphere following an intervention or the pump break.
MALFUNCTIONING, FAILURE, BREAKDOWN, ACCIDENT. MOST FREQUENT
PROBLEMS: CAUSES AND REMEDIES
There aren’t pump details which provide such cases of malfunctioning as to restrict or make its use dangerous.
In paragraph “Most frequent drawbacks: causes and remedy” is discussed with more details in this section.
Malfunctioning and Failure
In case of failure of mechanical parts you must immediately restore the original terms of security by replacing or
repairing the parts that have deficiencies.
In case of failure of the pump, proceed as follows:
-Turn the motor off;
-close the inlet and outlet valves;
-find the cause of the failure by checking the section “ Most frequent drawbacks: problems, causes,
remedies, residual risks".
The failure of a pumping plant can be attributed to:
-a pump failure;
-a failure or defect in the pipe;
−a failure due to an installation or a start not correctly executed;
−wrong choice of pump.
Breakdown
In the event of failure of pump alert verbally the staff present in the nearness of the damage that is verifying.
Accident
In case of accident, you must report the emergency to the plant responsible for the installation, in order to
secure the plant to reach with the emergency team the place where the accident happened.
Most frequent drawbacks: problems, causes, remedies, residual risks
INSUFFICIENT FLOWS
Causes
Remedies / actions to be taken
The head requested exceeds the pump head
expected.
Increase the speed rotation if possible.
Mount an impeller of greater diameter
Reduce the total head of the system if possible.
Increase the diameter of the discharge pipe.
Check that the discharge valve is fully open.
Replace the pump.
Ask your
M PUMPS PROCESS
distributor.
The pump rotates in the opposite direction. Check the direction of rotation.
Refer to section 3.5 of this manual
Air or steam trapped in the suction. Check the presence of air or steam trapped. Refer to section
3.4 of this manual.

Pag. 18/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
The liquid contains air or steam. The liquid
produces foam. Check the presence of vortices in the suction line. Enter
some in the fuel tank to prevent the formation of vortices.
Install a tank of sufficient capacity in the suction line to allow
gas to drag.
Insufficient inlet pressure, with the
generation of cavitation and loss of
efficiency.
Increase the static height at the suction.
Check that the intake is not blocked or are no bottlenecks.
Reduce the liquid temperature. Increase the diameter of the
intake pipes.
Reduce the length of inlet pipes. Open completely the inlet
valve. Check the viscosity of the liquid; refer to "technical
data" section of this manual, increase the temperature of the
liquid if necessary.
Wear ring, wear pump casing or impeller.
Check the condition of rotating ring wear and collar. Replace
if worn; refer to Chapter 10 of this manual.
The temperature of the liquid is close to
boiling point
Reduce the liquid temperature.
NO FLOW
Causes
Remedies / actions
The pump is defused
Re-prime the pump. Refer to section 3.5.1 of this manual.
Check for air leaks in the suction line
Suction line blocked
Ensure that there are no blind pipes, obstructed or valves
closed.
The magnetic coupling decouples
Reduce the flow: partially close the discharge valve. Reduce
the density of the liquid, if possible. Reduce the prevalence
of the pump (check in advance with your distributor
M PUMPS PROCESS
). Make sure the pump turns freely;
inspect the inside in case this does not happen. Reduce the
engine power installed (check in advance with your
distributor
M PUMPS PROCESS
). Adopt star-delta starting.
The motor stopped Check the power of the motor. Check the status of the
motor.
EXCESSIVE FLOW
Causes
Remedies / actions

ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE- Rev.03
Pag. 19/33
The head required is lower than that
provided by the pump Reduce the speed of rotation, if possible; reduce the impeller
diameter; partially close the discharge valve.
OVERHEATING OR MOTOR STOP
Excessive pumped liquid density
Reduce the flow by closing the valve outlet partially
The pump has seized or is about to seize.
Check the free rotation of the impeller. Check for internal
obstructions.
The motor and pump are misaligned
Refer to section 3.8 of this manual
The motor bearings are damaged or worn.
Replace the motor bearings, investigate the causes of
breakage.
Motor under dimensioned
Mount a more powerful motor (check in advance with your
distributor
M PUMPS PROCESS
).
Motor overload threshold set incorrectly
Check the security settings of the motor
The guard against the motor dry running
(where present) has failed or has been set
incorrectly.
Control flow decreases or fluid intake.
FUNCTIONING WITH NOISE DEFECTS AND/OR
VIBRATIONS
Causes
Remedies / actions
Insufficient inlet pressure, consequent
cavitation, insufficient lubrication of the
bearings (with mechanical damages if the
condition persists).
STOP IMMEDIATELY THE PUMP!
Refer to paragraphs 3.4, 3.5, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 of this manual
Wear, erosion and immediate damage to the
impeller and internal bearings.
Check inside the pump damages or obstructions.
Wear of the coupling motor-pump
Replace the coupling and proceed to the realignment of
pump and motor.

Pag. 20/33 ISM0210 Instruction Manual of series SCE - Rev.03
Ball bearings or motor failure. Check and replace them if necessary.
Uninsured motor or base plate.Make sure that the motor and base plate are firmly
anchored to foundations and do not produce any
abnormal vibration.
Misalignment or improper anchoring of the
pipes. Check correct alignment of pipes and supports, refer to
section 3.2 of this manual.
The pump was started while still rotating in
the opposite direction, for a previous start.
Stop immediately the pump and drain all the liquid from the
discharge line before restarting.
PERIODIC AND EXTRAORDINARY MAINTENANCE
Proper maintenance and use are essential factors to ensure the functionality and pump lifetime.
Cleaning components and magnet
To clean all surfaces of the couplings and centering surfaces, use possibly methyl alcohol. Use paper towels
instead. Do not use solvents and other corrosive liquids on magnet to avoid damaging it; any dirt can be
removed from the magnets by using gummed paper. Do not hack or put pressure on the magnet during its
handling, it would cause them, damages because of their fragility.
Periodic preventive maintenance
Instructions relating to maintenance activities whose implementation do not require specific skills that can then
be made by users of the pump, are given. They are operations and inspections planned on issues considered
important for technical, operational and security staff, determined on the basis of the knowledge gained from
M
PUMPS PROCESS
. If the hydraulic pump is washed with jet in pressure, prevent the entry of water into the
terminal of the motor.
DANGER
Do not throw water on the pump hot components: components can explode in case of
sudden cooling generating projection of metallic material and leakage of hot fluid in
pressure and hazardous to health. Do not give strokes and pressures on the bearings, you
would cause the formation of micro-cracks which can cause serious damages
.
N. Description control /
intervention: implementation
rules
Warnings and protective
measures be taken to perform
the maintenance properly and
safely
Time
2
Internal bearings
Check the status of bushings, sleeve
bearings and thrust bearings,
replace them if worn
After 2500 hours,
check any premature
wear, then every
5,000hours or every
year
.
3
Wear rings
Check the status of the wear ring,
consult the table of tolerances
After 2500 hours,
check for premature
wear, then every 5000
hours or every year.
4
Motor bearings
Unless other specifications, motor
bearings are greased for life, so
Table of contents
Other M Pumps Water Pump manuals
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands

Waukesha Cherry-Burrell
Waukesha Cherry-Burrell SPX FLOW Universal I Series instruction manual

KRAL
KRAL L Series operating instructions

Ribimex
Ribimex RIBILAND PRJET61 User and maintenance manual

YAMADA
YAMADA DP-Fs Series Maintenance manual
Viessmann
Viessmann Solar-Divicon DN20B Installation, Start-Up and Service Instructions

Server
Server 100239 quick start guide