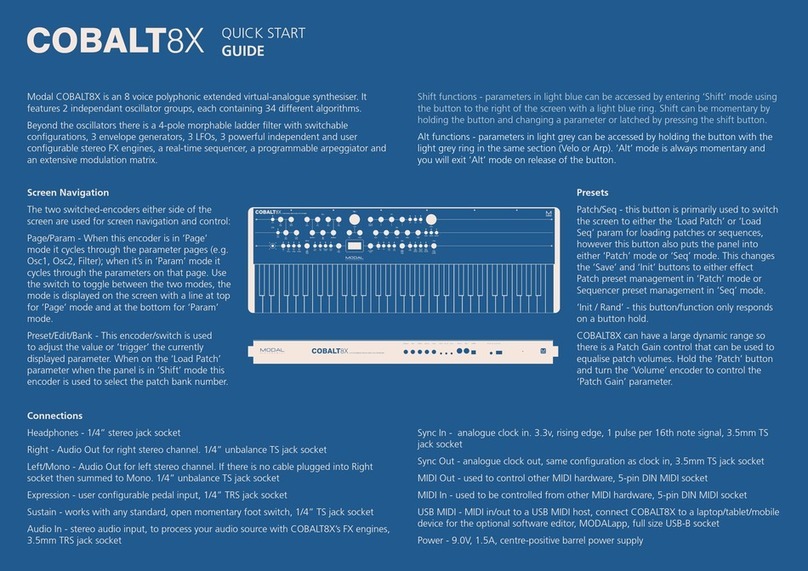
8 9
Specification
• True 8 voice polyphonic
• 120 carefully crafted wavetables split into 24 banks of 5 morphable waveform sets,
covering virtual analogue classics through to cutting edge EDM and many from the
original Modal 002 as well as a whole range of mathematically generated tables.
Additional PWM bank and 3 noise/modulation banks accessible on Oscillator 2
• 32 static wavetable modifiers including, de-rez, wave folders, wave shapers, phase
shapers and rectify that can be applied to the 120 wavetables to give a mind boggling
array of permutations and new waveshapes.
• 32 high resolution wavetable oscillators, 4 per voice
• 8 types of oscillator modifier including: Phase Mod (FM), Ring Mod, Amp Mod, Hard Sync
and Windowed Sync
• Voice Drift and Width controls that help to create massive stereo soundscapes
• Multiple keyboard modes, Mono, Poly, Unison 2, unison 4, unison 8, Stack 2 and Stack 4
• Inbuilt sophisticated programmable arpeggiator of 32 steps with rest capability with up to
2048 steps before repeating
• Glide/Portamento with both legato and staccato modes
• 4 Filter types. All filters types are 2 pole state-variable filters, the ‘Standard’ filters
are based on the resonant filter found in other Modal products (SKULPTsynth,
CRAFTsynth2.0). The ‘Classic’ types have a more rounded character and a softer
resonance response.
• 8 assignable modulation slots
• 4 additional fixed modulation routings for common assignments
• 11 modulation sources
• 52 modulation destinations
• 4-axis joystick that can be assigned to a huge range of modulation destinations and
virtually ‘locked’ when desired
• 3 dedicated envelope generators for AMP, MOD and FILTER that can be accessed
independently or all three simultaneously including negative (reverse) versions
• 2 Audio rate LFO’s with tempo sync (one poly, one global). Polyphonic LFO can sync to
frequency divisions
• Waveshaping distortion
• 3 incredibly powerful independent and user configurable stereo FX engines for Chorus,
Phaser, Flanger (Pos), Flanger (Neg), Tremolo, LoFi, Rotary, Stereo Delay, Ping-Pong Delay,
X-Over Delay and Reverb that can be arranged in any order
• 32-step programmable arpeggiator
• Real time sequencer with 512 notes with input quantise and four recordable / editable
parameter animations (Delay FX, LFO’s, sequencer and arpeggiator can be either clocked
internally or externally)
Specification
• 500 patch memories, all fully editable and ships with 300 factory programs
• 200 user patch spaces. Patch upload and download through the free MODALapp
• 100 sequencer presets that can be linked to any patch for quickly loading arrangements
• 100 FX presets
• 8 Quick Recall slots accessible from the panel for quickly loading your favourite patches
• Analogue clock sync in and out (configured to the KORG / Teenage Engineering
specification)
• MIDI DIN in and out
• Full size quarter inch jacks for stereo audio outs, headphones and external control such as
sustain and expression
• 3.5 mm stereo input with ability to route incoming audio through the FX
• FATAR TP9/S Full size 37 key keybed with both velocity and aftertouch
• 1.54 inch large OLED display – that provides instant visual feedback to the user at all
times of playing/editing
• Class compliant MIDI provided over USB connection to host computer or tablet
• Optional MODALapp software editor available for macOS, Windows, iOS and Android
• MODALapp can also be run within your Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), with VST3
and AU versions available
• Power: DC-9.0V - 1.5A center-positive
• Road ready Steel and Aluminium chassis
Dimensions
• Width: 555mm – 22 inches
• Depth: 300mm – 11-3/4 inches
• Height: 100mm – 4 inches