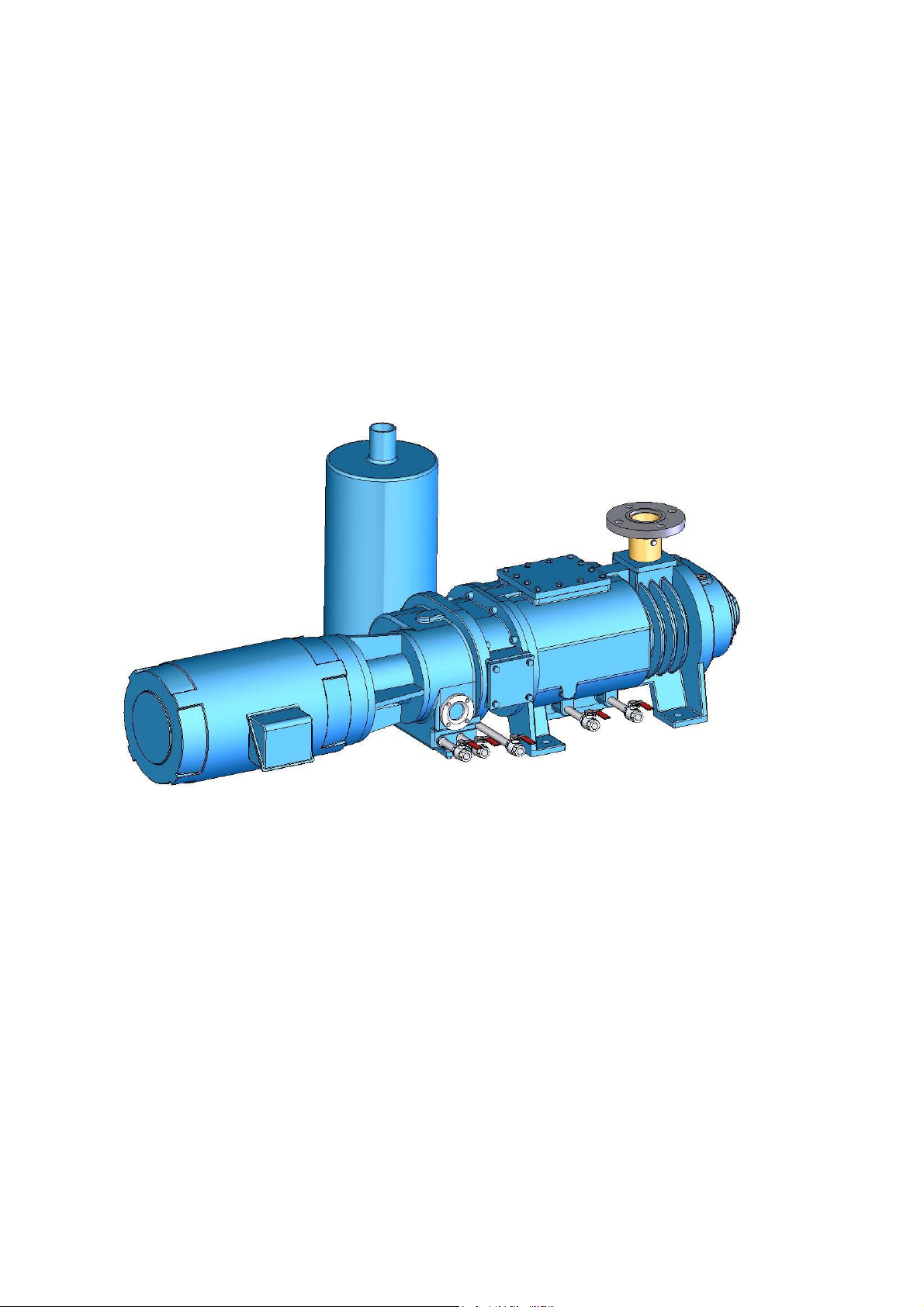
2.2. Piping
●Main Piping
(1) Clean inside of suction and discharge pipe to be free from rust, dust and foreign matters,
and place a strainer of 40 mesh on or over suction side.
(2) It is advisable to install expansion joint on the suction side as well as the discharge side of
the pump. Also, provide supports for piping so that no excessive load will be imposed on the
pump.
(3) In case Silencer is provided on discharge side, install it as near to connection as possible.
(4) Be sure to install a Non-return Valve adjacent to the suction port so that the pump will not
turn reversely. If preferred, install a gate valve instead, and assure to shut off prior to stopping
the pump.
(5) In case, there is a risk of condensate gas being collected on the pump discharge pipe, install
a recovery tank under the pump, then the condensed gas and water will be collected during
operation and can be discharged by opening of drain valve.
(6) Drain receiver should be installed under the drain valve to collect the discharged liquid.
●Cooling water piping
Cooling water piping is required to cool pump Front End plate & Casing. This piping should be
assembled with reference to the piping diagram and the outline drawing .
2.3 Preparation for Operation
(1) Remove dust and foreign particles such as welding slug from Vacuum pump and Piping.
(2) Check all suction and discharge connections are properly tightened and all piping properly
supported. Check cooling water piping as well.
(3) Fill oil up to the red point of the oil gauge. If oil is low, gear and bearing can seize, and if oil
is too high, the temperature will rise excessively, and can be cause for gear noise or other
negative effect on other parts.
(4) Let cooling water flow as specified in chart 1.3.
2.4 Operation
(1) Open suction valve, and turn on the power under no load condition to check rotating
direction. At this time, start up instantly.
(2) Run the pump under no load condition for 20-30 minutes to check any abnormal vibration or
heat. In case of any abnormality, stop operation and search for the cause. Often the cause is
improper installation or failure of alignment.
(3) Run the pump for 2-3 hours under normal load condition and check the temperature and
vibration.
(4) During operation, pay attention to level of Ampere drawn by the motor.
If case of abnormality, stop the pump immediately and check for cause. Often, the cause is
interference between rotors or between the periphery of rotor and the inner surface of casing.
All pumps are tested prior to shipping. However, full care and inspection is still necessary after
7