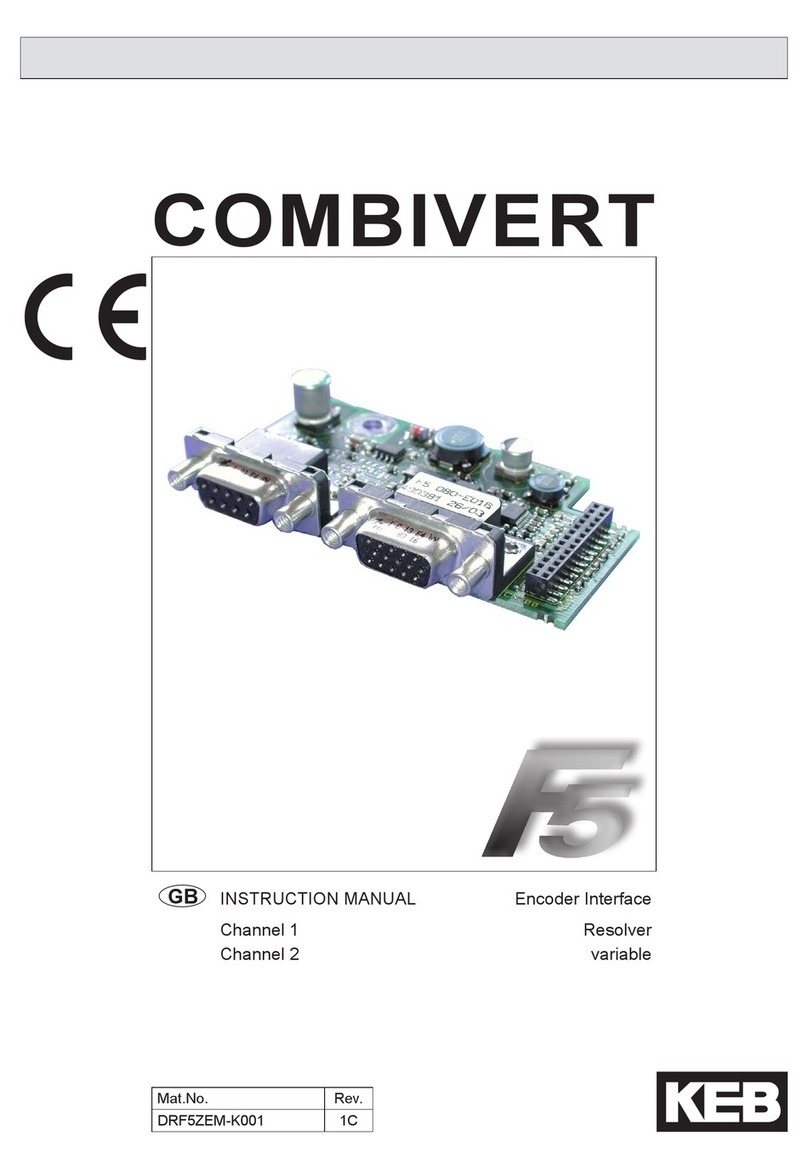
Profichip VPC3+S User manual

VPC3+S
User Manual
Revision 1.04

2
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
Liability Exclusion
We have tested the contents of this document regarding
agreement with the hardware and software described.
Nevertheless, there may be deviations and we do not
guarantee complete agreement. The data in the
document is tested periodically, however. Required
corrections are included in subsequent versions. We
gratefully accept suggestions for improvements.
Copyright
Copyright © profichip GmbH 2009-2012.
All Rights Reserved.
Unless permission has been expressly granted, passing
on this document or copying it, or using and sharing its
content are not allowed. Offenders will be held liable. All
rights reserved, in the event a patent is granted or a
utility model or design is registered.
This document is subject to technical changes.

Table of Contents
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
3
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
1Introduction................................................................5
2Functional Description ..............................................7
2.1 Overview.................................................................................... 7
3Pin Description...........................................................9
3.1 Pinout......................................................................................... 9
3.2 Pin Assignment (Overview).......................................................11
3.2.1 Asynchronous Intel Mode ..............................................13
3.2.2 Synchronous Intel Mode................................................14
3.2.3 Asynchronous Motorola Mode .......................................15
3.2.4 Synchronous Motorola Mode.........................................16
3.2.5 SPI Mode.......................................................................17
3.2.6 I2C Mode.......................................................................17
4Memory Organization...............................................19
4.1 Overview...................................................................................19
4.2 Control Parameters (Latches/Registers)....................................21
4.3 Organizational Parameters (RAM).............................................23
5ASIC Interface...........................................................25
5.1 Mode Registers.........................................................................25
5.1.1 Mode Register 0 ............................................................25
5.1.2 Mode Register 1 ............................................................27
5.1.3 Mode Register 2 ............................................................29
5.1.4 Mode Register 3 ............................................................31
5.2 Status Register..........................................................................32
5.3 Interrupt Controller....................................................................34
5.3.1 Interrupt Request Register.............................................35
5.3.2 Interrupt Acknowledge / Mask Register..........................38
5.4 Watchdog Timer........................................................................38
5.4.1 Automatic Baud Rate Identification................................39
5.4.2 Baud Rate Monitoring....................................................39
5.4.3 Response Time Monitoring............................................39
6PROFIBUS DP Interface...........................................41
6.1 DP Buffer Structure...................................................................41
6.2 Description of the DP Services..................................................44
6.2.1 Set_Slave_Add (SAP 55)...............................................44
6.2.2 Set _Prm (SAP 61) ........................................................45
6.2.3 Chk_Cfg (SAP 62).........................................................49
6.2.4 Slave_Diag (SAP 60).....................................................50
6.2.5 Write_Read_Data / Data_Exchange (Default_SAP).......52
6.2.6 Global_Control (SAP 58) ...............................................56
6.2.7 RD_Input (SAP 56)........................................................57
6.2.8 RD_Output (SAP 57) .....................................................57
6.2.9 Get_Cfg (SAP 59)..........................................................58
7 PROFIBUS DP Extensions.......................................59

Table of Contents
4
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
7.1 Set_(Ext_)Prm (SAP 53 / SAP 61)............................................59
7.2 PROFIBUS DP-V1....................................................................60
7.2.1 Acyclic Communication Relationships............................60
7.2.2 Diagnosis Model............................................................63
7.3 PROFIBUS DP-V2....................................................................64
7.3.1 DXB (Data eXchange Broadcast) ..................................64
7.3.2 IsoM (Isochronous Mode) ..............................................70
7.3.2.1 IsoM-PLL.........................................................74
7.3.3 CS (Clock Synchronization)...........................................80
8Hardware Interface...................................................87
8.1 Universal Processor Bus Interface ............................................87
8.1.1 Overview........................................................................87
8.1.2 Parallel Interface Modes................................................88
8.1.3 SPI Interface Mode........................................................91
8.1.4 I2C Interface Mode ........................................................97
8.1.5 Application Examples (Principles)................................103
8.1.6 Application with 80C32 (2K Byte RAM Mode)..............105
8.1.7 Application with 80C32 (4K Byte RAM Mode)..............106
8.1.8 Application with 80C165 ..............................................107
8.2 Dual Port RAM Controller........................................................107
8.3 UART......................................................................................108
8.4 ASIC Test................................................................................108
9PROFIBUS Interface...............................................109
9.1 Pin Assignment.......................................................................109
9.2 Example for the RS485 Interface ............................................110
10 Operational Specifications....................................111
10.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings.....................................................111
10.2 Recommended Operating Conditions......................................111
10.3 General DC Characteristics.....................................................111
10.4 Ratings for the Output Drivers.................................................112
10.5 DC Electrical Characteristics...................................................112
10.6 Timing Characteristics.............................................................113
10.6.1 System Bus Interface...................................................113
10.6.2 Timing in the Synchronous Intel Mode.........................114
10.6.3 Timing in the Asynchronous Intel Mode .......................116
10.6.4 Timing in the Synchronous Motorola Mode..................118
10.6.5 Timing in the Asynchronous Motorola Mode ................120
10.6.6 Timing in SPI Interface Mode.......................................123
10.6.7 Timing in I2C Interface Mode.......................................125
10.7 Package Specifications...........................................................126
10.7.1 LFBGA48.....................................................................126
10.7.2 LQFP48.......................................................................128
10.8 Processing Instructions...........................................................130
10.9 Ordering Information ...............................................................130
Revision History..........................................................133

Introduction 1
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
5
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
1 Introduction
Profichip’s VPC3+S is a communication chip with 8-Bit parallel processor
interface for intelligent PROFIBUS DP-Slave applications. Alternatively an
SPI or I2C interface can be used to communicate with the chip.
The VPC3+S handles the message and address identification, the data
security sequences and the protocol processing for PROFIBUS DP. In ad-
dition the acyclic communication and alarm messages, described in DP-V1
extension, are supported. Furthermore the slave-to-slave communication
Data eXchange Broadcast (DXB) and the Isochronous Bus Mode (IsoM),
described in DP-V2 extension, are also provided. For high-precision syn-
chronized motion control applications the chip is equipped with an HW-PLL
for IsoM.
Automatic recognition and support of data transmissions rates up to 12
Mbit/s, the integration of the complete PROFIBUS DP protocol, 4K Byte
communication RAM and the configurable processor interface are features
to create high-performance PROFIBUS DP-Slave applications. The device
is to be operated with 3.3V single supply voltage. All inputs are 5V tolerant.
Profichip’s VPC3+S is another member of profichip’s successful VPC3+
family. It is software compatible to other VPC3+ series devices however it
offers some unique features like serial processor interfaces, IsoM-PLL and
a very small package.
As there are also simple devices in the automation engineering area, such
as switches or thermo elements, that do not require a microcontroller for
data preprocessing, profichip offers a DP-Slave ASIC with 32 direct in-
put/output bits. The VPCLS2 handles the entire data traffic independently.
No additional microprocessor or firmware is necessary. The VPCLS2 is
compatible to existing chips.
Further information about our products or current and future projects is
available on our web page: http://www.profichip.com.

1Introduction
6
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
Notes:

Functional Description 2
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
7
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
2 Functional Description
2.1 Overview
The VPC3+S makes a cost optimized design of intelligent PROFIBUS DP-
Slave applications possible.
Due to the very flexible processor interface the VPC3+S supports a broad
range of processor types and families. Please check the corresponding
chapters of this manual for details. Here are just some common examples:
Intel: 80C31, 80C51, 80X86 and their derivates
Siemens: 80C166/165/167
Motorola: HC11-, HC16-, and HC916 types
ARM: all ARM derivates with parallel, SPI or I2C interface
The VPC3+S handles the physical layer 1 and the data link layer 2 of the
ISO/OSI-reference-model excluding the analog RS485 drivers.
The integrated 4K Byte Dual-Port-RAM serves as an interface between
the VPC3+S and the software/application. In case of using 2K Byte the
entire memory is divided into 256 segments, with 8 bytes each. Otherwise
in the 4K Byte mode the segment base addresses starts at multiple of 16.
Addressing by the user is done directly; however, the internal Micro
Sequencer (MS) addresses the RAM by means of the so-called base-
pointer. The base-pointer can be positioned at the beginning of a segment
in the memory. Therefore, all buffers must be located at the beginning of a
segment.
If the VPC3+S carries out a DP communication it automatically sets up all
DP-SAPs. The various telegram information is made available to the user in
separate data buffers (for example, parameter and configuration data).
Three buffers are provided for data communication (three for output data
and three for input data). As one buffer is always available for communica-
tion no resource problems can occur. For optimal diagnosis support, the
VPC3+S offers two Diagnosis-Buffers. The user enters the updated
diagnosis data into these buffers. One Diagnosis-Buffer is always assigned
to the VPC3+S.
The Bus Interface Unit is a parameterizable synchronous/asynchronous 8-
bit parallel interface for various Intel and Motorola microcontrollers/pro-
cessors. The user can directly access the internal 2K/4K Byte RAM or the
parameter latches and control registers via the 11/12-bit address bus.
Alternatively serial standard protocols like SPI or I2C can be used to access
the VPC3+S.
Procedure-specific parameters (Station_Address, control bits, etc.) must be
transferred to the Parameter Registers and to the Mode Registers after
power-on.

2Functional Description
8
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
The MAC status can be observed at any time in the Status Register.
Various events (e.g. various indications, error events, etc.) are entered in
the Interrupt Controller. These events can be individually enabled via a
mask register. Acknowledgement takes place by means of the acknowl-
edge register. The VPC3+S has a common interrupt output.
The integrated Watchdog Timer is operated in three different states:
BAUD_SEARCH, BAUD_CONTROL and DP_CONTROL.
The Micro Sequencer (MS) controls the entire process. It contains the DP-
Slave state machine (DP_SM).
The integrated 4K Byte RAM that operates as a Dual-Port-RAM contains
procedure-specific parameters (buffer pointer, buffer lengths,
Station_Address, etc.) and the data buffers.
In the UART, the parallel data flow is converted into the serial data flow and
vice-versa. The VPC3+S is capable of automatically identifying the baud
rates (9.6 Kbit/s - 12 Mbit/s).
The Idle Timer directly controls the bus times on the serial bus line.
The IsoM-PLL provides high-precision synchronization mechanisms as
defined in the PROFIBUS DPV2 protocol extension.

Pin Description 3
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
9
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3 Pin Description
3.1 Pinout The VPC3+S is available in two package versions: LFBGA48 or LQFP48.
Several pins are sharing different functions. Which pin function actually
applies depends on the interface mode selected by the configuration pins.
Four parallel interface modes as well as I2C and SPI mode with con-
figurable clock phase and clock polarity are supported. Please see the
following chapters for details.
Figure 3-1: VPC3+S LFBGA48 Pinout (TOP VIEW)

3Pin Description
10
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
TXD
RTS
RXD
RESET 25
48AB8 / SPI_SCK / I2C_SCK
DB3
11XDATAEXCH
10CLK
9SERMODE
8CLKOUT
7GND
6VCC
5XTEST0
4DIVIDER
3XCS / SPI_XSS
2AB10 / SPI_CPOL
1AB7 / SPI_MOSI
47XREADY / DTACK /SPI_MISO / I2C_SDA
46AB5 / I2C_SA5
45AB6 / I2C_SA6
44AB9 / SPI_CPHA
43GND
42VCC
41AB4 / I2C_SA4
40SYNC
39AB1 / I2C_SA1
38AB3 / I2C_SA3
37AB2 / I2C_SA2
26 DB0
27 DB1
28 MOT / XINT
29 XTEST1
30 VCC
31 GND
32 XWR / E_CLOCK / AB11
33
AB0 / I2C_SA0
34 XRD / R_W
35 ALE / AS / AB11
36
MODE
XCTS
INT
VCC
GND
DB7
DB2
DB4
DB6
DB5
Figure 3-2: VPC3+S LQFP48 Pinout (TOP VIEW)
Details about package outlines and dimensions are listed in section 10.7.

Pin Description 3
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
11
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3.2 Pin Assignment (Overview)
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Source / Destination
A1
48
AB8
I(S)
Address Bus 8
CPU
SPI_SCK / I2C_SCK
SPI: Serial Clock / I2C: Serial Clock
A2
47
XREADY / XDTACK
I(S)/O
READY / DTACK for external CPU
CPU
SPI_MISO / I2C_SDA
SPI: Master-In-Slave-Out / I2C: Serial Data
A3
7
GND
A4
6
VCC
A5
38
AB3
I
Address Bus 3
CPU
I2C_SA3
I2C: Slave Address 3
Configuration Pin
A6
37
AB2
I
Address Bus 2
CPU
I2C_SA2
I2C: Slave Address 2
Configuration Pin
B1
1
AB7
I(S)
Address Bus 7
CPU
SPI_MOSI
SPI: Master-Out-Slave-In
Configuration Pin
B2
46
AB5
I
Address Bus 5
CPU
I2C_SA5
I2C: Slave Address 5
Configuration Pin
B3
44
AB9
I
Address Bus 9
CPU
SPI_CPHA
SPI: Clock Phase
Configuration Pin
B4
41
AB4
I
Address Bus 4
CPU
I2C_SA4
I2C: Slave Address 4
Configuration Pin
B5
39
AB1
I
Address Bus 1
CPU
I2C_SA1
I2C: Slave Address 1
Configuration Pin
B6
36
AB0
I
Address Bus 0
CPU
I2C_SA0
I2C: Slave Address 0
Configuration Pin
C1
3
XCS
I
Chip-Select
CPU
SPI_XSS
SPI: Slave-Select
C2
2
AB10
I
Address Bus 10
CPU
SPI_CPOL
SPI: Clock Polarity
Configuration Pin
C3
45
AB6
I
Address Bus 6
CPU
I2C_SA6
I2C: Slave Address 6
Configuration Pin
C4
40
SYNC
O
Synchronization Pulse
CPU / Motion Control
C5
35
ALE /AS / AB11
I
Address Latch Enable / Address Strobe /
Address Bus 11
CPU
C6
34
XRD / R_W
I
Read / Read-Write
CPU
D1
18
VCC
D2
5
XTEST0
I
Test Pin 0 (to be connected to VCC)
Test Pin
D3
4
DIVIDER
I
Divider setting for CLKOUT: ‘0’: 12 MHz
‘1’: 24 MHz
Configuration Pin
D4
33
MODE
I
‘0’: Asynchronous Mode (Parallel Interface Mode)
‘1’: Synchronous Mode (Parallel Interface Mode)
‘0’: SPI (Serial Interface Mode)
‘1’: I2C (Serial Interface Mode)
Configuration Pin

3Pin Description
12
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Source / Destination
D5
32
XWR / E_CLOCK / AB11
I
Write / E-Clock (Motorola) / Address Bus 11
CPU
D6
19
GND
E1
31
GND
E2
8
CLKOUT
O
Clock Output (12 MHz or 24 MHz)
CPU / System
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface
‘1’: Serial Interface (SPI or I2C)
Configuration Pin
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface Intel Format
‘1’: Parallel Interface Motorola Format
Configuration Pin
E5
29
XTEST1
I
Test Pin 1 (to be connected to VCC)
Test Pin
E6
30
VCC
F1
10
CLK
I(S)
System Clock (48 MHz)
System
F2
11
XDATAEXCH
O
Indicates state ‘Data-Exchange’ for PROFIBUS DP
LED
F3
16
XCTS
I
Clear-To-Send (for FSK-Modem)
PB-Interface
F4
21
DB2
IO
Data Bus 2
CPU
F5
26
DB0
IO
Data Bus 0
CPU
F6
27
DB1
IO
Data Bus 1
CPU
G1
12
RESET
I(S)
Master-Reset (connect to port pin of CPU)
CPU
G2
15
RXD
I
Receive Data
PB-Interface
G3
17
INT
O
Interrupt
CPU / IRQ Controller
G4
20
DB7
IO
Data Bus 7
CPU
G5
22
DB4
IO
Data Bus 4
CPU
G6
25
DB3
IO
Data Bus 3
CPU
H1
13
TXD
O
Transmit Data
PB-Interface
H2
14
RTS
O
Request-To-Send
PB-Interface
H3
42
VCC
H4
43
GND
H5
23
DB6
IO
Data Bus 6
CPU
H6
24
DB5
IO
Data Bus 7
CPU
Figure 3-3: Pin Assignment
Notes: All signals beginning with ‘X’are LOW active.
VCC = +3.3 V
GND = 0 V
The assignment of AB11 depends on the parallel interface mode selected.
All unused inputs must be connected to GND.
Input Levels:
I :
LVTTL
I (S) :
LVTTL, Schmitt-Trigger

Pin Description 3
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
13
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
The following chapters are describing the different processor interface modes supported by
the VPC3+S. For every interface mode the settings of the configuration pins and the signals
necessary to communicate with the microcontroller are listed. Common signals for all
interface types (like clock divider, interrupt and Profibus interface signals are not explicitly
listed in this overview.
3.2.1 Asynchronous Intel Mode
In Asynchronous Intel Mode the data and address busses are separate
(non-multiplexed). Address line 11 is to be connected to pin C5 of the
VPC3+S.
XREADY mechanism is supported.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface
GND
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘0’: Intel Format
GND
D4
33
MODE
I
‘0’: Asynchronous Interface Mode
GND
C5
35
AB11
I
Address Lines Bit 11
CPU Address Bus 11
C2
2
AB10
I
Address Lines Bits [10:0]
CPU
Address Bus [10:0]
B3
44
AB9
I
A1
48
AB8
I(S)
B1
1
AB7
I(S)
C3
45
AB6
I
B2
46
AB5
I
B4
41
AB4
I
A5
38
AB3
I
A6
37
AB2
I
B5
39
AB1
I
B6
36
AB0
I
G4
20
DB7
IO
Data Bus [7:0]
CPU Data Bus [7:0]
H5
23
DB6
IO
H6
24
DB5
IO
G5
22
DB4
IO
G6
25
DB3
IO
F4
21
DB2
IO
F6
27
DB1
IO
F5
26
DB0
IO
C1
3
XCS
I
Chip-Select Signal (active low)
CPU Chip-Select
D5
32
XWR
I
Write Signal (active low)
CPU Write
C6
34
XRD
I
Read Signal (active low)
CPU Read
Figure 3-4: Interface Configuration: Asynchronous Intel Mode

3Pin Description
14
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3.2.2 Synchronous Intel Mode
In Synchronous Intel Mode the lower 8 bits of the address lines are
multiplexed with the 8 bit data bus DB[7:0]. The upper address lines (bits
10 to 8) need to be connected to the AB[2:0] inputs of the VPC3+S.
Address line 11 is to be connected to pin C1 of the VPC3+S.
XREADY mechanism is not supported in this interface mode.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface
GND
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘0’: Intel Format
GND
D4
33
MODE
I
‘1’: Synchronous Interface Mode
VCC
C1
3
AB11
I
Address Bit 11
CPU Address Bus 11
A6
37
AB2
I
Address Bit 10
CPU Address Bus 10
B5
39
AB1
I
Address Bit 9
CPU Address Bus 9
B6
36
AB0
I
Address Bit 8
CPU Address Bus 8
G4
20
DB7
IO
Data Bus [7:0]
multiplexed with lower address bits [7:0]
ALE used to latch the lower address bits.
CPU Data/Address
Bus [7:0]
H5
23
DB6
IO
H6
24
DB5
IO
G5
22
DB4
IO
G6
25
DB3
IO
F4
21
DB2
IO
F6
27
DB1
IO
F5
26
DB0
IO
C2
2
AB10
I
In Synchronous Intel Mode these inputs are used to
generate the internal Chip-Select signal.
Chip-Select is active if all inputs are ‘0’.
Use one (inverted)
CPU Address Line for
generating the
VPC3+S Chip-Select
signal.
Connect all other
inputs to GND.
B3
44
AB9
I
A1
48
AB8
I(S)
B1
1
AB7
I(S)
C3
45
AB6
I
B2
46
AB5
I
B4
41
AB4
I
A5
38
AB3
I
C5
35
ALE
I
Address Latch Enable
The lower address bits [7:0] are latched with the falling
edge of ALE
CPU ALE
D5
32
XWR
I
Write Signal (active low)
CPU Write
C6
34
XRD
I
Read Signal (active low)
CPU Read
Figure 3-5: Interface Configuration: Synchronous Intel Mode

Pin Description 3
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
15
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3.2.3 Asynchronous Motorola Mode
In Asynchronous Motorola Mode the data and address busses are separate
(non-multiplexed). When using HC11 types with a multiplexed bus the
address signals AB[7:0] must be generated from the DB[7:0] signals
externally. Address line 11 is to be connected to pin D5 of the VPC3+S.
XDTACK mechanism is supported.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface
GND
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘1’: Motorola Format
VCC
D4
33
MODE
I
‘0’: Asynchronous Interface Mode
GND
D5
32
AB11
I
Address Lines Bit 11
CPU Address Bus 11
C2
2
AB10
I
Address Lines Bits [10:0]
CPU
Address Bus [10:0]
B3
44
AB9
I
A1
48
AB8
I(S)
B1
1
AB7
I(S)
C3
45
AB6
I
B2
46
AB5
I
B4
41
AB4
I
A5
38
AB3
I
A6
37
AB2
I
B5
39
AB1
I
B6
36
AB0
I
G4
20
DB7
IO
Data Bus [7:0]
CPU Data Bus [7:0]
H5
23
DB6
IO
H6
24
DB5
IO
G5
22
DB4
IO
G6
25
DB3
IO
F4
21
DB2
IO
F6
27
DB1
IO
F5
26
DB0
IO
C1
3
XCS
I
Chip-Select Signal (active low)
CPU Chip-Select
C5
35
AS
I
Address Strobe (active low)
CPU Address Strobe
C6
34
R_W
I
Read-Write Signal (‘1’ = Read)
CPU Read-Write
Figure 3-6: Interface Configuration: Asynchronous Motorola Mode

3Pin Description
16
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3.2.4 Synchronous Motorola Mode
In Synchronous Motorola Mode the data and address busses are separate
(non-multiplexed). When using HC11 types with a multiplexed bus the
address signals AB[7:0] must be generated from the DB[7:0] signals
externally. Address line 11 is to be connected to pin C5 of the VPC3+S.
XDTACK mechanism is not supported.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘0’: Parallel Interface
GND
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘1’: Motorola Format
VCC
D4
33
MODE
I
‘1’: Synchronous Interface Mode
VCC
C5
35
AB11
I
Address Lines Bit 11
CPU Address Bus 11
C2
2
AB10
I
Address Lines Bits [10:0]
CPU
Address Bus [10:0]
B3
44
AB9
I
A1
48
AB8
I(S)
B1
1
AB7
I(S)
C3
45
AB6
I
B2
46
AB5
I
B4
41
AB4
I
A5
38
AB3
I
A6
37
AB2
I
B5
39
AB1
I
B6
36
AB0
I
G4
20
DB7
IO
Data Bus [7:0]
CPU Data Bus [7:0]
H5
23
DB6
IO
H6
24
DB5
IO
G5
22
DB4
IO
G6
25
DB3
IO
F4
21
DB2
IO
F6
27
DB1
IO
F5
26
DB0
IO
C1
3
XCS
I
Chip-Select Signal (active low)
CPU Chip-Select
D5
32
E_CLOCK
I
E-Clock
CPU E-Clock
C6
34
R_W
I
Read-Write Signal (‘1’ = Read)
CPU Read-Write
Figure 3-7: Interface Configuration: Synchronous Motorola Mode

Pin Description 3
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
17
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
3.2.5 SPI Mode
The VPC3+S can be interfaced like an SPI compatible memory device.
Depending on the setting of CPOL and CPHA four different SPI modes can
be selected. All unused inputs (including DB[7:0]) must be connected to
GND.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘1’: Serial Interface
VCC
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘0’: not used in this mode
GND
D4
33
MODE
I
‘0’: SPI Mode
GND
C2
2
SPI_CPOL
I
Clock Polarity
VCC or GND
B3
44
SPI_CPHA
I
Clock Phase
VCC or GND
C1
3
SPI_XSS
I
Slave-Select Signal (active low)
CPU Slave-Select
A1
48
SPI_SCK
I(S)
Serial Clock
CPU SCK
B1
1
SPI_MOSI
I
Master-Out-Slave-In (Serial Data Input)
CPU MOSI
A2
47
SPI_MISO
O
Master-In-Slave-Out (Serial Data Output)
CPU MISO
Figure 3-8: Interface Configuration: SPI Mode
3.2.6 I2C Mode
The VPC3+S can be interfaced like an I2C compatible memory device. The
VPC3+S is always in slave mode, master mode is not supported. The slave
address can be configured by using the AB[6:0] inputs. All unused inputs
(including DB[7:0]) must be connected to GND.
Ball
BGA
Pin
QFP
Signal Name
In/Out
Description
Connect to
E3
9
SERMODE
I
‘1’: Serial Interface
VCC
E4
28
MOT/XINT
I
‘0’: not used in this mode
GND
D4
33
MODE
I
‘1’: I2C Mode
VCC
C3
45
I2C_SA6
I
I2C Slave Address
VCC or GND
B2
46
I2C_SA5
I
VCC or GND
B4
41
I2C_SA4
I
VCC or GND
A5
38
I2C_SA3
I
VCC or GND
A6
37
I2C_SA2
I
VCC or GND
B5
39
I2C_SA1
I
VCC or GND
B6
36
I2C_SA0
I
VCC or GND
A1
48
I2C_SCK
I(S)
Serial Clock
CPU SCK
A2
47
I2C_SDA
I(S) / O
Serial Data Line
CPU SDA
Figure 3-9: Interface Configuration: I2C Mode

3Pin Description
18
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
Notes:

Memory Organization 4
VPC3+S User Manual
Revision 1.04
19
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
4 Memory Organization
4.1 Overview
The internal Control Parameters are located in the first 21 addresses. The
latches/registers either come from the internal controller or influence the
controller. Certain cells are read- or write-only. The internal working cells,
which are not accessible by the user, are located in RAM at the same
address locations.
The Organizational Parameters are located in RAM beginning with address
16H. The entire buffer structure (for the DP-SAPs) is based on these pa-
rameters. In addition, general parameter data (Station_Address,
Ident_Number, etc.) and status information (Global_Control command, etc.)
are also stored in these cells.
Corresponding to the parameter setting of the Organizational Parameters,
the user-generated buffers are located beginning with address 40H. All
buffers or lists must begin at segment addresses (8 bytes segmentation for
2K Byte mode, 16 bytes segmentation for 4K Byte mode).
Address
Function
000H
:
015H
Control Parameters
(latches/registers) (21 bytes)
Internal working cells
016H
:
03FH
Organizational Parameters (42 bytes)
040H
:
:
7FFH (FFFH)
DP-buffers: Data in (3)*
Data out (3)**
Diagnosis data(2)
Parameter data (1)
Configuration data (2)
Auxiliary buffers (2)
SSA-buffer (1)
DP-V1-buffer: SAP-List (1)
Indication / Response buffers ***
DP-V2-buffer: DXB out (3)****
DXB-buffers (2)
CS-buffer (1)
PLL-buffer (1)
Figure 4-1: Memory Table
* Data in means input data from DP-Slave to DP-Master
** Data out means output data from DP-Master to DP-Slave
*** Number of buffers depends on the entries in the SAP-List
**** DXB out means input data from another DP-Slave (slave-to-slave communication)

4Memory Organization
20
Revision 1.04
VPC3+S User Manual
Copyright © profichip GmbH, 2012
Internal VPC3+S RAM (2K/4K Byte)
Segment 0
Segment 1
Segment 2
8/16 bit segment addresses
(pointer to the buffers)
Segment 254
Segment 255
Building of the physical buffer address:
2K Byte Mode:
7
0
Segment base address (8 bit)
0
0
0
0
0
Offset (3 bit)
+
10
0
Physical address (11 bit)
4K Byte Mode:
7
0
Segment base address (8 bit)
0
0
0
0
Offset (4 bit)
+
11
0
Physical address (12 bit)
Other manuals for VPC3+S
1
Table of contents
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands
Oki
Oki Semiconductor VoiceKit2000 instruction manual

InWin
InWin MR24 user manual
7th Sense
7th Sense medialon Showmaster G Hardware user's guide
Multitech
Multitech ISI552PC owner's manual

Global American Inc.
Global American Inc. 3301730 Quick installation guide

Ebmpapst
Ebmpapst D3G160-BD05-02 operating instructions