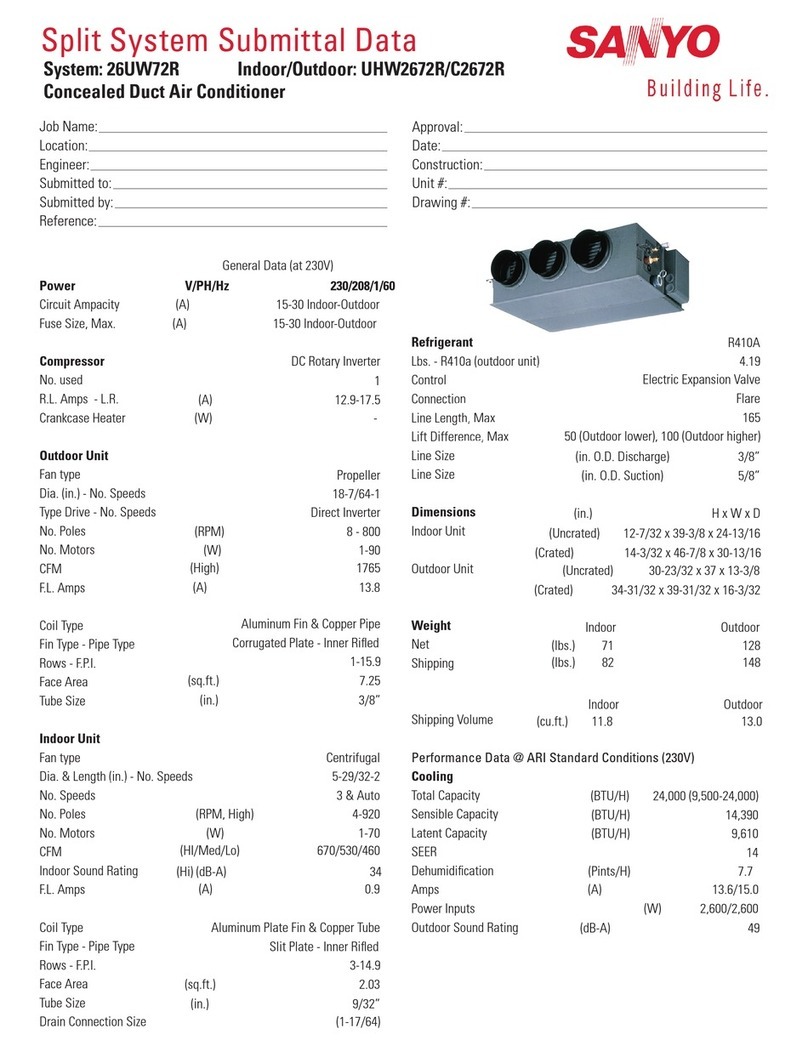
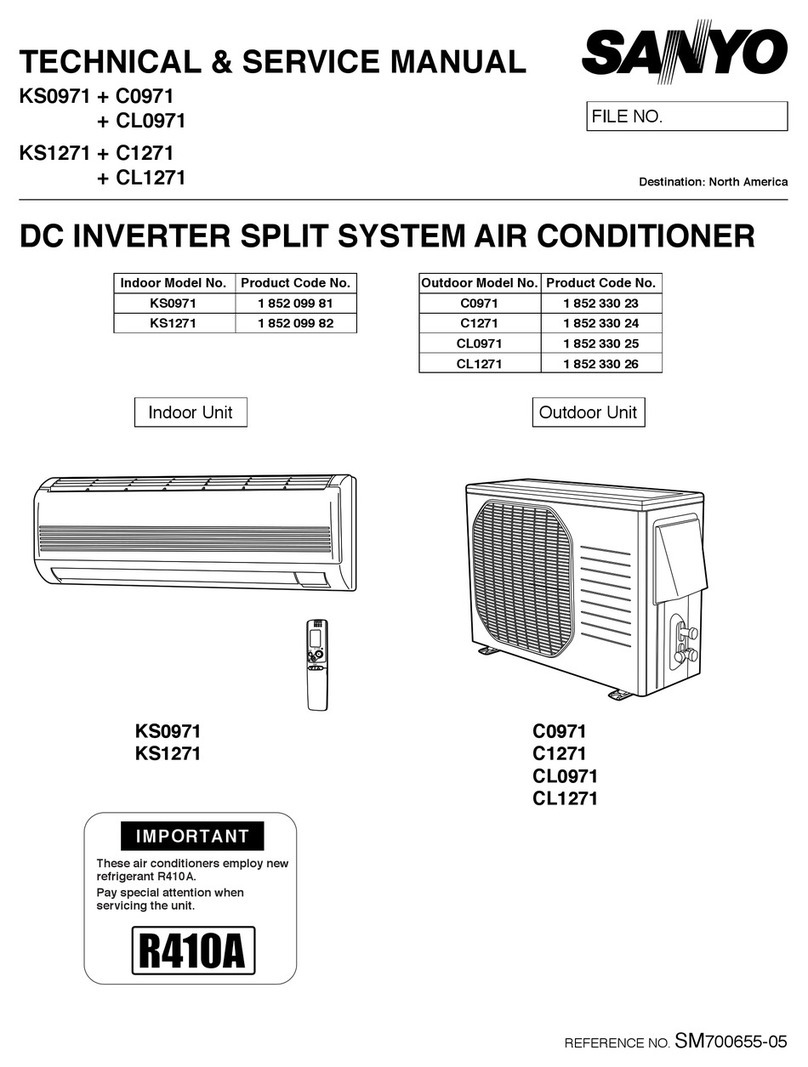
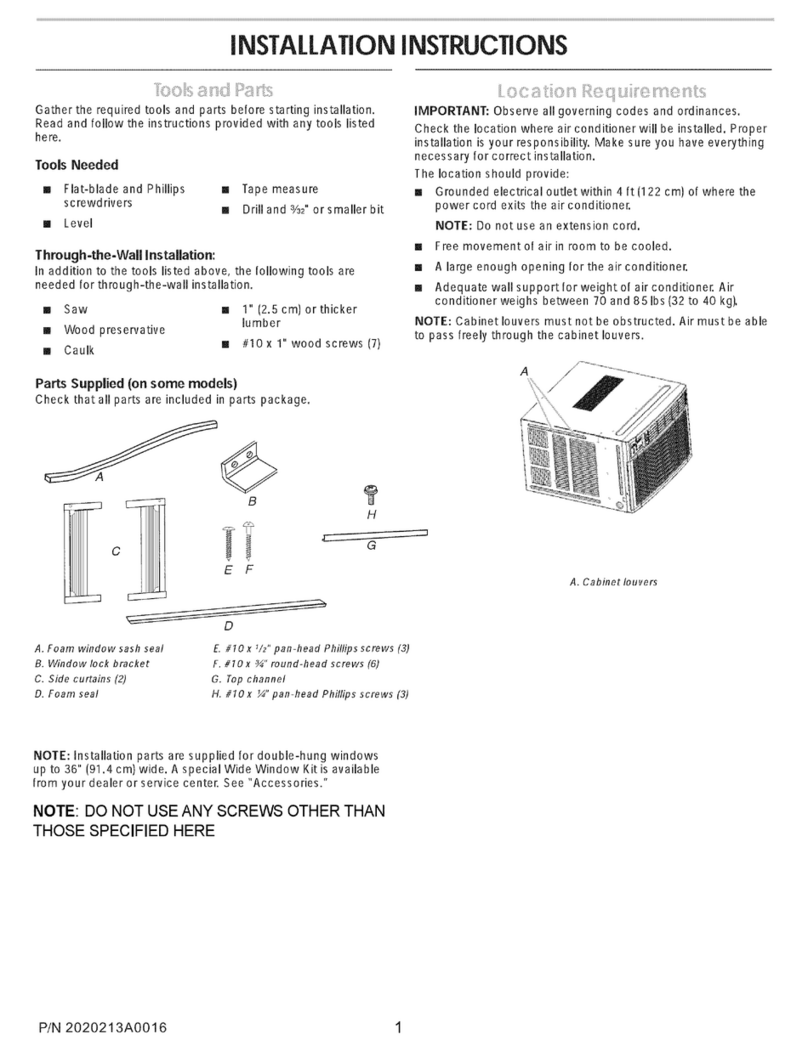
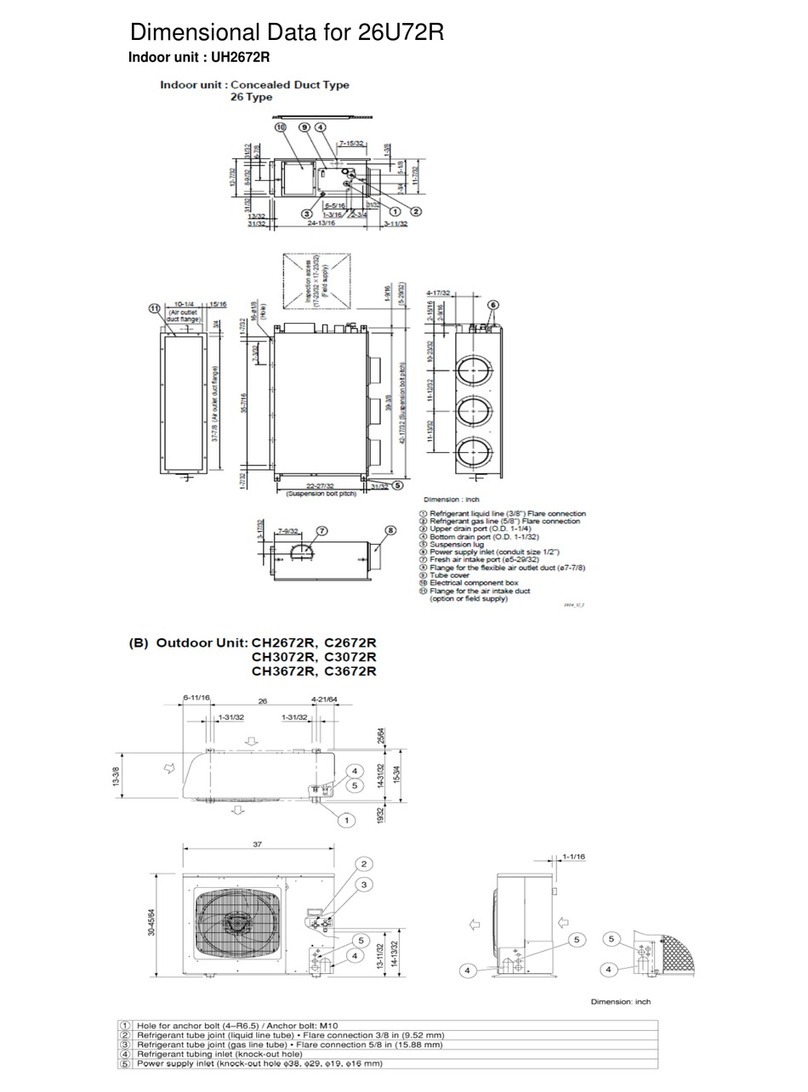
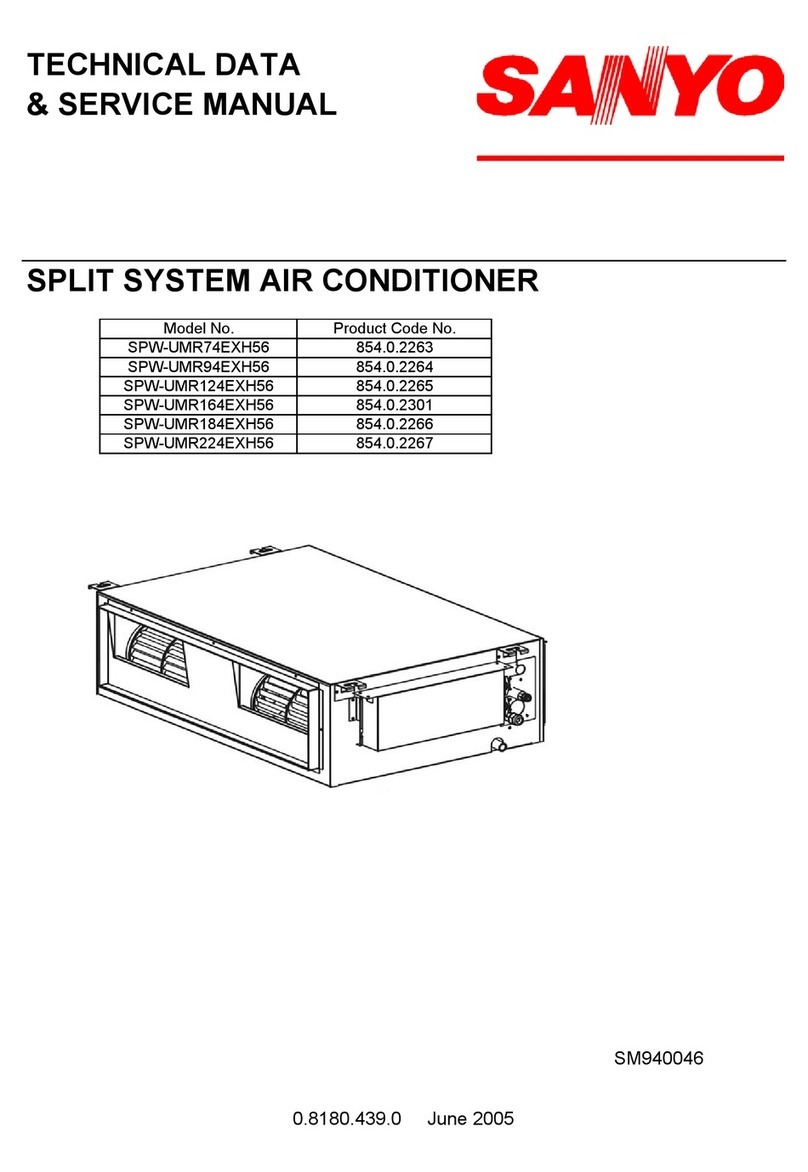
2
IMPORTANT!
Please Read Before Starting
This air conditioning system meets strict safety and operat-
ing standards. As the installer or service person, it is an
important part of your job to install or service the system so it
operates safely and efficiently.
For safe installation and trouble-free operation, you must:
●Carefully read this instruction booklet before beginning.
●Follow each installation or repair step exactly as shown.
●Observe all local, state, and national electrical codes.
●This product is intended for professional use.
Permission from the power supplier is required when
installing an outdoor unit that is connected to a 16 A
distribution network.
●Pay close attention to all warning and caution notices
given in this manual.
This symbol refers to a hazard or
unsafe practice which can result
in severe personal injury or death.
This symbol refers to a hazard or
unsafe practice which can result
in personal injury or product or
property damage.
If Necessary, Get Help
These instructions are all you need for most installation
sites and maintenance conditions. If you require help for a
special problem, contact our sales/service outlet or your
certified dealer for additional instructions.
In Case of Improper Installation
The manufacturer shall in no way be responsible for
improper installation or maintenance service, including fail-
ure to follow the instructions in this document.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
When Wiring
ELECTRICAL SHOCK CAN CAUSE
SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
ONLY A QUALIFIED, EXPERIENCED
ELECTRICIAN SHOULD ATTEMPT TO
WIRE THIS SYSTEM.
• Do not supply power to the unit until all wiring and tubing
are completed or reconnected and checked.
• Highly dangerous electrical voltages are used in this sys-
tem. Carefully refer to the wiring diagram and these
instructions when wiring. Improper connections and inad-
equate grounding can cause accidental injury or death.
• Ground the unit following local electrical codes.
• Connect all wiring tightly. Loose wiring may cause over-
heating at connection points and a possible fire hazard.
When Transporting
Be careful when picking up and moving the indoor and outdoor
units. Get a partner to help, and bend your knees when lifting
to reduce strain on your back. Sharp edges or thin aluminum
fins on the air conditioner can cut your fingers.
When Installing…
…In a Room
Properly insulate any tubing run inside a room to prevent
“sweating” that can cause dripping and water damage to
walls and floors.
…In Moist or Uneven Locations
Use a raised concrete pad or concrete blocks to provide a
solid, level foundation for the outdoor unit. This prevents
water damage and abnormal vibration.
…In an Area with High Winds
Securely anchor the outdoor unit down with bolts and a
metal frame. Provide a suitable air baffle.
…In a Snowy Area (for Heat Pump-type Systems)
Install the outdoor unit on a raised platform that is higher
than drifting snow. Provide snow vents.
When Connecting Refrigerant Tubing
• Ventilate the room well, in the event that is refrigerant
gas leaks during the installation. Be careful not to allow
contact of the refrigerant gas with a flame as this will
cause the generation of poisonous gas.
• Keep all tubing runs as short as possible.
• Use the flare method for connecting tubing.
• Apply refrigerant lubricant to the matching surfaces of
the flare and union tubes before connecting them, then
tighten the nut with a torque wrench for a leak-free con-
nection.
• Check carefully for leaks before starting the test run.
When Servicing
• Turn the power OFF at the main power box (mains)
before opening the unit to check or repair electrical parts
and wiring.
• Keep your fingers and clothing away from any moving
parts.
• Clean up the site after you finish, remembering to check
that no metal scraps or bits of wiring have been left
inside the unit being serviced.
Ventilate any enclosed areas when installing or testing
the refrigeration system. Escaped refrigerant gas, on
contact with fire or heat, can produce dangerously toxic
gas.
• Confirm after installation that no refrigerant gas is leak-
ing. If the gas comes in contact with a burning stove, gas
water heater, electric room heater or other heat source,
it can cause the generation of poisonous gas.