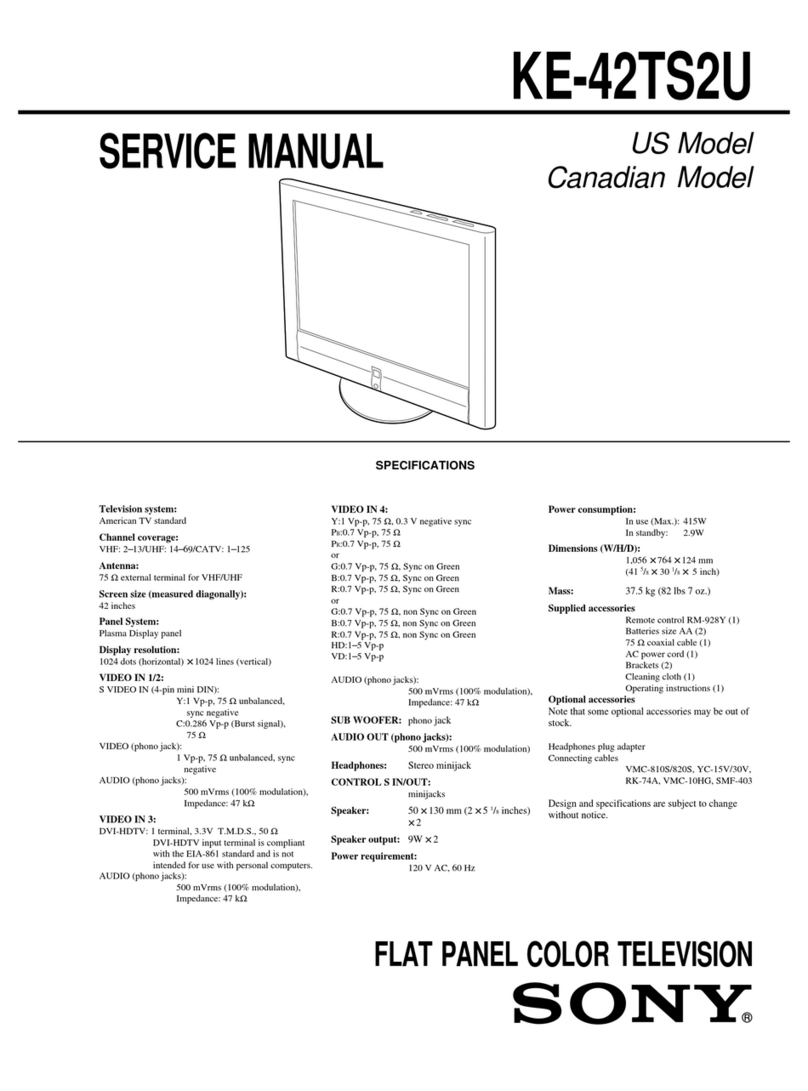
7
Deflection
Horizontal
When the set is turned ON and +9 volts is received by the YCJ, the YCJ
will output horizontal drive pulses. These pulses are amplified and output
to the horizontal yoke and FBT. The horizontal yoke uses the horizontal
output to control the beam scan across the face of the tube.
The FBT is used to create several voltages. They are High Voltage, 200
Volts, +12 and –15 volts, and ABL. The High Voltage, necessary for
beam acceleration, is connected to the second anode of the picture tube.
The 200 volts is used to power the video amp located on the C board.
The +12 and –15 volt lines are created to power the Vertical Deflection IC.
If these signals are missing, the set will indicate a vertical problem even
though the problem is actually in the horizontal or FBT section. The ABL
signal is input to the YCJ so that it can adjust the levels of the video signal
to keep the brightness at a consistent level.
The Horizontal Deflection circuit also returns a sample pulse, HP, to the
YCJ to ensure that the phase of the input and output is the same. The HP
signal is also input to the Quadra-pole circuit to create the signal needed
to shape the beam in the corners of the picture tube.
Pincushion
The pincushion correction is controlled by the E/W signal from the YCJ
when the horizontal drive pulses are output. This signal is a 60 Hz pa-
rabola signal that is used to dynamically widen the picture as the beam
scans from top to bottom. This signal also rides on a DC level, which is
used to maintain the overall width of the picture. This DC level is changed
using the HSIZ adjustment in the VP section of the service menu.
Vertical
The vertical drive signals are output from the YCJ when communications
are established between the Tuning Micon and the YCJ. These drive
signals are complementary, 180 degrees out of phase, and are sent to
the Vertical Output circuit.
There are two types of vertical drive signals used. One is for normal 4:3
aspect ratio video and the other is for 16:9 compressed video. The Verti-
cal Deflection circuit outputs the V Out signal to the vertical yoke. This
signal is used to control the up and down beam scan of the tube.
The Vertical deflection circuit also outputs the VP signal. The VP signal is
a sample of the pump-up pulse used to boost the B+ inside of the vertical
output IC. This signal is input to the YCJ for vertical protection and also to
the Quadra-pole circuit to create the necessary output to control the beam
shape at the corners of the tube.
The Vertical Interval Timing (VITM) signal from the YCJ is fed back to the
Tuning Micon to control the timing of the I2C bus. This ensures that I2C
data will only be sent during the vertical-blanking interval. If the VTIM
signal is missing, there will be no OSD and the PIP window will roll verti-
cally.
Quadra-pole Focus
Due to the flat screen in a set that uses a FD Trinitron tube, the focus in
the four corners of the set has changed. While the dots are still in focus at
the four corners, the spot of the beam has changed from round to ellipti-
cal. The Quadra-pole circuit is used to make these beam spots round.
The beam spots are made round again by supplying a signal to four coils
mounted on the yoke. The magnetic fields created by the signals applied
to the coils reshape the beam spots.
The VP and HP signals are samples of the output signals of the vertical
and horizontal deflection circuits. These signals are wave shaped to cre-
ate two differential parabola signals and applied to the four coils. Their
magnetic fields reshape the beam.