SQN SQN-4S Series Instruction Manual

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
SQN-4S Series IVe User's Handbook
Contents
11 AUDIO LEVEL METERS 9 MASTER GAIN CONTROL
6 AUXILIARY MONITOR INPUTS 7 MICROPHONES
10 BASS CUTS 14 MIXING AND MATRIXING
19 CONNECTOR LIST 13 MONITORING HEADPHONES
17 CONNECTOR WIRING - 12 WAY 12 OUTPUT LIMITERS
18 CONNECTOR WIRING - 10 WAY 3 OUTPUTS
5 CALIBRATION OF THE RECORDER 2 POWERING THE MIXER
1 INTRODUCTION 15 SLATING MICROPHONE
8 LINE INPUTS 16 WARRANTY & SERVICE
4 LINE-UP TONE
1. INTRODUCTION The basic information necessary to allow a recording engineer to operate the
SQN-4S audio mixer is permanently displayed on its baseplate and cannot be lost. The aim of these
instructions is to explain the mixer’s facilities and functions in more detail to those who are already
familiar with the microphones and techniques that are employed by professional sound recordists.
Users of the earlier SQN mixers will naturally want to know in what respects the SERIES IVe differs
from the previous model. The new mixer again has four input channels and two main outputs. In
addition, access has been provided to the Post-Fader outputs of all of the channels so that it is
possible to feed four fader-controlled (unbalanced) outputs to an external recorder. Pre-fade listening
to all of the input channels is included, as is a ‘slating’ microphone. The power wiring allows the
fuse-protected feeding of external power to other equipment, controlled by the mixer’s Power
Selector switch.
MIXING and MATRIXING. The SQN-4S SERIES IVe returns to a form of the control format
popularised by the earlier SQN-4S SERIES III mixers. In addition to the normal routing of individual
channels, the mixer can be configured as a Stereo Pair, with or without MS matrixing together with
two other pan-pottable channels. The modes of operation for the CH1/CH2 pair are selected by the
[GANG 1-2] switch:
1. TWIN MONO
2. STEREO
3. MID-SIDE (with matrixing to or from AB stereo)
The effects on the operation of the other controls of selecting these three modes are described in
section 14 below.
2. POWERING THE MIXER
1. INTERNAL BATTERY. The SQN-4S should be powered by Mallory Type MN 1500
or another manufacturer's equivalent AA size alkaline cells. The quiescent consumption
of the mixer is approximately 135mA at 12V and with dynamic microphones about 10
hours of continuous operation can be expected from fresh cells.
Page 1 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
Rechargeable nickel cadmium cells may be employed for maximum economy, but types
fitted with solder tags may be found mechanically unsuitable. If all cells are good they
may be recharged in series using an external charger unit, which can be connected to
the 4-way connector [DC] next to the battery compartment door. The endurance of
nickel cadmium cells will be about half that of alkaline cells.
For maximum life, lithium cells giving 3 volts per cell can be used, since the power
supply will accept inputs up to 24 volts. The use of ordinary ‘dry cell’ carbon zinc cells,
which may leak and cause extensive damage, is definitely not recommended. In any
case, when used in the SQN-4S they give a small fraction (about one fifth) of the life of
alkaline cells, so they are a false economy. If such cells are fitted in an emergency, it is
most important that they be removed immediately after use. Similarly, any type of
battery should be removed if the mixer is to be stored for any length of time or
transported, particularly by air.
To fit the cells, slide the battery door catch on the right side of the mixer towards the
front panel to release the door and insert two rows of four cells in series, so that the
lower tube has the positive poles facing the door and the upper tube the negative poles,
as is indicated on the door itself. If the cells are inserted with incorrect polarity the
mixer will not function; an internal protection circuit prevents damage to the mixer
power supply. When operating from the internal battery supply, switch the rotary power
selector switch, situated at the front of the connector panel, to the [BAT] position to
power the mixer. A green LED between the meters lights up to indicate that the mixer is
switched on.
The right channel meter doubles as a voltmeter for the power supply when the adjacent
[BATT] push button switch is depressed. The mixer is guaranteed to work down to a
battery voltage of 6 volts, so that as long as the battery meter reads on scale,
performance will be to specification. If the voltage is allowed to fall lower (to about 4.8
V) then eventually the internal power rails will fall. This will affect the headroom of the
output and monitor amplifiers and the setting of the Line-Up tone; ultimately the
performance of the whole mixer will be degraded. It is worth noting that as the battery
voltage falls, the current drawn by the power supply will increase to maintain the
required power input. The battery voltage is, therefore, likely to fall quite quickly as the
cells become exhausted.
2. EXTERNAL POWER SOURCE. A direct current supply in the range 6 to 24 volts can
be connected to the 4-Way connector [DC] next to the battery door. In order not to
restrict the usable types of powered microphones, the power supply must be capable of
delivering 2.5W while maintaining an output voltage in the required range.
The mixer’s power input terminals float with respect to the SQN-4S ground, so a supply
which does not share a ground with the SQN-4S may be used, e.g. a camera battery.
The power supply input of the SQN-4S is protected against connection of an external
voltage with reversed polarity. If it is desired to power the SQN-4S from an external
DC supply at higher voltage than 24V, reference should be made to the manufacturers
To power the SQN-4S from an external supply the rotary Power Selector Switch on the
front of the connector panel must be turned to the [EXT] position.
Page 2 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
3. EXTERNAL POWER FEED. When the mixer is being powered from an external
supply, that supply is also made available at the 4-WAY connector [PT] on the main
connector panel. This is intended to supply power to other devices with which the
mixer may be working. This power feed is short-circuit protected by self resetting
thermal fuses and is switched on by the mixer’s power switch in either the [BAT] or
[EXT] position. Many users of these mixers prefer to power them and several extra
pieces of equipment from an NP-1 camera battery, the whole being kept together in a
special carrying bag. An extremely long endurance can be expected from the NP-1 but
it is necessary to be careful that the battery is not allowed to discharge below the
manufacturer’s recommended minimum of 10V (use the [BATT] test); the mixer will
continue to work but the battery will have its life reduced.
3. OUTPUTS The mixer is provided with two balanced line driver amplifiers of substantial capacity.
The output transformers of these amplifiers also carry windings providing isolated, nominally
‘Mic Level’ outputs. Additionally, unbalanced feeds of the two main outputs and the ‘Post Fader’
outputs of all input channels are available at a nominal line level of -10dBu with 200 Ohm source
resistance. All of these signals are made available on the connectors at the end of the mixer. The
connection lists for the multi-way connectors are given in sections 17 and 18, reproduced from the
mixer base label.
The connections for the two XLR-3M connectors are to the usual convention :
1 GND, 2 LIVE, 3 RETURN.
Two switches on the base of the mixer allow the feed to the [MAIN] connector [A] or the XLR
connectors to be taken from the Line Level or Mic. Level outputs .
4. LINE-UP TONE A calibration Tone of 1kHz with distortion below 0.1% may be injected into both
output channels by setting the 3-way front panel [TONE/MIC] switch to the left. The form that the
tone takes depends on the setting of the [GANG 1-2] switch. When this switch is in the unganged [0]
position the tone is continuous in both channels. Either of the other two positions gives an EBU
coded tone signal (the left channel interrupted for 250ms every 3s) to indicate that the recording
which follows is true stereophony. The tone mutes and replaces the main audio. The calibration level
for a given meter reading is indicated on the baseplate of the mixer and, unless specially requested, it
will be at the Nominal Line Level (see the next section).
5. CALIBRATION OF THE RECORDER The recorders that are used with the SQN-4S are almost
invariably fitted with some form of input gain control. In these circumstances the absolute calibration
levels of both the mixer and the recorder become irrelevant: what must be considered are the relative
calibration points Nominal Line Level (0VU) and Nominal Peak Level on the meters of both
instruments and how they are to be related.
The basic calibration used at SQN is to place the Nominal Line Level at PPM4, ‘TEST’ or 0VU and
then to treat the Nominal Peak Level as being 8dB above this, in the case of the PPM or VU meter or
6dB above in the case of the Nordic type of meter. The limiter is then set to come into operation on a
steady tone at 1dB below the Nominal Peak Level. This ensures that the mixer output will not exceed
the Nominal Peak Level when measured using a Peak Programme Meter. The Line-Up tone is then
usually set to the Nominal Line Level. In any case, the calibration points, including the limiter setting
are shown on the individual mixer baseplate.
When interfacing to an analogue recorder with its typical slow overload characteristic, what is
required is to place the mixer’s Nominal Peak Level at the correct point which will ensure that the
Page 3 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
recorder will not be overloaded by a limited transient output from the mixer. Most of the ENG
recorders use VU meters, with which the Peak Level is off scale. The reference point we use,
therefore, is the Nominal Line Level - the level to which the mixer’s Line-Up tone is set. Experience
has shown that most of the usual ENG recorders are calibrated so that their Nominal Line Level or
0VU is only 6dB below the level at which distortion is beginning to increase. Accordingly, it has
become the practice to adjust the recorder’s gain control to place the mixer’s Line-Up tone at -2dB on
the recorder’s VU meter. Some recordists prefer to go further and leave themselves a little more
headroom on the recorder by placing the line up tone at -4dB on the recorder’s meter.
Interfacing to a digital recorder with its much more sudden and unforgiving overload characteristic
requires that the Nominal Peak Level of the mixer be placed below the peak level of the recorder.
This is because the limiting, as carried out on the mixer assumes that the following recorder is
tolerant of some degree of overload for periods up to 1ms, hence the emphasis on the measurement
using a Peak Programme Meter in the paragraph above. Fortunately, digital recorders, because of
their clipping characteristics, are almost always fitted with fast peak meters, reading on a sample by
sample basis. It is easy to set the matching between the mixer and the recorder experimentally using
limited transients such as sharp handclaps. Typically, the Line-Up tone should be placed 12dB below
the allowed peak level.
6. AUXILIARY MONITOR INPUTS The SQN-4S Series IV features twin auxiliary inputs on its 12-
way [MAIN] connector [A] which are intended to accept a return signal from whatever recorder the
mixer is feeding. The input sensitivity is set by adjusting the screwdriver-operated potentiometer
marked [MONITOR SENSITIVITY ADJUST] in the base of the mixer and can usually be fixed with
sufficient accuracy by ear by operating the [MIXER AUX] switch situated below the Master fader to
and fro with the line-up tone on and adjusting for parity of loudness. This feature allows before/after
comparison of off-tape monitoring, or, when used with a recorder that lacks off tape monitoring, it
can be used as a check that mixer outputs are at least reaching the recording inputs. The [MIXER
AUX] switch affects only the headphone signals.
Many ENG recorders feature an ‘Earphone Monitor’ output on a 3.5mm jack, intended for the
cameraman’s use. This often carries audio warning of tape end or other errors, but because it is fed
from the recording head the practice has grown of using it for audio confidence monitoring even
though it is usually Dolby encoded, contaminated by time-code noise, unbalanced and at very low
level (typically -16dBu). Cable looms incorporating quad stereo leads in a single flexible cable of
only 7mm diameter have been developed at SQN for use in interfacing such recorders with the 12-
way [MAIN] socket [A] of the mixer. They are available in straight or coiled formats.
7. MICROPHONES The four identical XLR-3F microphone input connectors are wired to conform
with the IEC standard (Pin 1 ground, Pin 2 in phase and positive for T-powering). The SQN-4S is
designed to accommodate all professional microphones and assumes a source impedance for dynamic
microphones in the range 150-600 Ohms. Condenser microphones, of course, will present source
impedances much lower than this but because of the absence of input transformers in the mixer, the
frequency response will be unaffected. It is outside the scope of this manual to describe in any detail
the various types of microphone which may be employed, but the type will determine the settings of
switches set into the baseplate of the mixer. While the SQN-4S has sufficient current capacity to
supply any make of condenser microphone, the use of microphones which have a particularly large
current drain with battery-powered equipment will need careful consideration. Some marked
improvement in performance or special tonal characteristic should be required as compensation for
the reduced battery life. There are some powered microphones that are switchable or automatically
switch between 48V and 12V phantom powering. These will typically have their power consumption
Page 4 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
reduced by a half in the 12V phantom mode with unimpaired performance.
The primary purpose of the Microphone Attenuators [ATTEN] is to provide a rough level match
between the input signals from microphones of varying sensitivities so as to allow comfortable
handling of the gain controls. The ‘attenuators’ are, in fact, switched gain controls so that there is no
need to fear a worsening of noise performance from their use.
It is, of course, not good practice to rely on attenuators (or gain controls) when using sensitive
condenser microphones close to loud sounds, such as motor sports or pop music, since such signals
may well overload the microphone’s own first stage. In those conditions the ambient noise level can
even prevent such a disaster being detected on your headphones. The use of dynamic microphones
may be more appropriate in these cases.
Rotary faders were selected for the SQN-4S because of their inherently better environmental sealing
and because they provide more mechanical movement in a small space than can a slider type. The
specially designed control knobs incorporate some of the advantages of the slider in that they can be
pushed from the side and their position is unequivocally seen and felt. Turning over a considerable
arc is achieved with the tip of the finger or thumb resting on the point of the arrow design.
8. LINE INPUTS All four of the microphone inputs may be individually switched for use as balanced
line inputs. This is achieved simply by switching a fixed 50dB attenuator in front of the microphone
amplifier. The attenuator and fader controls operate as before.
A pair of unbalanced inputs, feeding directly into the left and right mixing busses is also available on
the [SUBSIDIARY I/O] connector, [B]. These inputs are primarily intended for cascading two
mixers.
9. MASTER GAIN CONTROL The Master fader controls the gain of the two output channels
simultaneously. There is a reserve of gain of 3dB above the 0dB calibration point (which is located
by a mechanical detent), so that this control can be used to raise the overall level of a mix as well as
to fade in and out.
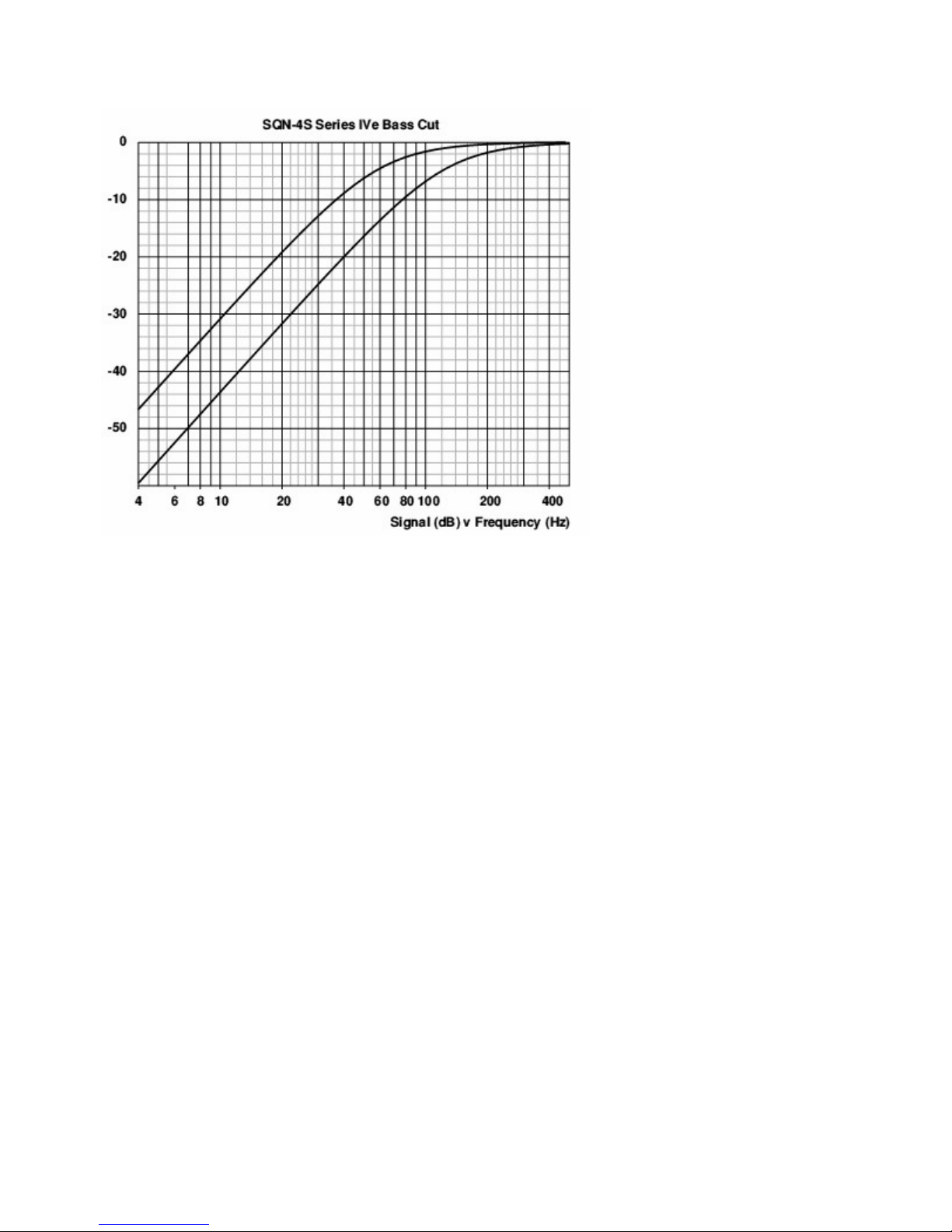
10. BASS CUTS A Bass Cut switch for each microphone channel is situated next to its fader
allowing for bass attenuation of the signal with cutoff frequency that depends on the setting as shown
in the accompanying graph. These are employed for a variety of purposes, such as reduction of
‘boominess’ in hard or ‘live’ acoustic locations, or from deep voices, as well as reducing extraneous
traffic rumble, ‘mains hum’ from electrical appliances and so on. Perhaps the most common use for
bass cuts is to assist in the reduction of wind noise outdoors, but a suitable windgag on the
microphone will also be essential.
Page 5 of 10
SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
11. AUDIO LEVEL METERS The basic type of metering employed on the SQN-4S is the Peak
Programme Meter (PPM). This was chosen as providing the maximum information about the
relationship between the signal level and the overload point of the recorder. Admittedly, peak meters
do not necessarily give a true representation of the loudness of the signal and some recordists prefer
the VU type of meter which we can also provide. The meters can only give a useful indication of the
recording level when the combination of mixer and recorder has been calibrated. Each meter is
permanently illuminated while the mixer is switched on, allowing operation in dim light. The
illumination requires minimal current from the batteries.
For those unfamiliar with the BSI (BBC style) PPM scale, the intervals between scale graduations
represent a 4dB difference, so that with the nominal Line Level (0dBu) represented by 4, the nominal
Peak Output Level of the mixer (+8dBu) occurs at 6 on the scale. This 'Nominal Peak' is a
simplification of the arguments, since in practice the BBC has adopted various preferred peak levels
for different sound sources and even individual musical instruments. Other PPM scales have not
followed the BBC design and are all expressed in decibels, which makes them more readily
intelligible. They also usually feature a TEST arrow at 0dBu (0.775V) for calibration purposes. The
'nominal peak' level referred to above tends to be seen as +6dB where the scale is calibrated in 3dB
steps (e.g. the 'Nordic Norm' pattern adopted by the Scandinavian Broadcasting Consortium) or +8dB
where calibration is in 4dB increments (e.g. the SMPTE 'preferred' scale published in 1989 where this
peak level is scaled as '0').
VU meters also vary in their calibration. The original VU measured zero at zero dBm in a 600 Ohm
system. Modern practice, based originally on the improved high level performance of analogue
recording tape, is to place zero VU at +4dBm. Either calibration can be provided and will be noted on
the mixer baseplate.
12. OUTPUT LIMITERS Location recording frequently puts the recording engineer in a situation in
which he or she has no control over the ambient sound level. Accordingly, the SQN-4S has been
Page 6 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
provided with a pair of output peak limiters that may be confidently employed at all times. Coming
into operation just below peak level, theyaccommodate overloads of up to 20dB with an attack time
of half a millisecond and a release time of 100ms.
Peak limiting is an extremely non-linear process that relies on the masking characteristics of the ear
to render the effect essentially inaudible when executed properly and used in moderate amounts. It is
bad practice to make a habit of 'riding' the limiters: the LEDs should only light on the occasional
unexpected peak if the levels are correctly set. Allowing the limiters to be operated by low frequency
or sub-audio rumbles will cause modulation of the more audible midrange and high frequency audio.
In the worst case this may manifest itself as apparently random audible clicks. The bass cuts should
be used to remove dominant low frequency signals so that the limiters are operated only by signals in
the wanted audible range.
The Limiters are actuated by a switch [LIMITER] towards the right of the front panel and in the
[M]ono position each output channel is separately limited, with actual limiting being indicated by an
LED for each channel, placed between the meters. With stereo recording, limiting can introduce a
further problem since, if only one channel of a stereo pair is subjected to limiting, the effect is to shift
the stereo image. The [LIM] switch, therefore, has a third [S]tereo position in which the degree of
limiting is governed by the higher of the two output channel levels. This setting should be used when
the mixer output is stereo, of either type AB or MS.
13. MONITORING HEADPHONES The quarter inch jack [PH] of the SQN-4S will accept any
standard stereo plug. Headphones of any impedance may be employed although impedances of
around 200 Ohms will make best use of battery power. For location work, it is advisable to employ
headphones with good ear sealing even though they can be uncomfortable when worn for long
periods of time. Increasing the headphone level to drown the directly audible sound in noisy
situations could prove fatiguing or even damaging to the hearing in the long term, particularly if the
limiters are not used. The control knob at the bottom left of the front panel allows the headphone
output level to be adjusted - down to zero if desired.
A rotary [PHONES] switch on the front panel allows the operator to select various sources for the
monitored signals, including the output of an MS matrix which will allow an MS signal being output
from the mixer to be monitored as the equivalent AB signal. This switch has the following functions.
• S Stereo
• R Right Channel
• L Left Channel
• MS MS Matrix (MS stereo equivalent)
• L-R Left minus Right (MS stereo equivalent Right)
• L+R Left plus Right (MS stereo equivalent Left or Phase Check).
Below the [PHONES] switch is a pair of three position toggle switches, sprung to their centre
positions which control pre-fade listening to all of the input channels.
14. MIXING & MATRIXING CONTROLS The SQN-4S SERIES IVe mixer is intended to work in
various modes and particularly to accomodate the use of Mid-Side microphones and Mid-Side
recording. The CH1/CH2 pair is treated as a potential Stereo Channel, with or without MS matrixing,
while the CH3/CH4 pair can be routed or panpotted into the stereo image. This is in addition to the
usual routing of individual channels to either output.
The operation of the CH1/CH2 pair is controlled by the [GANG 1-2] and [PHASE] switches as
Page 7 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
follows:
1. TWIN MONO with the [GANG 1-2] switch at [0]. The CH1/CH2 faders operate
independently. The routing switches at the end of the mixer can direct the signals to
either or both of the two mixing busses.
2. STEREO with the [GANG 1-2] switch at [S]. The input and output from the pair are
treated as an AB stereo signal. The gains of both channels are controlled by the CH1
fader and the [BAL] pot on the end of the mixer acts as a balance control The CH2
fader acts as an attenuator on the CH2 signal and should be kept at 100% rotation for
normal stereo use.
MS USE of the STEREO MODE: If an MS signal is passed through the mixer with the
[GANG 1-2] switch at [S]. the CH2 fader can be used as a width control. If the balance
control is kept in the centre detented position then the CH2 fader will be able to vary
the MS width from 0 to 100%. Turning the balance control to favour CH2 will allow
the side signal to be increased beyond 100% while still being under the control of the
CH2 fader.
3. MID-SIDE with the [GANG 1-2] switch at [MAT]. The input to the pair is treated as an
MS stereo signal which is matrixed into AB stereo. The gains of both channels are
controlled by the CH1 fader. The CH2 fader acts as an MS width control by altering the
relative level of the CH2 side signal: a setting of 8 will give a relative level of 100% or
normal width. The [BAL] pot on the end of the mixer acts as a balance control for the
resultant AB stereo signal. The CH1 and CH2 routing switches at the side of the mixer
are inoperative.
The [PHASE] switch acts on CH2, independently of the settings of the other switches. When it is
moved to the right (arrow), it inverts the phase of the signal. This has the incidental effect of
interchanging left and right in an MS encoded input.
The controls available for the CH3/CH4 pair are the routing switches and PANpots on the end panel
of the mixer. These allow either of the channels to be routed directly to either output channel or to be
panpotted between them. Note that when either of CH3 or CH4 is sent equally to both outputs using
the PANpots, the level at each output will be 3dB lower than if the signal is routed to just one output.
This is due to the nature of the panpotting process which requires the sum of the powers in the two
channels to remain constant at all settings.
SIGNAL DISCONNECT: If PIN 11 of the SUBSIDIARY I/O connector is linked to GND, the
operation of the signal routing for CH3 and CH4 is changed so that they may be switched out of the
mixing bus. Selecting PAN for CH3 or CH4 will now switch the channel out of the mix instead of to
the PANpot. This is for the benefit of those who wish to use the channels separately to feed other
equipment.
15. SLATING MICROPHONE A microphone is mounted behind the front panel near the centre of
the mixer. This microphone, brought into use by moving the [TONE/MIC] switch on the front panel
to the right, is intended for recording identification announcements and slating marks on the output
channels. The output of the microphone is levelled by a 2:1 compressor and overrides the main audio,
appearing on the mixer outputs and in the monitoring system. If the monitoring mode is set to [AUX]
at the time the button is pressed, it automatically reverts to the internal or [MXR] setting. This is so
that the recordist, if working with a recorder equipped with off-tape monitoring will not have to talk
over a delayed version of the announcement. The inclusion of the compressor means that a usable
recording can be made by speaking in a normal voice over a range of 1.5m to 250mm from the mixer,
depending upon the ambient noise level.
Page 8 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
16. WARRANTY & SERVICE The SQN-4S is guaranteed for a period of 12 months from the date of
purchase. This guarantee covers defects in manufacture, workmanship and materials and includes the
cost of parts, labour and return carriage. The full terms of the guarantee are given in the printed copy
of this document delivered with the mixer..
18. SCREW-LATCHING CONNECTOR WIRING (10W)
Screw-latching connectors are now provided only to special order. All input and output connectors
are now normally either XLR latching or Push-Pull latching types. The connection list below applies
to mixers fitted with the the screw-latching version of the MAIN I/O connector. This optional fitting
is intended to provide direct compatibility with cables made for earlier models.
Page 9 of 10

SQN-4S IVe User's Handbook
.
19. CONNECTOR LIST
The following is a list of the manufacturers part numbers for the connectors to mate with those on the
mixer
MIXER CONNECTOR MATING CONNECTOR MANUFACTURER
MAIN I/O [A] (STANDARD) PRC05P12M Tajimi
MAIN I/O [A] (SCREW) RM15PD10P Hirose
SUBSIDIARY I/O [B] HR10-10P12P Hirose
POWER INPUT [DC] HR10A7P4P Hirose
POWER THROUGH [PT] HR10A7P4P Hirose
©1999, 2001 SQN Electronics Ltd
Page 10 of 10
Other SQN Music Mixer manuals


















