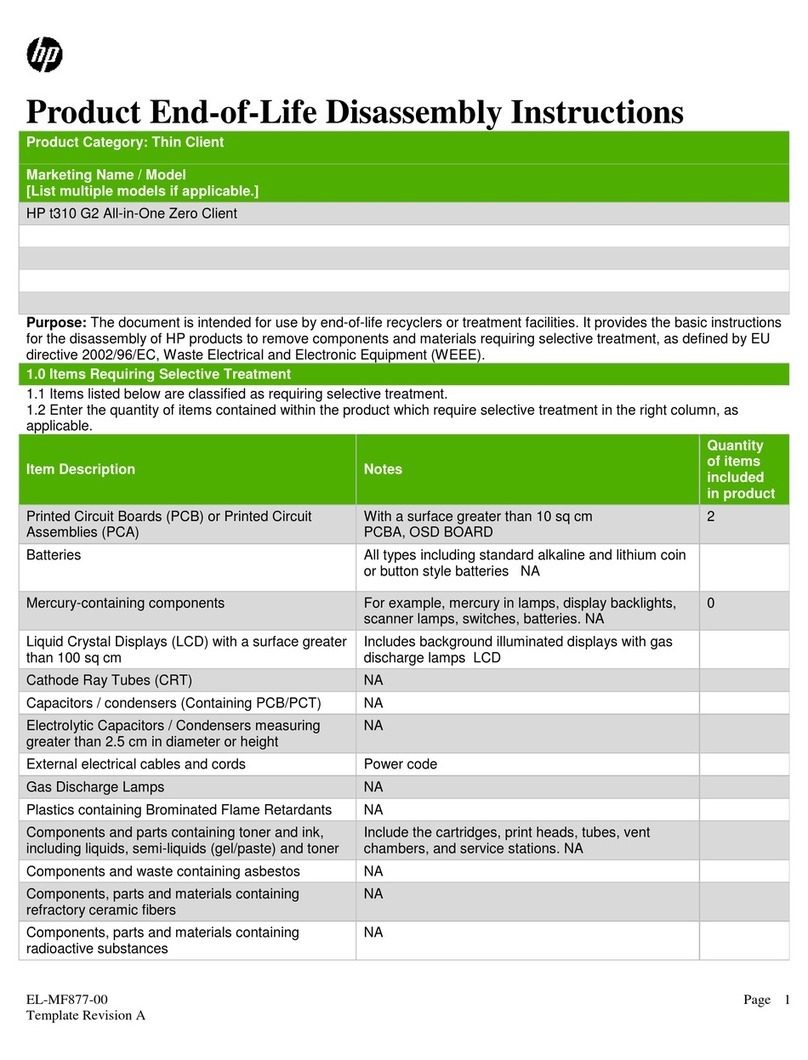
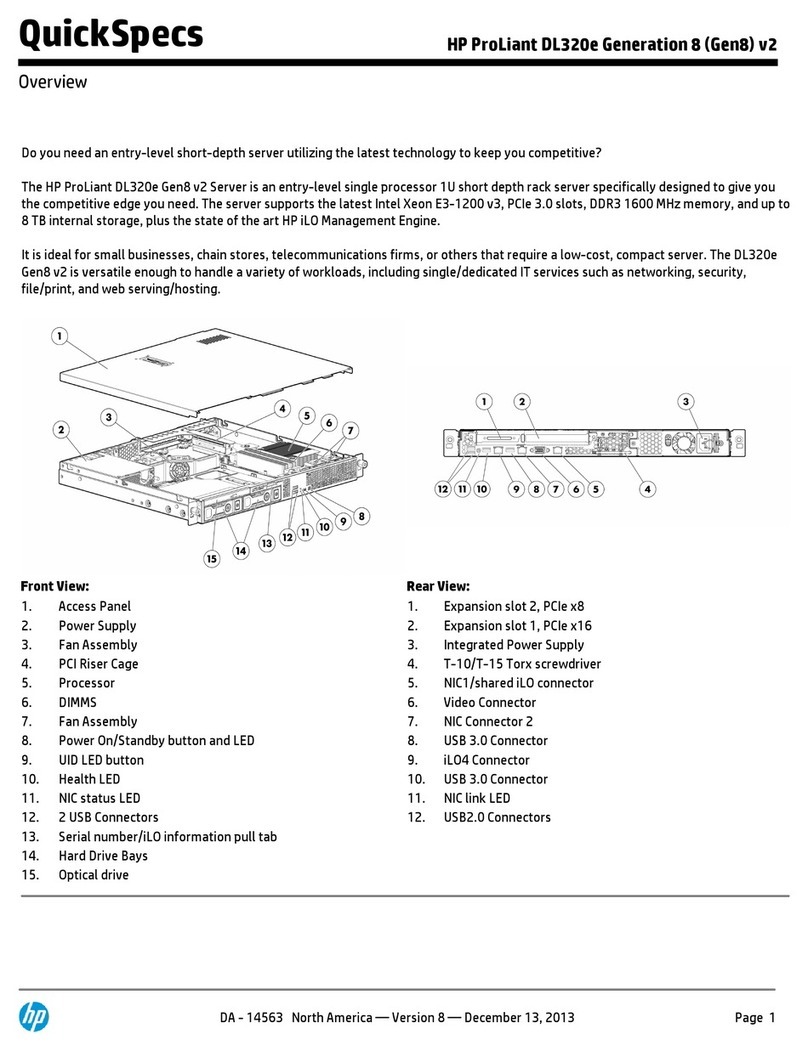
SSV IGW/400-UART User manual

IGW/400
-
UAR
T
WLAN Device Serve
r
First Steps
SSV Embedded Systems
Heisterbergallee 72
D-30453 Hannover
Phone: +49-(0)511-40000-0
Fax: +49-(0)511-40000-40
Date: 2005-09-26
For further information regarding our products please visit us at www.ssv-embedded.de

IGW/400-UART – Content
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 2
CONTENT
1INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................3
1.1 Block Diagram..........................................................................................................................3
1.2 Features IGW/400-UART.........................................................................................................3
2GETTING STARTED.........................................................................................................4
2.1 Connecting the WLAN Antenna...............................................................................................4
2.2 Connecting the Plug-in Connector............................................................................................5
2.3 Connecting the Temperature Sensor SMT-160 ........................................................................7
2.4 Connecting the Power Supply...................................................................................................8
2.5 Arranging and Testing the WLAN Connection on the PC .....................................................10
2.6 Accessing the Temperature Sensor.........................................................................................12
CONTACT .............................................................................................................................13
DOCUMENT HISTORY.........................................................................................................13
COPYRIGHT .........................................................................................................................13

IGW/400-UART – Introduction
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 3
1 INTRODUCTION
The WLAN Device Server IGW/400-UART integrates typical measurement and control
interfaces into a 802.11b/g-compatible WLAN.
This very compact system acts as small, easy to use interface converter, which collects
any data of industrial automation components and transmits it via WLAN.
This document describes the hardware components of the IGW/400-UART. For further
information about the individual components of this product you may follow the links
from our website at http://www.ssv-comm.de.
Our website contains a lot of technical information, which will be updated in regular pe-
riods.
1.1 Block Diagram
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the IGW/400-UART. UART1 correlates with the
RS232 connector (COM1) and the EI/Os correlate with the 14-pin environment interface
of the IGW/400-UART.
Figure 1: Block diagram of IGW/400-UART
1.2 Features IGW/400-UART
•One 14-pin environment interface with RS232/RS422
•One 10/100Mbps Ethernet interface (LAN)
•One RS232 connector (COM1)
•One reverse SMA connector for WLAN antenna
•One power LED (green)
•One WLAN activity LED (red)
•Size 131 x 70 x 26 mm (without antenna)

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 4
2 GETTING STARTED
2.1 Connecting the WLAN Antenna
The first step is to connect the WLAN antenna (which is part of the Starter Kit) with the
provided interface at the backside of the IGW/400-UART. Please note, that the antenna
has to be screwed until stop with the interface.
Figure 2: Connecting the WLAN antenna
The IGW/400-UART uses frequencies in the scope of 2.4 GHz. Therefore special anten-
nas are needed. Please only use antenna equipment, which is offered resp. tested and re-
leased by SSV. A wrong antenna might lead to permanent damage to the
IGW/400-UART!

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 5
2.2 Connecting the Plug-in Connector
Plug the 14 pin plug-in connector into the corresponding interface at the frontside of the
IGW/400-UART. Then connect the two wires of the power supply cable with the 14 pin
plug-in connector. For this purpose a screwdriver is needed, which is usually part of the
Starter Kit. Please pay attention to the colors of the wires and to the pin assignment of the
14 pin plug-in connector.
Figure 3: Connecting the plug-in connector
Connect now the four wires of the RS232 adapter cable with the 14-pin plug-in connec-
tor. Please pay also attention to the colors of the wires and to the pin assignment of the
14-pin plug-in connector.

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 6
Figure 4: Pin assignment of plug-in connector
Pin Wire color Signal
1 red VCC
2 black GND
Table 1: Pin assignment of power supply cable
Pin Wire color Signal
4 green RXD
5 yellow TXD
7 red RTS
9 blue GND
Table 2: Pin assignment of RS232 adapter cable
Pin Wire color Signal
1 Not connected
2 green RXD
3 yellow TXD
4 Not connected
5 blue GND
6 Not connected
7 red RTS
8 Not connected
9 Not connected
Table 3: Pin assignment of Sub-D connector of RS232 adapter cable

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 7
2.3 Connecting the Temperature Sensor SMT-160
Plug now the intelligent temperature sensor SMT-160 on the 9 pin Sub-D connector of
the RS232 adapter cable. This sensor delivers temperature data to the RS232 interface of
the IGW/400-UART permanently. This data should be transmitted to your PC via
WLAN.
Figure 5: Connecting the temperature sensor
The temperature sensor SMT-160 has no case. Please avoid the direct touch of the traces
of the SMT-160. The circuits on the SMT-160 can be damaged by electrostatic discharge.

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 8
2.4 Connecting the Power Supply
The IGW/400-UART is now ready for use. Connect the plug-in power supply which is
part of the Starter Kit with the connector of the power supply cable. Plug the plug-in
power supply into an outlet to provide the IGW/400-UART with power. Check if the red
power LED at the frontside is on.
Figure 6: Connecting the power supply
Please pay attention to the polarity of the power connector: the + pole is in the center!
Figure 7: Polarity of the power connector

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 9
The IGW/400-UART is now accessible from your PC. Please note the settings of the
WLAN interface (ex factory settings). The following table gives an overview.
Parameter Setup Value
Network Interface WLAN
Network Name SSV_IGW400
Ad Hoc Mode Settings Enable
Ad Hoc Mode Settings: Network Name SSV_IGW400
Ad Hoc Mode Settings: Country USA
Ad Hoc Mode Settings: Network Channel 11
IP Address 192.168.3.126
Network Mask 255.255.255.0
UART1 Settings 9.600 bps, N, 8, 1
UART2 Settings 9.600 bps, N, 8, 1
UART1 TCP/IP Access TCP, Port 10001
UART2 TCP/IP Access TCP, Port 10002
Wireless Network Security None
Table 4: WLAN settings IGW/400-UART
For the first WLAN connection test you should adapt your PC to the ex factory settings
of the IGW/400-UART for convenience.

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 10
2.5 Arranging and Testing the WLAN Connection on the PC
This step requires a PC with an IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g WLAN interface. This
interface can be formed with an USB WLAN stick, a WLAN PC card or similar exten-
sions. If you install such an extension, please follow the instructions of the manufacturer
absolutely.
The WLAN interface of your PC can operate in two different modes: the ad-hoc mode
and the infrastructure mode. The ad-hoc mode corresponds to a wireless point-to-point
connection, e.g. your PC and the IGW/400-UART. The infrastructure mode is needed if
you want to connect your PC with a WLAN access point. The software of your PC
WLAN extension allows to choose between both operating modes. Details can be found
in the manual of the manufacturer and in the help system of the WLAN extension.
Figure 8: Arranging the WLAN connection
Set the WLAN interface of your PC to ad hoc mode. If your WLAN PC software allows
it, search for available WLAN devices which run also in ad hoc mode. Most WLAN PC
applications offer a button to start the search. The founded WLAN communication part-
ners are shown in a small window. Usually you can choose your desired communication
partner. Your WLAN PC software should find a communication partner with the identi-
fier (network name / SSID) SSV_IGW400. Connect the WLAN interface of the PC with
that device.
Older WLAN PC applications which do not support the automatic search for WLAN de-
vices must be configured manually with the WLAN parameters of the IGW/400-UART.
In that case choose the WLAN channel 11 and the name (network name / SSID)
„SSV_IGW400“.
Change the IP address for the WLAN interface of your PC to 192.168.3.1 and the subnet
mask to 255.255.255.0. On a Windows PC you can do that via the system settings. Refer
to the Windows help for more information.

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 11
Figure 9: Testing the WLAN connection with ping
The IP address of the IGW/400-UART is set ex factory to 192.168.3.126. Open a window
with a command prompt on your PC and enter
ping 192.168.3.126
The connection between your PC and the IGW/400-UART will be tested. A succesful
ping means that there is a running WLAN connection between both systems.

IGW/400-UART – Getting Started
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 12
2.6 Accessing the Temperature Sensor
There is a running WLAN connection between your PC and the IGW/400-UART. Now it
is possible to access the measured data of the temperature sensor SMT-160 via WLAN.
Figure 10:Accessing the temperature sensor
The simplest way to access the IGW/400-UART is Telnet. Open a window with a com-
mand prompt on your PC and enter
telnet 192.168.3.126 10002
Afterwards the measured data of the temperature sensor SMT-160 is shown continuously.
By touching the sensor (Attention: please assure that you are NOT electrostatic char-
ged!) you can manipulate the temperature measurement.

IGW/400-UART – Contact
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 13
CONTACT
SSV Embedded Systems
Heisterbergallee 72
D-30453 Hannover
Phone: +49-(0)511-40000-0
Fax: +49-(0)511-40000-40
Internet: www.ssv-embedded.de
DOCUMENT HISTORY
Revision Date Remarks Name
1.0 2005-09-26 first version WBU
COPYRIGHT
The content of this document can change any time without announcement. There is taken
over no guarantee for the accuracy of the statements. The user assumes the entire risk as
to the accuracy and the use of this document. Information in this document is provided
‘as is’ without warranty of any kind.
Some names within this document can be trademarks of their respective holders.
© 2005 SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS. All rights reserved.
Table of contents
Other SSV Server manuals