Teleconnect Socrates Series User manual

Teleconnect GmbH
Am Lehmberg 54
01157 Dresden/Germany
© 2019 Teleconnect GmbH
SOCRATES Series
SHDSL.EVB.4CH
User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 2/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Revision History:
Current Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05
Revision
Date
Comment
1.0.0
2019-02-05
Initial release

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 3/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Table of Contents
1Introduction .................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Scope of this Document.......................................................................................... 5
1.2 General Introduction................................................................................................ 5
1.3 Content of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board Kit............................................ 6
2Block Diagram................................................................................................................ 7
3Interfaces....................................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Design Overview..................................................................................................... 9
3.2 SHDSL Interface..................................................................................................... 9
3.3 Ethernet Interface via PHY.....................................................................................12
3.4 Ethernet Interface via Switch..................................................................................14
3.5 Power Supply Input................................................................................................14
3.6 Power Consumption...............................................................................................15
3.7 Serial Interface (UART)..........................................................................................15
3.8 Debug interface......................................................................................................16
3.9 Control and Monitoring Interface ............................................................................16
3.9.1 Buttons............................................................................................................16
3.9.2 DIP switches...................................................................................................17
3.9.3 Rotary switch (10 pole)....................................................................................18
3.9.4 Rotary switch (16 pole)....................................................................................18
3.9.5 LEDs...............................................................................................................18
4Software........................................................................................................................20
4.1 Updating Firmware.................................................................................................20
4.1.1 Preparation .....................................................................................................20
4.1.2 Using the in-system programmer ....................................................................20
4.2 SHDSL.EVB.4CH Firmware 3.0 .............................................................................22
4.3 Functions and packages ........................................................................................23
5User Interfaces..............................................................................................................24
5.1 Establish a Connection...........................................................................................24
5.2BSI - Basic Status/SHDSL Interface.......................................................................24
5.3 CLI - Command Line Interface ...............................................................................26
5.3.1 Login...............................................................................................................26
5.3.2 CLI commands................................................................................................27
5.3.3 Password modification ....................................................................................28
5.3.4 Configuring the system....................................................................................29
5.3.5 Firmware update.............................................................................................30
6Operation......................................................................................................................33
6.1 Start-up with two boards.........................................................................................33
7Using SHDSL.EVB.4CH as Module...............................................................................34
7.1 Scope.....................................................................................................................34
7.2 Connection.............................................................................................................34
7.3 Protection...............................................................................................................34
8Literature.......................................................................................................................35
Appendix A. Quick Start-up guide....................................................................................36

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 4/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
List of Figures
Figure 1: Structure of SHDSL Link .........................................................................................5
Figure 2: Main components of SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board .......................................6
Figure 3: Block Diagram of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board.......................................7
Figure 4: Functions of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board..............................................9
Figure 5: SHDSL Interface .....................................................................................................9
Figure 6: (Extract from) Schematic of SHDSL Hybrid ...........................................................11
Figure 7: Ethernet interface..................................................................................................12
Figure 8: Schematic of Ethernet Interface via PHY...............................................................13
Figure 9: Schematic of Ethernet Interface via Switch............................................................14
Figure 10: SAM-BA menu: select connection and board.......................................................21
Figure 11: SAM-BA menu: select firmware image and download them.................................21
Figure 12: SAM-BA menu: press execute.............................................................................22
Figure 13: CLI menu tree......................................................................................................27
Figure 14: CLI example: config/show ?.................................................................................28
Figure 15: CLI example: password modification ...................................................................28
Figure 16: CLI example for show modified SHDSL configuration..........................................29
Figure 17: CLI example for net configuration........................................................................30
Figure 18: CLI example for show stored firmware list ...........................................................31
SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 5/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
1Introduction
1.1 Scope of this Document
This document describes the hardware and software to get started with the SHDSL 4-Channel
Evaluation Board from the Teleconnect SOCRATES series. The product code
“SHDSL.EVB.4CH” used for this document.
Teleconnect (http://www.teleconnect.de/xdsl/socrates-evb) provides all necessary
documentations for recreating of the hardware. This includes schematic, components layout
placement, board outline, PCB layout, bill of materials and available software features. Gerber
files are available upon request at shdsl@teleconnect.de.
1.2 General Introduction
The new SHDSL.EVB.4CH reference design targeting industrial designs enables customers
to take advantage of Intel®SHDSL Chipset (previously known as "Lantiq SOCRATES™-4E")
for long reach broadband connectivity. It is the first ever ready-to-copy reference design
developed for the Intel®SHDSL Chipsets. The SHDSL/Ethernet Bridge Modem was developed
by Teleconnect and measures only about 11 x 12,5 cm. It is available for online purchase
through:
•Würth Elektronik webshop (http://www.we-online.com/socratesdemo).
Teleconnect offers dedicated support for board and software customizations. With this
Evaluation Board you get an Evaluation License for the Software Packages P1-P2-P3-P4-P5-
P6-P8-PD including bootloader and firmware update. For more information please see chapter
4.3 Functions and packages. With this, for the first time ever, even smaller companies without
DSL expertise can include SHDSL and Long-Reach-Ethernet connectivity into their designs.
SHDSL’s unique rate/reach performance makes it the product of choice in an ever more
diversified field of applications rangingfrom business broadband access to enterprise networks
and industrial communications.
Known as long haul Ethernet, SHDSL was included in the Ethernet standard IEEE 802.3-2008
[1], where it is named 2BASE-TL. Standard Ethernet has a maximum reach of 100 m. SHDSL
has a reach beyond 15 kilometers.
Using SHDSL enables costumer to transmit Ethernet over only one unshielded twisted wire
pair or over any other cable. An example structure of SHDSL is shown at Figure 1.
Figure 1: Structure of SHDSL Link

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 6/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
1.3 Content of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board Kit
The evaluation kit contains the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board shown in Figure 2. Beside
this you need a power source provided via short and high quality micro USB cable. For
Ethernet and SHDSL connection, standard Ethernet patch cables can be used.
Figure 2: Main components of SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board
Please consider the changes for the chip manufacturers (Lantiq was acquired by Intel®). In the
past, the SHDSL transceiver PEF 24628 E was offered by Lantiq as SOCRATES™-4E with
identical PEF number. Now the SHDSL chipset is offered by Intel®as Intel® SHDSL Chipset.
This also applies to the Ethernet PHY.In the past, the XWAY™PHY11G was offered by Lantiq,
now the chip is called Intel®Ethernet Network Connection GPY112 and offered by Intel®.
In 2016, Microchip agreed to buy Atmel®. That´s the reason why the Atmel®microcontroller
ATSAM4S is now part of Microchip product spectrum.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 7/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
2Block Diagram
Figure 3 shows the block diagram of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board.
Figure 3: Block Diagram of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board
The SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board consists of the following blocks:
•SHDSL transceiver Intel®SHDSL Chipset (PEF 24628 E) (previously known as "Lantiq
SOCRATES-4E" with same PEF number).
The functionality of the Evaluation Board could also be realized with the 1ch versions
of the Intel®SHDSL Chipsets (PEF 21628 E). Teleconnect provides 1ch SHDSL
Evaluation Board also (product code: SHDSL.1CH.EVB [2]).
You can use one up to four channels with SHDSL.EVB.4CH.
•Intel®Ethernet Network Connection GPY112 (PEF 7072), Version 1.6 (previously
known as "Lantiq PHY11G").
The GPY112 is a Gigabit Ethernet PHY. However, in this application only
10/100BaseTX is available.
•Ethernet switch LAN9353 is prepared for future use cases. It cannot be used at the
current development stage.
•CPLD LCMXO2-640U is for the adaption between PHY interface, Switch interface and
SHDSL chipset.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 8/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
•Microcontroller Microchip ATSAM4SD32C (previously known as "Atmel
ATSAM4SD32C").
The microcontroller is used for configuration, controlling and monitoring. The
requirements of the microcontroller are very low, e.g. an 8-bit controller has enough
performance for SHDSL. We use the ARM®based microcontroller to provide a highly
flexible evaluation platform.
•RJ45 connectors (shielded for Ethernet and unshielded for SHDSL), both from Würth
Elektronik eiSos GmbH
•Micro USB connector Type B (Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH),
•SHDSL Hybrid including SHDSL transformer (Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH),
•Ethernet magnetics (Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH),
•DC/DC converter from 5 V to 3.3 V, 1.5 V and 1.0 V. Three voltage regulators from
MPS (Mini-Module Family) are used.
•XTAL for SHDSL-transceiver, Ethernet-PHY and Microcontroller (Geyer Electronic),
•Input and Output components (Würth Elektronik eiSos GmbH):
otwo Rotary switches and one DIP switch 5 pole,
otwo Push buttons,
oISP pin header for debugging of the microcontroller,
onine LEDs.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 9/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
3Interfaces
This chapter describes the interfaces and header pinouts of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation
Board.
3.1 Design Overview
The design with its main function blocks and important componentsare shown in Figure 4. The
description for it is given in the following section.
Figure 4: Functions of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board
3.2 SHDSL Interface
The SHDSL interface is divided in SHDSL connector, SHDSL Transformer, Protection, Hybrid
and SHDSL data pump (see Figure 5).
Figure 5: SHDSL Interface
Additional primary protection is necessary depending on requirements. There is no primary
protection on the evaluation board available.
The connector X107 is an unshielded RJ45 connector. It is used for connecting the
SHDSL.EVB.4CH up to four SHDSL lines (according ITU-T G.991.2 [3]). Table 1 shows the
pin definition of X107.
Erase Button
Micro USB:
Power and UART
emulation
Reset Button
Alternative
Power: +5,0V
Alternative
UART
JTAG:
Connection to
AVR debugger/
programmer
Select Mode
Select Bitrate
Ethernet
Connector
SHDSL
Connector
Green LED:
Ethernet Link/
Activity
Amber LED:
Ethernet Error
detected
Green LEDs:
SHDSL line states
(connection established, Training, Idle)
Green LED:
Power
Amber LED:
Status
Red LED:
Error
SHDSL
transceiver
(SHDSL data
pump)
V101
SHDSL
Hybrid
Several
components
Secondary
Protection
D101/D102/
D103/D104
Transformer
L101/L102/
L103/L104
Primary
Protection
Not
available
Connector
X107
X105/X106/
X108/X109

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 10/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Table 1: Pin Definition of X107
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
SHDSL line #2 –Ring
2
SHDSL line #2 –Tip
3
SHDSL line #3 –Ring
4
SHDSL line #1 –Tip
5
SHDSL line #1 –Ring
6
SHDSL line #3 –Tip
7
SHDSL line #4 –Ring
6
SHDSL line #4 –Tip
Typical lines are unshielded twisted pair cables. Any standard Ethernet cable is also usable.
Beside the RJ45 connector X107 SHDSL.EVB.4CH provides the possibility to use the pin
header X105 (SHDSL line #1), X106 (SHDSL line #2), X108 (SHDSL line #3) and X109
(SHDSL line #4) spaced 2.54 millimeters (0.1 in). Table 2 gives the pin definition.
Table 2: Pin Definition of X105, X106, X108 and X109
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
SHDSL line #X –Tip (X = 1...4)
2
SHDSL line #X –Ring (X = 1...4)
The pin header X105 (SHDSL line #1), X106 (SHDSL line #2), X108 (SHDSL line #3) and
X109 (SHDSL line #4) are not mounted by default. It is possible to mount it on both PCB sides
to get an easy test adapter for evaluation or to use the SHDSL.EVB.4CH as a module.
Figure 6 shows the schematic of the SHDSL hybrid with line transformer L101, L102, L103
and L104 and SHDSL data pump V101 (PEF 24628 E).
Components and layout are influencing the SHDSL performance. Teleconnect can assist you
with the selection of additional line protection at raw ambient conditions.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 11/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Figure 6: (Extract from) Schematic of SHDSL Hybrid
SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 12/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
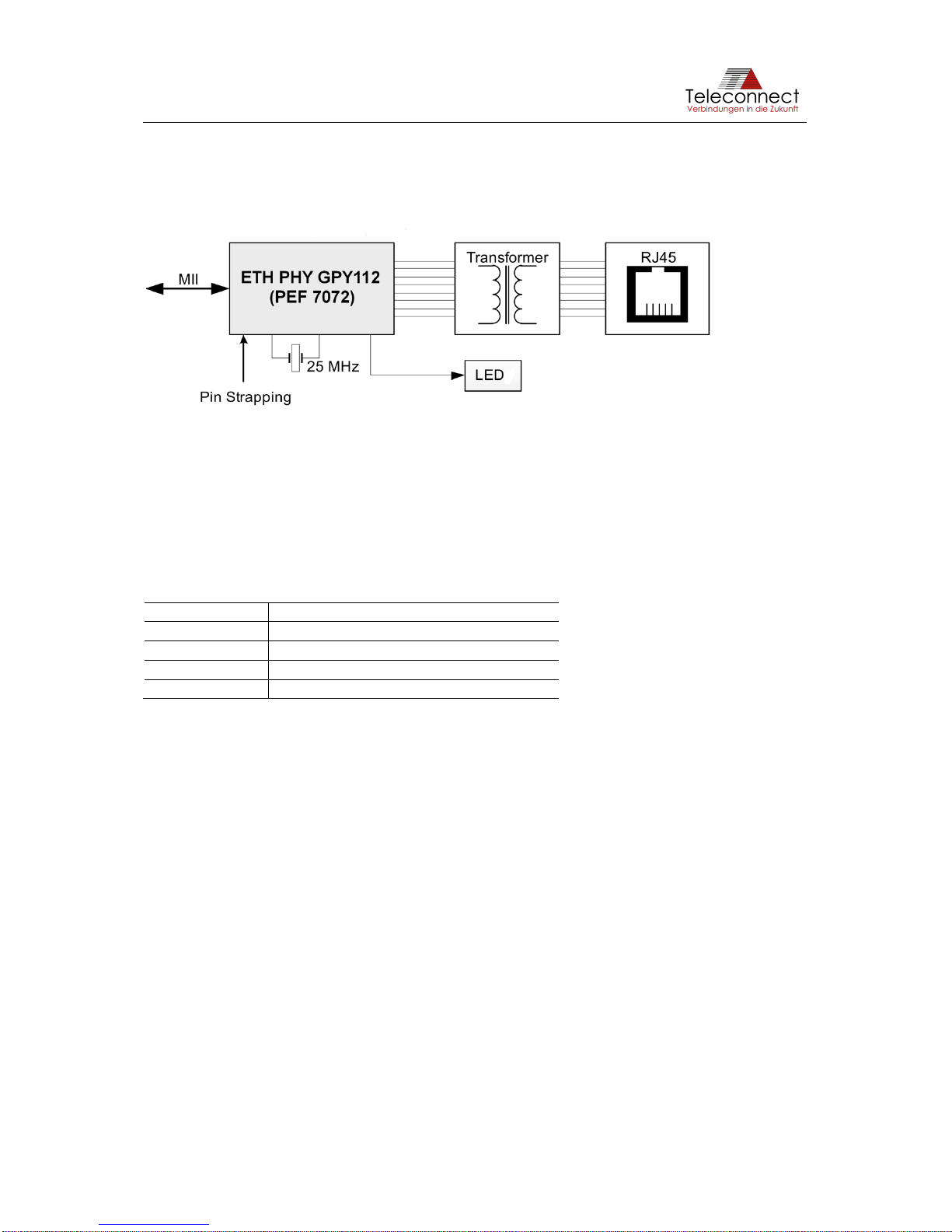
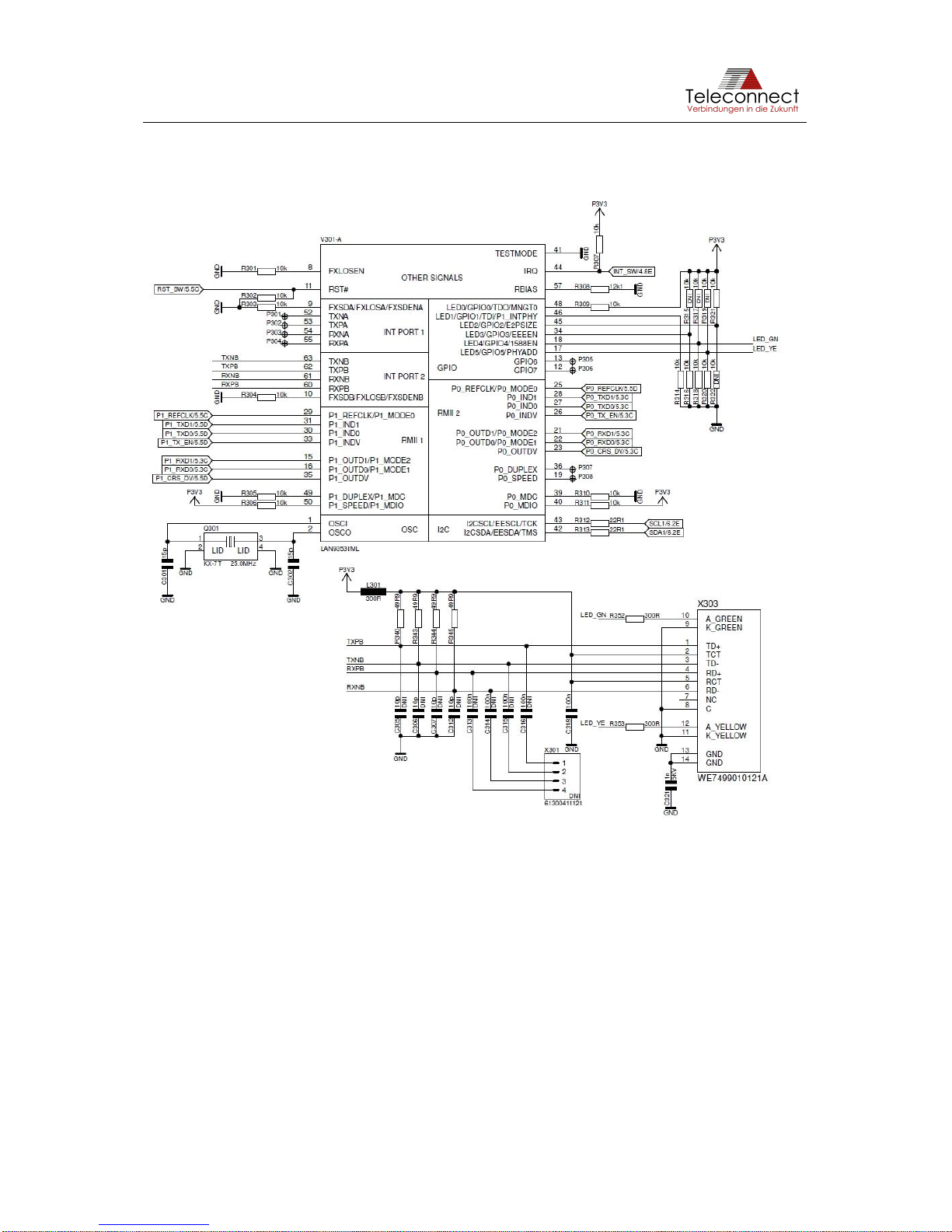
3.3 Ethernet Interface via PHY
The useable Ethernet interface via PHY is divided in connector, transformer (magnetics) and
Ethernet PHY (see Figure 7).
Figure 7: Ethernet interface
The shielded RJ45 connector X304 is a standard Ethernet interface. It is compatible with
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet according to IEEE 802.3 [1] and can be connected to a
twisted pair medium such as CAT5 cable infrastructure.
Beside the RJ45 connector, SHDSL.EVB.4CH provides the possibility to use the pin header
X302 spaced 2.54 millimeters (0.1in). Table 3 gives the pin definition.
Table 3: Pin Definition of X302
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
TX/RX1 +
2
TX/RX1 -
3
TX/RX2 +
4
TX/RX2 -
The pin header X302 is not mounted by default. It is possible to mount it on both PCB sides to
get an easy test adapter for evaluation or to use the SHDSL.EVB.4CH as module (see
chapter 7).
The transformer L302 connects the connector to the Ethernet PHY GPY112 V201 (PEF7072).
The connection to the SHDSL data pump Intel®SHDSL Chipset V101 is realized via standard
MII interface.
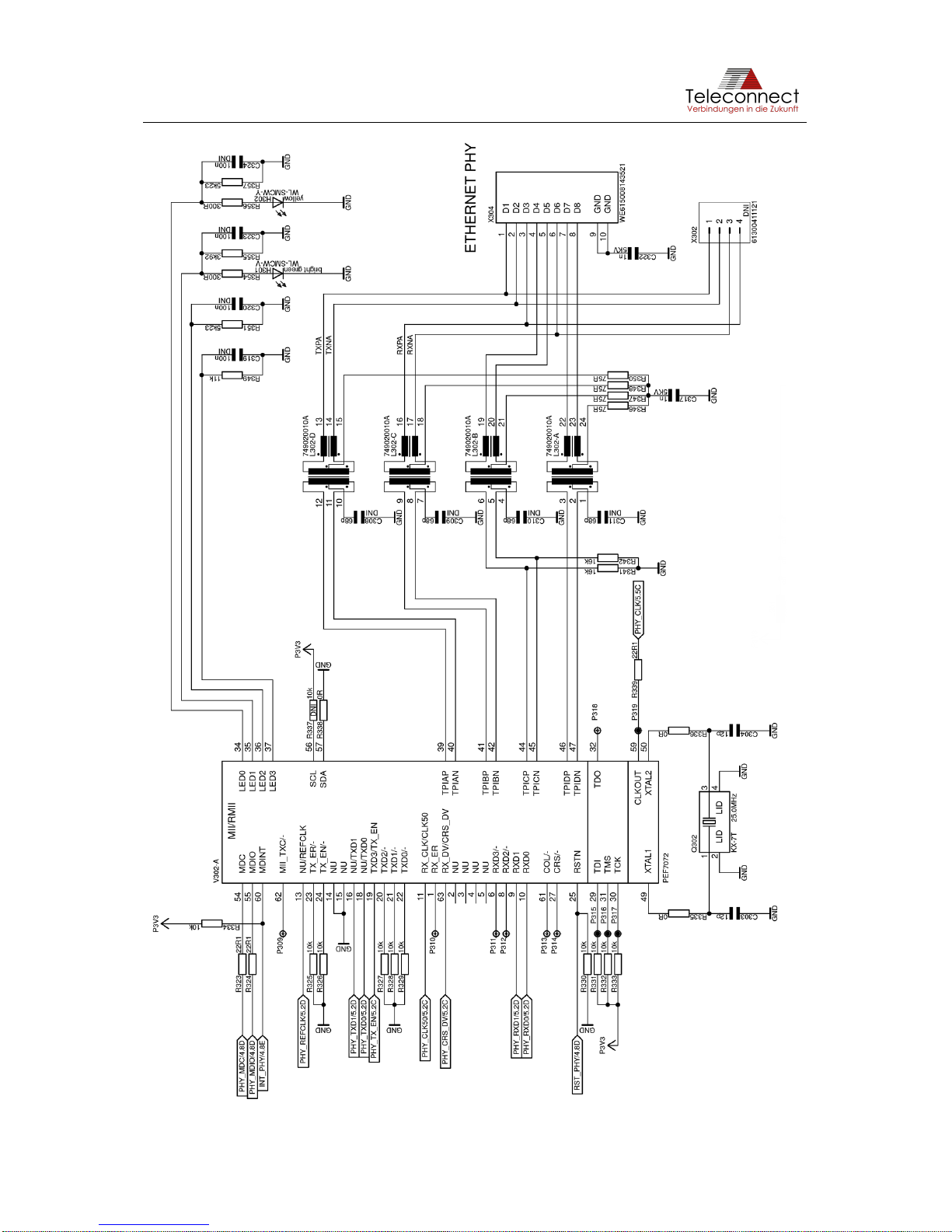
Figure 8 shows the schematic of the Ethernet interface via PHY.
SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 13/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Figure 8: Schematic of Ethernet Interface via PHY
SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 14/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
3.4 Ethernet Interface via Switch
The SHDSL.EVB.4CH consists also an Ethernet interface via switch. It cannot be used at the
current development stage. Figure 9 shows the schematic of the Ethernet interface via Switch.
Figure 9: Schematic of Ethernet Interface via Switch
3.5 Power Supply Input
For the power supply a Micro USB connector Type B with standard pin assignment (according
to USB specification) is used. This enables the EVB to utilize a standard 5V USB plug-in power
supply as power source. We recommend using power supply with at least 1000 mA (better:
2000 mA) output current and a cable with low voltage-drop.
As from our tests it is also possible to connect the Micro USB connector to any self-powered
USB host interface with a short and high-quality USB cable.
Beside the Micro USB connector SHDSL.EVB.4CH provides the possibility to use the pin
header X801 spaced 2.54 millimeters (0.1 in) for power supply. Table 4 gives the pin definition.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 15/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
Table 4: Pin Definition of X601
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
+ 5 V (4.7 … 6.0 V)
2
- (Ground)
The pin header X801 is not mounted by default. It is possible to mount it on both PCB sides
getting an adapter or using the SHDSL.EVB.4CH as module.
The Micro USB connector is also usable for data transmission to the processor. In that case
UART emulation provides a serial interface.
3.6 Power Consumption
The power consumption of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board is nearly independent from
the traffic on the line. It is maximum 4,9 W.
Boundary conditions:
•Intel®SHDSL Chipsets (PEF 24628 E)
•Firmware: 3.0-R2563
•Function: CO
•Cable length: 1 m
•Power Back Off inactive
•Power 5 V
Table 5: Power Consumption of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH Evaluation Board with full traffic
1-Channel
Bitrate [Kbps]
per SHDSL line
Power [mA]
Power Consumption [W]
TCPAM
Ethernet active
no connection
630
3,15
auto
no
192
710
3,55
16
yes
512
710
3,55
16
yes
2048
720
3,60
16
yes
5696
740
3,70
32
yes
15288
740
3,70
128
yes
4-Channel
Bitrate [Kbps]
per SHDSL line
Power [mA]
Power Consumption [W]
TCPAM
Ethernet active
no connection
660
3,30
auto
no
192
800
4,00
16
yes
512
800
4,00
16
yes
2048
890
4,45
16
yes
5696
940
4,70
32
yes
15288
940
4,70
128
yes
3.7 Serial Interface (UART)
SHDSL.EVB.4CH features a serial interface (UART) for controlling and monitoring purposes.
The interface is usable in two ways: UART emulation via USB interface and TTL-compatible
interface via connector X601. Both interfaces have the same function and can work
simultaneously.

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 16/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
The pin header X601, also named “UART”, is not mounted by default. It is possible to mount
any 2.54 millimeters (0.1 in) spaced pin header at both sides of the PCB. So, the soldering
pads are usable as an easy test adapter for evaluation or as a module placed on a host board.
Table 6 shows the pin definition of X601.
Table 6: Pin Definition of X601
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
+ 3.3V
2
TX (sending data from SAM4S)
3
RX (receiving data by SAM4S)
4
Ground
3.8 Debug interface
The controlling processor of SHDSL.EVB.4CH is Microchip ATSAM4SD32C. Based on the
powerful ARM®Cortex®-M4 core, the SAM4S series gives improved performance, low power
consumption and an easy to use processor. The processorgives much more performance and
periphery than SHDSL chipset needs. This offers a good basis for the development of own
software.
With the connector X602 (“JTAG”) SHDSL.EVB.4CH provides a compatible interface to
Microchips development and debugging tools. For example, the SAM-ICE™Microchips JTAG
Emulator for ARM®core-based microcontrollers is usable.
X602 is a 2.54 millimeter (0.1 in) spaced pin header. The pin definition is given at Table 7.
Table 7: Pin Definition of X602
Pin Number
Pin Name / Function
1
TCK
2
Ground
3
TDO
4
+ 3.3V
5
TMS
6
Reset (NRST)
7
Not used
8
Not used
9
TDI
10
Ground
3.9 Control and Monitoring Interface
SHDSL.EVB.4CH provides on board software usable for many standard applications. For
configuration and status information, several buttons, switches and LEDs are available. The
following section gives more information.
3.9.1 Buttons
There are two buttons available. The first is the button S601 called “RESET”. Pressing this
button triggers hardware reset of the processor and theSHDSL interface. The software restarts
and makes new initialization of SHDSL.EVB.4CH.
The second button is the button S602 called “ERASE” with two functions. During reset (Reset
button is also pressed) the whole flash memory will be cleared. This is only necessary for
updating a complete firmware image including bootloader for example. A normal firmware
update can be done bythe CLI firmware update procedure. Please see chapter 5.3.5 Firmware
update for further information. During runtime and active BSI mode (DIP switch 3 = 0),
SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 17/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
additional information about software, SHDSL firmware version and SHDSL configuration will
be printed to serial interfaces (UART and USB) if the button “ERASE” is pressed.
Please see Figure 4 for the location of the buttons.
3.9.2 DIP switches
There is a protective tab on top of DIP switch. Please remove it from the DIP switch before first
use. The dual in-line package switch S604 is used for selection of operation mode. If the switch
position is stable for more than four seconds the software will accept the new setting and
reconfigure the SHDSL chipset.
There are five switches available. Table 8 describes the function of the DIP switch called
“MODE”.
Table 8: Function of “MODE” Switch S604
Switch
number
Description
Switch function
1
Device Mode
On: STU-C (Master, CO mode)
Off: STU-R (Slave, CPE mode)
2
Extended Rates
On: Enables extended bitrates (64...15336kbps)
Off: ITU-T standard bitrates (192...5696kbps)
3
User Interface Mode
On: CLI is active (only with SW Packages P3)
Off: BSI is active
4
Line using (LU1)
The number of used SHDSL lines will be defined
LU2
LU1
Number of SHDSL lines
0
0
4 lines (1-4) (normal mode)
0
1
3 lines (1, 2 and 4)
1
0
2 lines (1 and 4)
1
1
1 line (1)
5
Line using (LU2)
SHDSL is a point to point connection. SHDSL interconnections need two different device
modes, called SHDSL Termination Unit Central Office (STU-C) and SHDSL Termination Unit
Remote (STU-R). Switch 1 is usable for device mode selection. Please ensure to switch one
modem to STU-C and the other to STU-R. Otherwise no data transmission will be established.
Beside the standard data rates according to ITU-T G.991.2 [3] Intel®SHDSL Chipset provides
higher (and lower) data rates. Intel®SHDSL Chipset is capable to use about three times higher
transmission speed compared to high speed standard SHDSL connections. The lower bitrates,
for example, match better to ISDN-BRI. Switch 2 selects full performance or compatibility to
other SHDSL equipment. For SHDSL systems with Intel®SHDSL Chipset on both sides Intel®
recommend using the extended bitrates (switch 2 on). For highest interoperability let switch 2
off.
If more than one SHDSL line will be used the datarate settings will be set to all lines. It therefor
follows that the data rate will be a multiple of number of lines and data rate.
Example:
configured data rate: 192 Kbps
number of SHDSL lines: two
complete data rate: 2 x 192 Kbps = 384 Kbps
Note: The test mode configuration via switch number 4 and 5 like at the SHDSL.EVB.1CH is
not supported with SHDSL.EVB.4CH. This configuration can be done by the CLI (chapter 5.3).

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 18/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
3.9.3 Rotary switch (10 pole)
The rotary switch S603 (named “BITRATE”) is used for selection of the bitrates. Table 9 shows
choice of bitrates.
If the switch position is stable for more than 4 seconds the software will accept the new setting
and reconfigure the SHDSL chipset. An established data transmission will be interrupted
during reconfiguration.
Table 9: Selectable Bitrates of SHDSL.EVB.4CH
Switch
position
Extended Rates
(DIP switch 2)
Line probing
Bitrate [Kbps]
PAM
0 (default)
Off
Enabled
192…5696
Auto
1
Off
Disabled
192
16
2
Off
Disabled
384
16
3
Off
Disabled
512
16
4
Off
Disabled
768
16
5
Off
Disabled
1536
16
6
Off
Disabled
2048
16
7
Off
Disabled
2304
32
8
Off
Disabled
3072
32
9
Off
Disabled
5696
32
Switch
position
Extended Rates
(DIP switch 2)
Line probing
Bitrate [Kbps]
PAM
0 (default)
On
Enabled
64…15336
Auto
11
On
Disabled
64*
4
2*
On
Disabled
192*
4
3*
On
Disabled
192*
8
4*
On
Disabled
2496*
4
5*
On
Disabled
5056*
8
6*
On
Disabled
7616*
16
7*
On
Disabled
10176*
32
8*
On
Disabled
12736*
64
9*
On
Disabled
15288*
128
The best choice for most applications is switch position 0 which enables the Power
Measurement Modulation Session (PMMS), also called “Line Probing”. PMMS works like an
automatic mode, in that case SHDSL chipset selects the highest given bitrate for actual noise
floor and loop length. The bitrate differs depending on extended rates that are enabled or not
(see Table 8). The target SNR margin is always set to 6 dB.
3.9.4 Rotary switch (16 pole)
The rotary switch S501 (named “HARDWARE CONFIG”) cannot be used at the current
development stage.
3.9.5 LEDs
Nine LEDs indicating the current state of SHDSL.EVB.4CH. For the location of the LEDs
please have a look at Figure 4 on page 9.
1
The configuration of fixed bitrates in extended rates mode is only possible by SHDSL Master (CO
mode, STU-C). The SHDSL Slave (CPE mode, STU-R) ignores the switch position and always uses
line probing (switch position 0).

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 19/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
The green LED H801 “POWER” indicates that power is connected. This LED is on if the board
is active and off if the SHDSL.EVB.4CH is not powered up.
The four green LEDs H501 - H505 signaling the status of the SHDSL lines. The LED is off if
SHDSL is not active (e.g. during initialization). If the SHDSL chipset is initialized, the LED
blinks slowly (approximately 1Hz). The SHDSL chipset is ready to work and waits for detecting
counterpart station. Once the counterpart station is detected, the training process starts and
the LED blinks faster (approximately 3 Hz). This process takes some seconds and if the
SHDSL chipset can establish a SHDSL link the LED stops blinking.
The state of the Ethernet port is indicated by the green LED H301 and the amber LED H302.
The LEDs are off if the Ethernet PHY hasn’t detected any Ethernet counterpart. The green
LED goes on if an Ethernet link is established. The amber LED starts blinking if data
transmission is active.
The amber blinking LED H505 (“STATE”) shows the normal status of the SHDSL.EVB.4CH. If
the amber LED stops blinking or switch off a software error has occurred. In this case the
software Watchdog will be resetting the board after 30 seconds.
A red LED H506 (“ERROR”) indicates an error state. For normal operation this LED is off. The
LED is on or starts blinking if an error has occurred. The error type will also print to the serial
interface (USB UART emulation and hardware UART).

SHDSL.EVB.4CH User Manual
Revision: 1.0.0, 2019-02-05 20/37 shdsl@teleconnect.de
4Software
4.1 Updating Firmware
The control and monitor processor ATSAM4SD32C supports Microchip SAM Boot Assistance
(SAM-BA), an open set of tools for programming the Microchip ARM®core-based
microcontrollers. This is only necessary for updating a complete firmware image including
bootloader for example. A normal firmware update can be done by the CLI firmware update
procedure. Please see chapter 5.3.5 Firmware update for further information.
The following section provides a guide on how to install the in-system programmer and how to
use it.
4.1.1 Preparation
If you have already installed the SAM-BA programmer, please go to the next section.
Please regard, that to date SAM-BA revision 2.18 is proven to work correctly with the
microcontroller device SAM4S at SHDSL.EVB.4CH. Subject to change without notice.
This is a guide on how to install the in-system programmer on your PC.
1. Download the version 2.18 of SAM-BA in-system programmer from Microchip web
page (http://www.microchip.com). (regard comment above)
2. Install the downloaded software on your PC. Follow the instruction of the installer of
user interface (more info: see "sam-ba user guide.pdf" or "usb_notice.html")
3. Connect the SHDSL.EVB.4CH with a Micro-USB 2.0 cable (USB-Micro-B connector
to USB-A connector) to your PC and clear the whole memory including the firmware
of EVB by pressing "RESET" and "ERASE" button at the same time.
4. Install the driver for the unknown device.
(For Microsoft Windows 10 users this step is not necessary.)
Please select "search for driver software at local computer". The driver is located in
your installation directory "<your SAM-BA installation directory>\drv".
Attention: do not select "automatic search for driver software" (search in the internet).
Select "Install from ATMEL Rousset" trust. After a while the driver software "AT91
USB to Serial Converter" is installed successfully and assigned to a COM port.
For more information please have a look at "<your SAM-BA installation
directory>\doc\usb_notice.html"
If you have installed another revision than 2.18, you may experience errors with the driver.
Or if Windows version (8 or lower) loads another driver version via Windows Update called
The “Bossa Program Port” driver should work for Windows 10.
4.1.2 Using the in-system programmer
Before starting, prepare the new firmware image. You cannot generate it by yourself. Please
use latest firmware image only provided by Teleconnect:
http://www.teleconnect.de/xdsl/socrates-evb
You need the firmware image in *.bin file format.
1. Connect the SHDSL.EVB.4CH to your PC using the micro USB cable.
2. Press both buttons of the EVB (“RESET” and “ERASE”) at the same time. This clears
the whole memory including the firmware of EVB.
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents