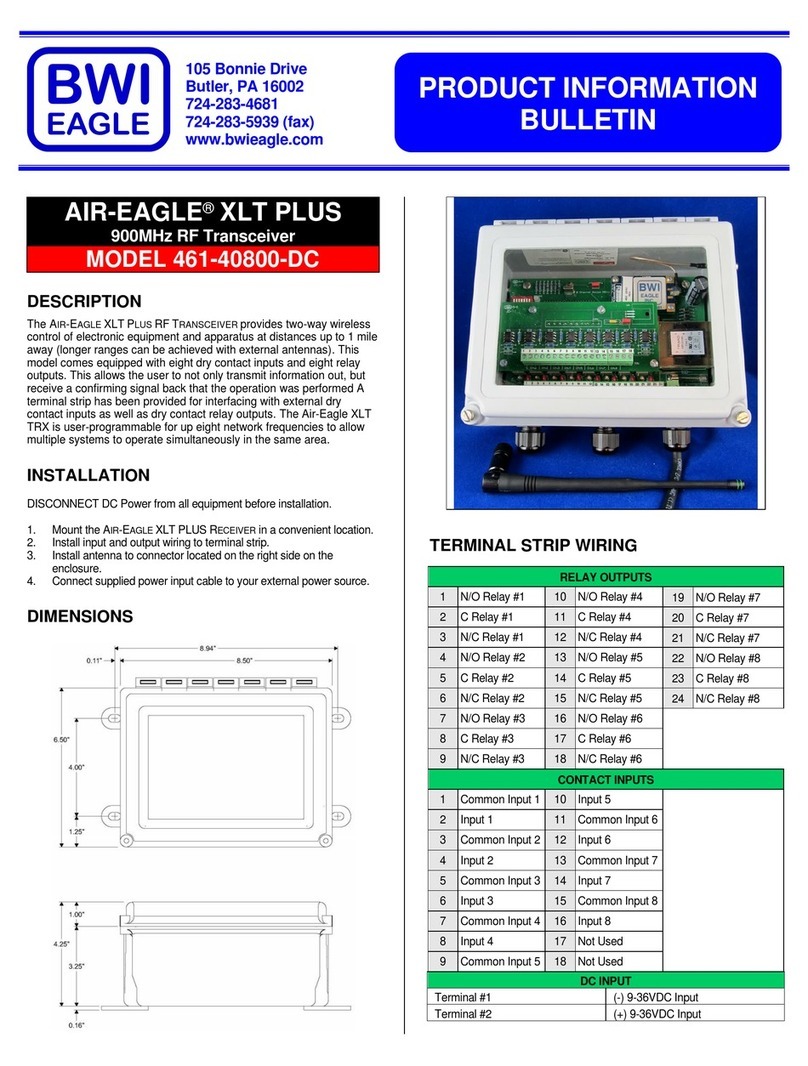
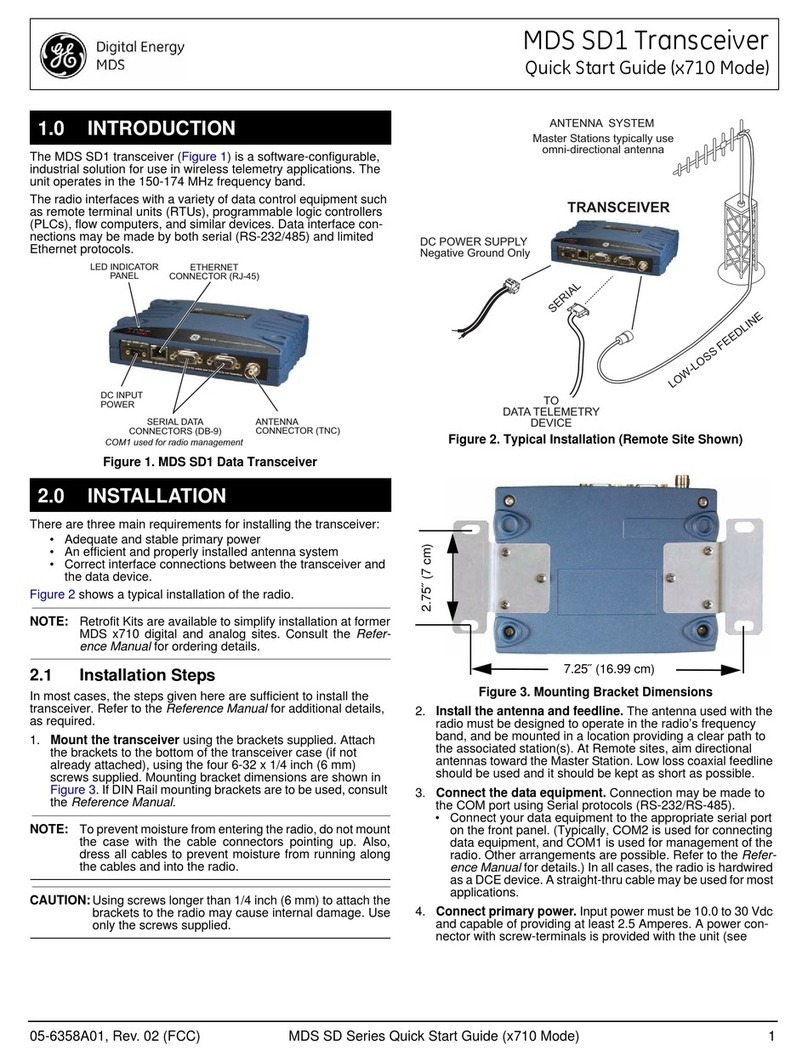
11
Circuit Description
Receive Signal Path
Incoming RF from the antenna jack is delivered to the
RF Unit and passes through a low-pass filter consisting of
coils L1003, L1006, and L1007, capacitors C1002, C1007,
C1013, C1017, C1022, C1025, C1029, and C1169, and
antenna switching diode D1007 (RLS135).
Signals within the frequency range of the transceiver
enter a varactor-tuned band-pass filter consisting of coils
L1014 and L1015, capacitors C1057, C1058, C1064,
C1071, and C1073, and diodes D1012 (HVC355B),
D1013 (HVC355B), D1016 (HVC355B), and D1017
(HVC355B), then are amplified by Q1015 (2SC5006)
and enter a varactor-tuned band-pass filter consisting of
coils L1021 and L1024, capacitors C1084, C1086, C1095,
C1097, and C1248, and diodes D1026 (HVC355B) and
D1027 (HVC355B), before first mixing by first mixer
Q1025 (SGM2016AM).
Buffered output from the VCO is amplified by Q1009
(2SC5005) to provide a pure first local signal between
405.75 and 440.75 MHz for injection to the first mixer
Q1025. The 44.25 MHz first mixer product then passes
through monolithic crystal filter XF1002 (HDF0042, 5.5
kHz BW) to strip away unwanted mixer products, which
is then amplified by Q1032 (2SC4215Y).
The amplified first IF signal is applied to FM IF sub-
system IC Q1036 (TA31136FN), which contains the sec-
ond mixer, second local oscillator, limiter amplifier, noise
amplifier, and RSSI amplifier.
The second local signal is produced from the PLL ref-
erence/second local oscillator of 14.60 MHz crystal X1001.
The 14.60 MHz reference signal is tripled by Q1036, ca-
pacitor C1123, and coil L1005, and the resulting the 43.8
MHz second local signal is then delivered to the mixer
section of Q1036 which produces the 450 kHz second IF
when mixed with the first IF signal.
The second IF then passes through the ceramic filter
CF1001 (ALFYM450F=K on “Wide” channels) or
CF1002 (ALFYM450G=K on “Narrow” channels) to strip
away all but the desired signal, and is then applied to the
limiter amplifier in Q1036, which removes amplitude
variations in the 450 kHz IF, before detection of the speech
by the ceramic discriminator CD1001 (CDBC450CX24).
Detected audio from Q1036 is applied to the audio high-
pass filter, and then passes via the volume control to the
audio amplifier Q1039 (NJM2070M), which provides up
to 1/2 Watt to the optional headphone jack or a 4-ohm
loudspeaker.
Squelch Control
The squelch circuitry consists of a noise amplifier and
band-pass filter within Q1036, and noise detector D1030
(1SS355).
When no carrier is received, noise at the output of the
detector stage in Q1036 is amplified and band-pass fil-
tered by the noise amplifier section of Q1036 and the net-
work between pins 7 and 8, and then is rectified by D1030.
The resulting DC squelch control voltage is passed to
pin 37 of the microprocessor Q1014 (M37516E6HP). If
no carrier is received, this signal causes pin 24 of Q1014
to go high and pin 20 to go high. Pin 24 signals Q1056
(RT1P441U) to disable the supply voltage to the audio
amplifier Q1039, while pin 20 holds the green (Busy) half
of the LED off, when pin 24 is high and pin 20 is high.
Thus, the microprocessor blocks output from the au-
dio amplifier, and silences the receiver, while no signal is
being received (and during transmission, as well).
When a carrier appears at the discriminator, noise is
removed from the output, causing pin 37 of Q1014 to go
low and the microprocessor to activate the “Busy” LED
via Q1014.
The microprocessor then checks for CTCSS or CDCSS
code squelch information, if enabled. If not transmitting
and CTCSS or CDCSS is not activated, or if the received
tone or code matches that programmed, audio is allowed
to pass through the audio amplifier Q1039 (NJM2070M)
to the loudspeaker by the enabling of the supply voltage
to it via Q1037.
Transmit Signal Path
Speech input from the microphone is amplified by
Q1017 (NJM2902V), after pre-emphasis by C1059 and
R1045, the audio is amplified in another section of Q1017.
The processed audio may then be mixed with a CTCSS
tone generated by Q1014 (M37516E6HP) for frequency
modulation of the PLL carrier (up to ±5 kHz from the
unmodulated carrier) at the transmitting frequency.
If a CDCSS code is enabled for transmission, the code
is generated by microprocessor Q1014 (M37516E6HP)
and delivered to D1004 (HVC350B) for CDCSS modu-
lating.
The modulated signal from the VCO Q1005 (2SK508-
K52) is buffered by Q1008 (2SC5005). The low-level
transmit signal then passes through the T/R switching di-
ode D1014 (DAN235E) to the amplifier Q1009
(2SC5005), driver amplifier Q1012 (2SC3357) and
Q1016 (2SK2973), then the amplified transmit signal is
applied to the final amplifier Q1021 (2SK2974), which
delivers up to 5 watts output power.
The transmit signal then passes through the antenna
switch D1007 (RLS135) and is low-pass filtered, to sup-
press harmonic spurious radiation before delivery to the
antenna.