INS Header
A three-pin header labeled INS on the back of the Listen Four allows you to connect another
module as an auxiliary stereo input. Whatever signal is fed into the header will appear on the
outputs without any attenuation. The INS header has pins for the left channel (bottom pin),
right channel (top pin), and ground (center pin). The input impedance is 47k.
A typical use would be to daisy-chain multiple Listen modules to create a mixer with eight or
more channels. To do this, the OUTS header on one module is connected to the INS header
on the other module. See the Daisy-chaining section for details.
Another use would be to connect a 1/4” (6.35mm) adaptor module such as the Listen Up.
This would allow you to use a stereo signal on two 1/4” cables as a fifth stereo input channel.
OUTS Header
A three-pin header labeled OUTS on the back of the module allows you to send the main
output mix to another module with a compatible header. The pin order and pin dimensions of
this header are the same as the INS header (see previous section). The output impedance is
1k. It will not damage the circuitry if the pins are shorted to ground.
The Main Level and Mod/Line switch will effect the level on the OUTS header. If you’re
connecting to another Listen module, it’s recommended to flip the switch to Mod. If you’re
connecting to a 1/4” adaptor module and you require line-level outputs, flip the switch to Line.
The Main Level knob acts as a volume knob. The main outputs and headphone outputs will
still be active and are unaffected by the use of the OUTS header.
Daisy-chaining
Multiple Listen modules can be connected to form
a large mixer. For example, connecting two Listen
Four modules creates an eight channel stereo
mixer: the four inputs of the first Listen Four are
added to the four inputs of the second Listen Four
(see photo on the left).
You can daisy-chain as many modules as you
want. Connecting a Listen Four Quarters after
the two Listen Fours in the example above will
create a 12 channel mixer with 1/4” balanced
outputs, and two sub-mix outputs.
You can also connect a WAV Recorder module to
the end of a chain of Listen modules, allowing you
to record the main outputs without using patch
cables.
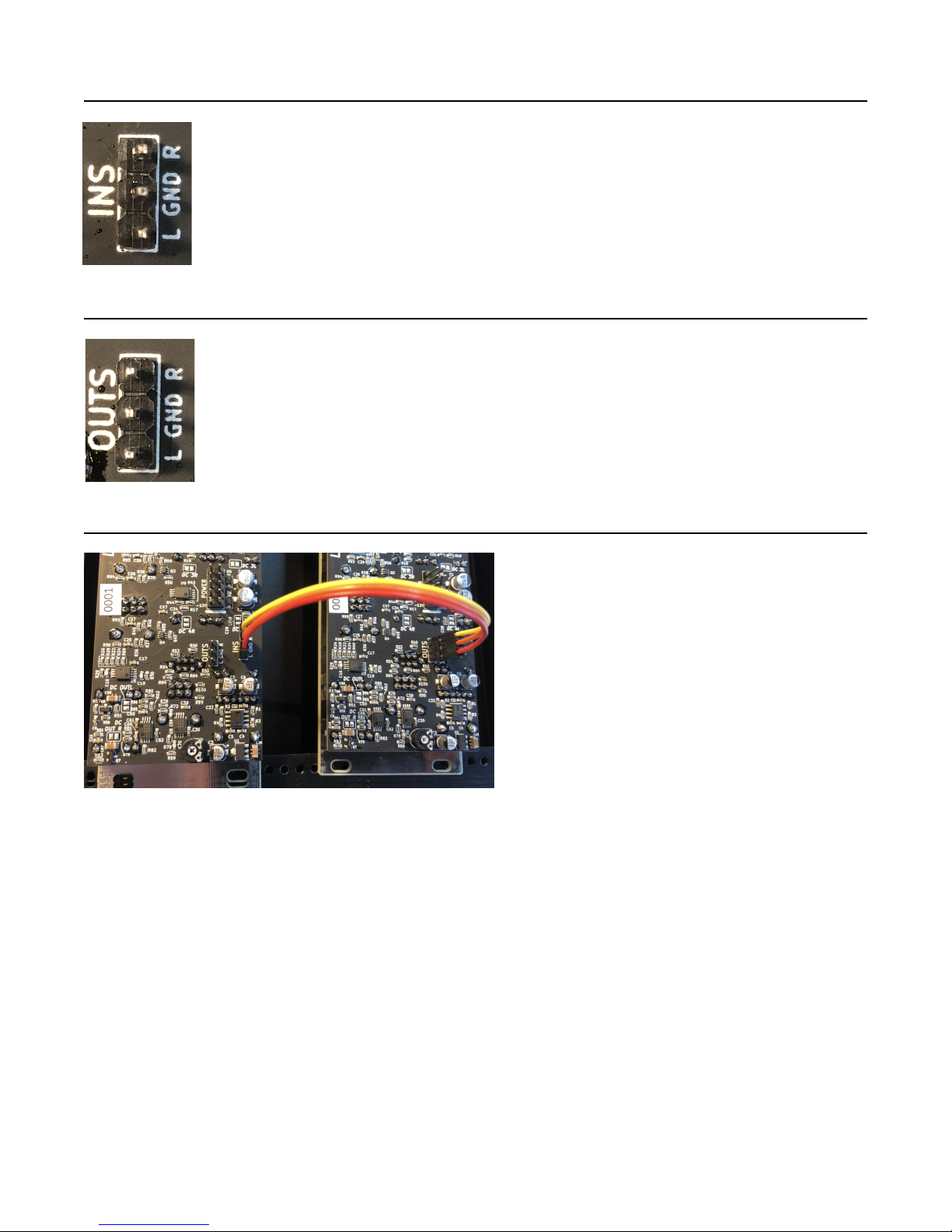
How to Daisy-chain
To daisy-chain two modules, use a 3-pin cable to connect the OUTS header of one module to the INS header of
another. You can continue to connect more modules in the same way, OUTS to INS.
A suitable connecting cable can be purchased from 4ms Company or many of our dealers. You also can find or
create your own cable. The cable must fit a single row of three pins with a pin spacing of 0.1” (2.54mm). The pins
are 0.2” tall (5mm), which is the same spacing, size and length as the pins on standard Eurorack power headers.
Make sure the same color wire is on top on both sides of the connecting cable. If one side is reversed, the left and
right channels will be reversed (though no damage or malfunction will occur).
Main Mixes and Sub-mixes
The Main Level knob controls the level that’s passed to the next Listen module via the OUTS header. By
patching related signals into the same Listen module, you can create sub-mixes with a single knob for level
control.
For example, see the photo above. Two Listen Four modules are connected such that one module’s OUTS
header connects to the other module’s INS header. Let’s say you patch some polyrhythmic drum sounds into the
first Listen Four, and patch some processed field recordings into the second Listen Four. The output jacks on
the second Listen Four will be a mix of everything (the drums and field recordings), and the Main Level knob will
control the overall level. The output jacks on the first Listen Four will be a sub-mix of just the drums, and its Main
Level knob will control just the level of the drums in both the sub-mix and the overall mix.