8 | INSTALLATION
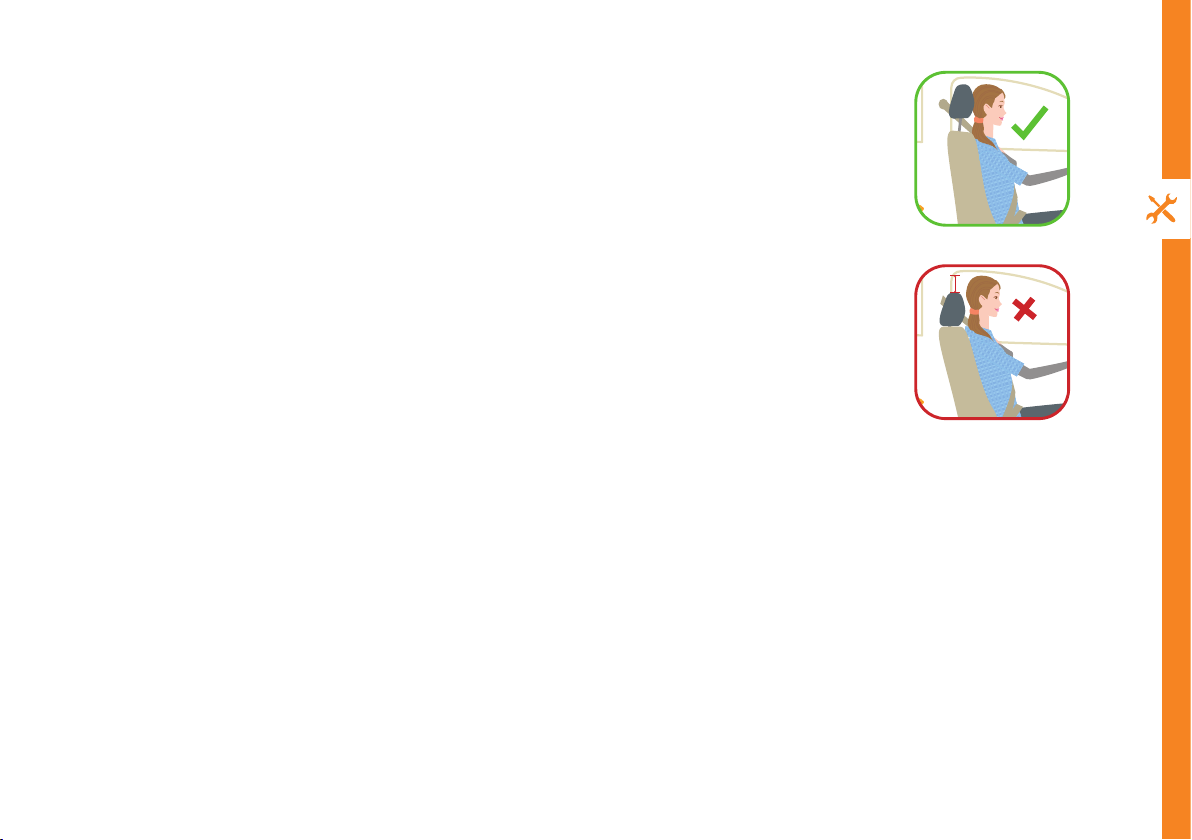
A head restraint is designed to limit the movement of the head and provide support in an
accident. A properly adjusted head restraint will help to protect you against whiplash, and
potentially save you from a long-term injury.
How to adjust your head restraint
Picture 1: This picture shows a well-adjusted head restraint, which will reduce the risk of
suering a whiplash injury.
The seat back angle is relatively upright, and this allows the head restraint to be positioned
close to the back of the head.
The top of the head restraint is level with the top of the occupant’s head, which will also
help to prevent injury.
Picture 2: This picture shows a poorly adjusted head restraint.
Even though the top of the head restraint is level with the top of the occupants head, a
large gap exists between the back of the occupant’s head and the head restraint.
This gap – which is marked in the picture – means that the head can move and tilt further
back, increasing the risk of injury.
Picture 1: A well adjusted head restraint
Picture 2: A poorly adjusted head restraint
PLaceMeNt aNd PositioN