TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION .....................................................................................................5!
1.1 Installing ArKaos GrandVJ –PC......................................................................5!
1.2 Installing ArKaos GrandVJ –MAC...................................................................5!
1.3 Registering ArKaos GrandVJ...........................................................................5!
1.4 Registration process ........................................................................................6!
1.4.1 Activation Code.......................................................................................6!
1.4.2 Serial Key................................................................................................7!
1.4.3 Demo ......................................................................................................7!
2 INTRODUCTION TO THE SOFTWARE..................................................................8!
2.1 Basics ..............................................................................................................8!
2.2 Overview..........................................................................................................8!
2.3 Terminology .....................................................................................................9!
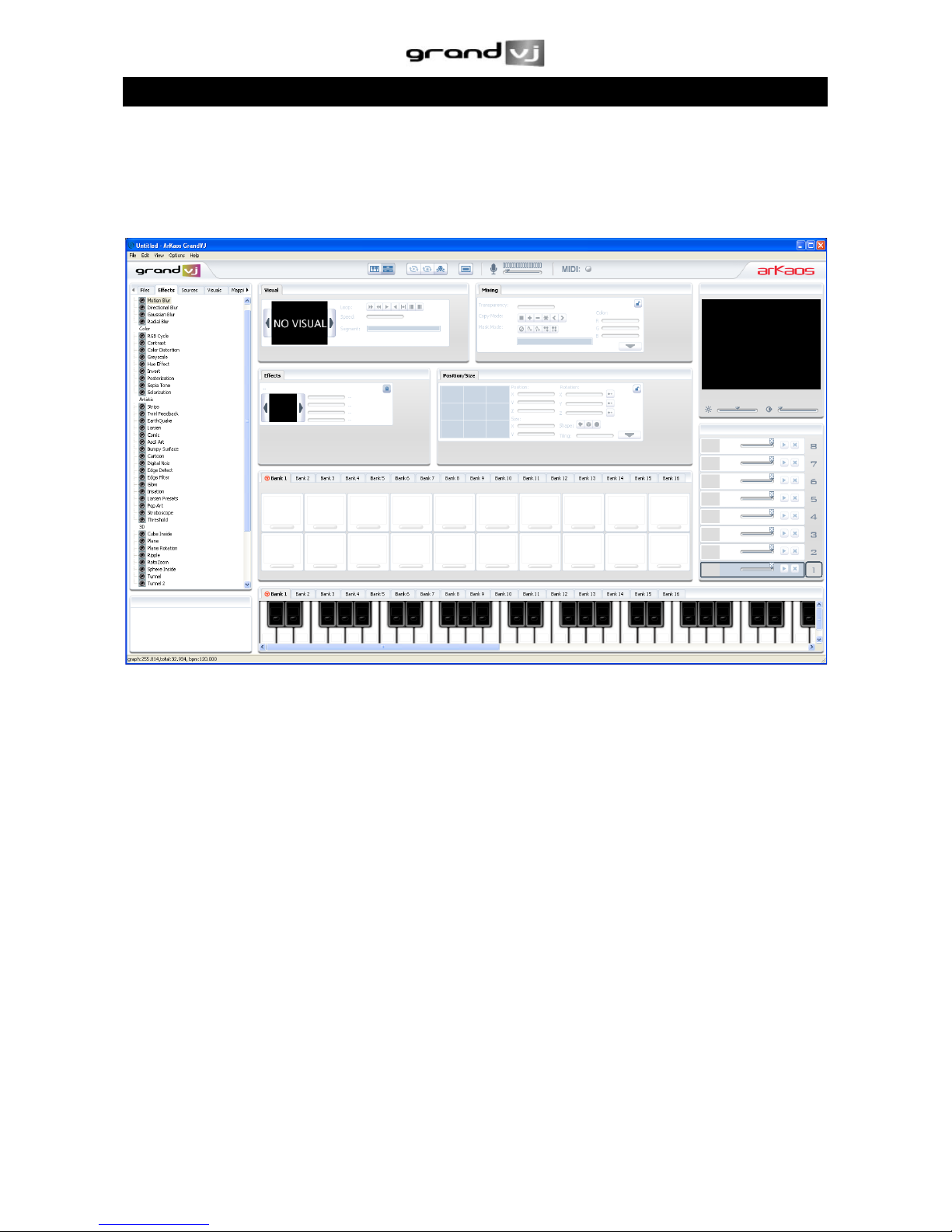
3 INTERFACE WALK-THROUGH............................................................................10!
3.1 Browser Panel ...............................................................................................11!
3.2 Master Preview ..............................................................................................11!
3.3 Banks............................................................................................................12!
3.4 Parameter Panel............................................................................................12!
3.5 Layer Preview (mixer mode only) ..................................................................12!
3.6 Tool bar..........................................................................................................13!
3.7 Help Box ........................................................................................................13!
4 USING THE APPLICATION ..................................................................................14!
4.1 Application Modes .........................................................................................14!
4.1.1 Synth Mode...........................................................................................14!
4.1.2 Mixer Mode ...........................................................................................14!
4.2 Controller Mapping ........................................................................................15!
5 REFERENCE.........................................................................................................16!
5.1 Managing Cells ..............................................................................................16!
5.1.1 Basics ...................................................................................................16!
5.1.2 Triggering and Mapping Cells...............................................................16!
5.1.3 Cell parameters.....................................................................................17!
5.1.4 Cell Parameter Mapping .......................................................................20!
5.1.5 Cell Copy / Paste ..................................................................................20!
5.2 Banks.............................................................................................................21!
5.2.1 Bank Control ........................................................................................21!
5.2.2 Bank Operations ...................................................................................21!
5.3 Layers (Mixer Mode)......................................................................................22!
5.3.1 Layer Previews .....................................................................................22!
5.3.2 Layer Parameters .................................................................................22!
5.3.3 Layer Control ........................................................................................23!
5.4 The Mapping List ...........................................................................................24!
6 THE PREFERENCES DIALOG .............................................................................25!
6.1 Display Tab....................................................................................................25!
6.2 MIDI ...............................................................................................................26!
6.3 Performances ................................................................................................26!
6.4 Output ............................................................................................................27!
6.5 Advanced.......................................................................................................27!
6.6 Registration....................................................................................................27!
7 PERFORMANCE AND SETUP CONSIDERATIONS ............................................28!
7.1 Movie Compression .......................................................................................28!
7.2 Widescreen & Multiscreen Presentation........................................................29!
7.3 Introduction ....................................................................................................29!
7.4 Definitions ......................................................................................................29!
7.4.2 Case Studies.........................................................................................30!
7.4.3 Monitor Setup For Wide Screen Or Multi-Screen Projection ................31!
7.5 Soft-Edge.......................................................................................................37!
7.5.1 Calibration.............................................................................................38!
8 SUPPORT, INFORMATION AND CONTACT .......................................................39!
8.1 Solutions ........................................................................................................39!
8.1.1 Users discussion forum.........................................................................39!
8.1.2 Knowledgebase articles........................................................................39!
8.1.3 Trouble ticket system............................................................................39!
8.1.4 Distributors and resellers ......................................................................39!
9 NOTES ..................................................................................................................40!