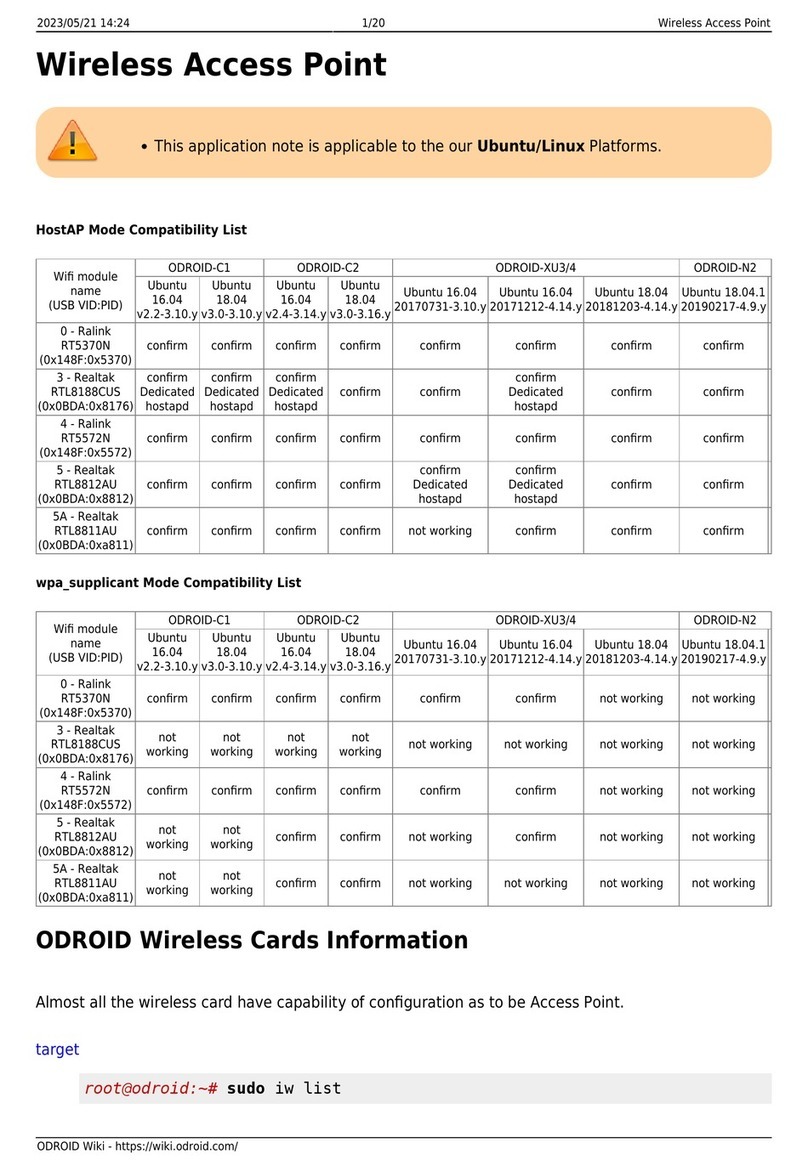
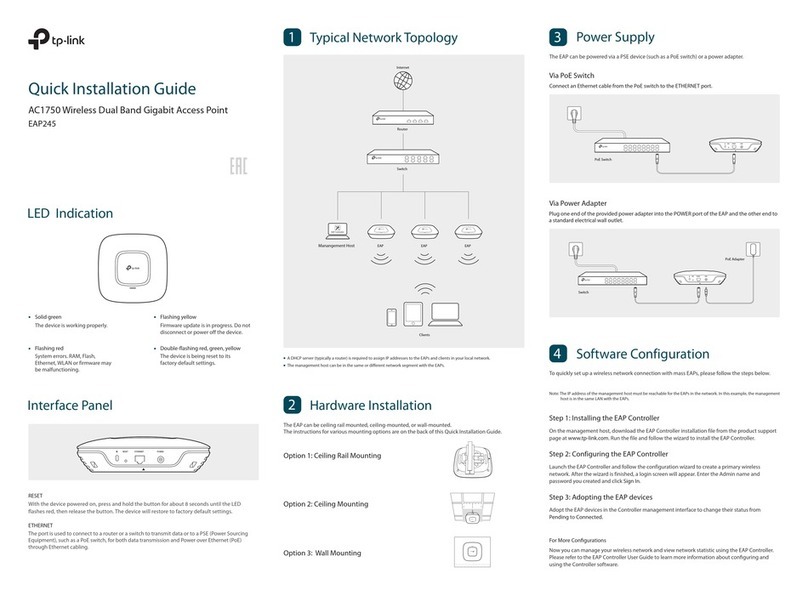
BelAir Networks BelAir 100SN User manual

BelAir100SN
Page 1 of 212
Release: 11.0
Document Date: May 31, 2010
Document Number: BDTM11001-A01
Document Status: Released
Security Status: Confidential
Customer Support: 613-254-7070
1-877-BelAir1 (235-2471)
techsupport@belairnetworks.com
© Copyright 2010 by BelAir Networks.
The information contained in this document is confidential and proprietary to BelAir Networks. Errors and Omissions Excepted.
Specification may be subject to change. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Protected by U.S. Patents: 7,171,223, 7,164,667, 7,154,356, 7,030,712 and D501,195. Patents pending in the U.S. and other countries.
BelAir Networks, the BelAir Logo, BelAir200, BelAir100, BelAir100S, BelAir100C, BelAir100T. BelAir20, BelAir100i, BelAir100SN, BelAir100N, BelView and BelView
NMS are trademarks of BelAir Networks Inc.
BelAir100SN
User Guide

May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 2 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
BelAir100SN User Guide Contents
Contents
About This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Command Line Interface Basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
BelAir100SN Access Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
User and Session Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
IP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
System Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
BelAir100SN Auto-configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Ethernet Interface Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Cable Modem Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Card Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Wi-Fi Radio Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring Wi-Fi Radio Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Configuring Wi-Fi Access Point Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Wi-Fi AP Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Wi-Fi Backhaul Link Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Mobile Backhaul Mesh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Mobile Backhaul Point-to-point Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Operating in High Capacity and Interference Environments. . . . 134
DHCP Relay Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Network Address Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Using Layer 2 Tunnels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Quality of Service Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Layer 2 Network Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Performing a Software Upgrade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
For More Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Technical Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Definitions and Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Appendix A: Node Configuration Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Appendix B: BelAir100SN Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Detailed Table of Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200

BelAir100SN User Guide About This Document
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 3 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
About This Document
This document provides the information you need to install and configure the
BelAir100SN™, and the procedures for using the BelAir100SN Command Line
Interface (CLI).
This document may contain alternate references to the product. Ta b l e 1 shows
possible synonyms to the product name.
Typo gr aph ic a l
Conventions
This document uses the following typographical conventions:
• Text in < > indicates a parameter required as input for a CLI command;
for example, < IP address >
• Text in [ ] indicates optional parameters for a CLI command.
• Text in { } refers to a list of possible entries with | as the separator.
• Parameters in ( ) indicate that at least one of the parameters must entered.
Related
Documentation
The following titles are BelAir reference documents:
•
BelAir100SN Installation Guide
•
BelAir100SN Troubleshooting Guide
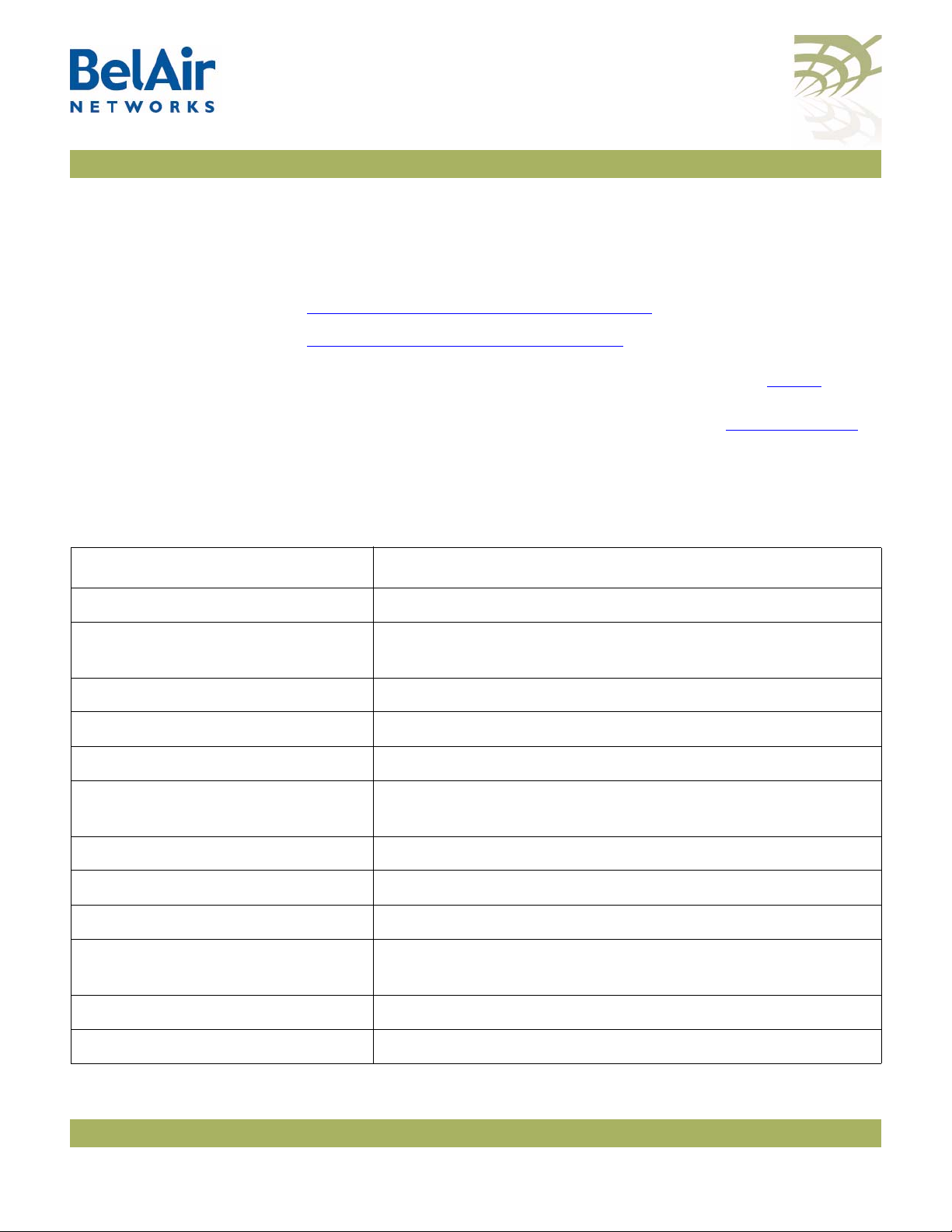
Table 1: Product Name Synonyms
Product Name Synonym
BelAir100SN™ BA100S
BelAir100i™ BA100, BA100T
BelAir20™ BA20

BelAir100SN User Guide System Overview
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 4 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
System Overview
The BelAir100SN is a Wi-Fi access point that meets IEEE 802.11n standards. It
is fully interoperable with existing 802.11a/b/g standards, providing a
transparent, wireless high speed data communication between the wired LAN
and fixed or mobile devices.
The BelAir100SN can operate as a standalone device, or participate in a BelAir
Networks mesh as an edge node or to terminate the mesh.
The 802.11n Wi-Fi radios provide user traffic wireless access to the
BelAir100SN and can form point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, or
multipoint-to-multipoint mesh backhaul links.
All the members of a multipoint-to-multipoint mesh use a proprietary
algorithm based on RSTP to automatically control the creation of loops within
the mesh. This loop management function is fully transparent to customers and
under normal operating conditions, you do not need to modify any settings.
Hardware
Description
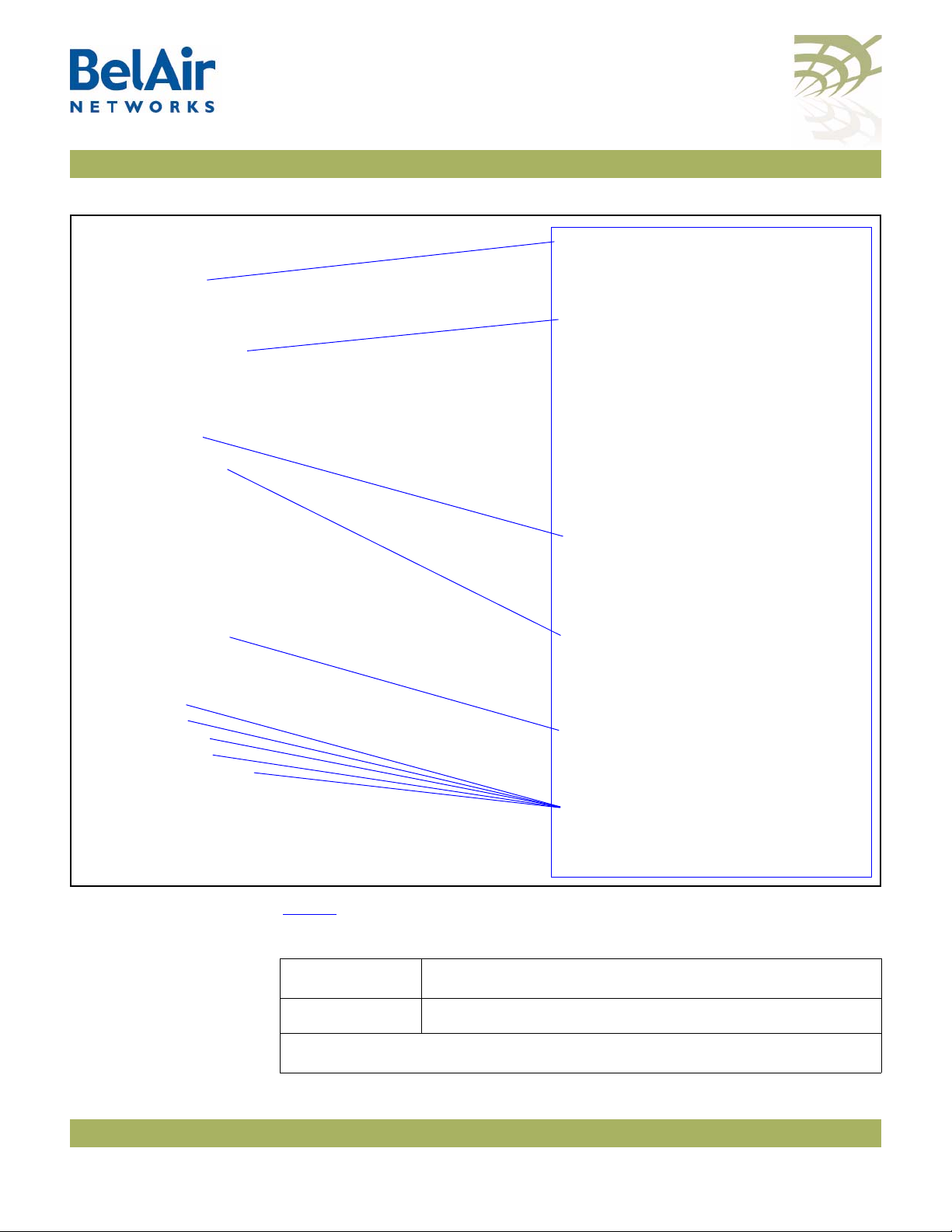
Figure 1 on page 5 shows the relationship between the main BelAir100SN
hardware modules. The BelAir100SN consists of the following modules:
• one Dual Radio Unit (DRU) providing:
—a wireline 10/100/1000 Base-TX Ethernet interface to the Internet
—a 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi radio and a 5 GHz Wi-Fi radio using enhanced
performance links. Each radio can act as an Access Point (AP) or provide
backhaul links. An AP provides user traffic wireless access to the
BelAir100SN. Backhaul links connect to other BelAir radios to create a
radio mesh.
• a Power Protection Module (PPM) providing a wireline DOCSIS interface
and a plant interface for power
• a Cable Modem (CM)
• a Power Supply Unit (PSU)
• external antennas
• one environmental enclosure
• an external connector field
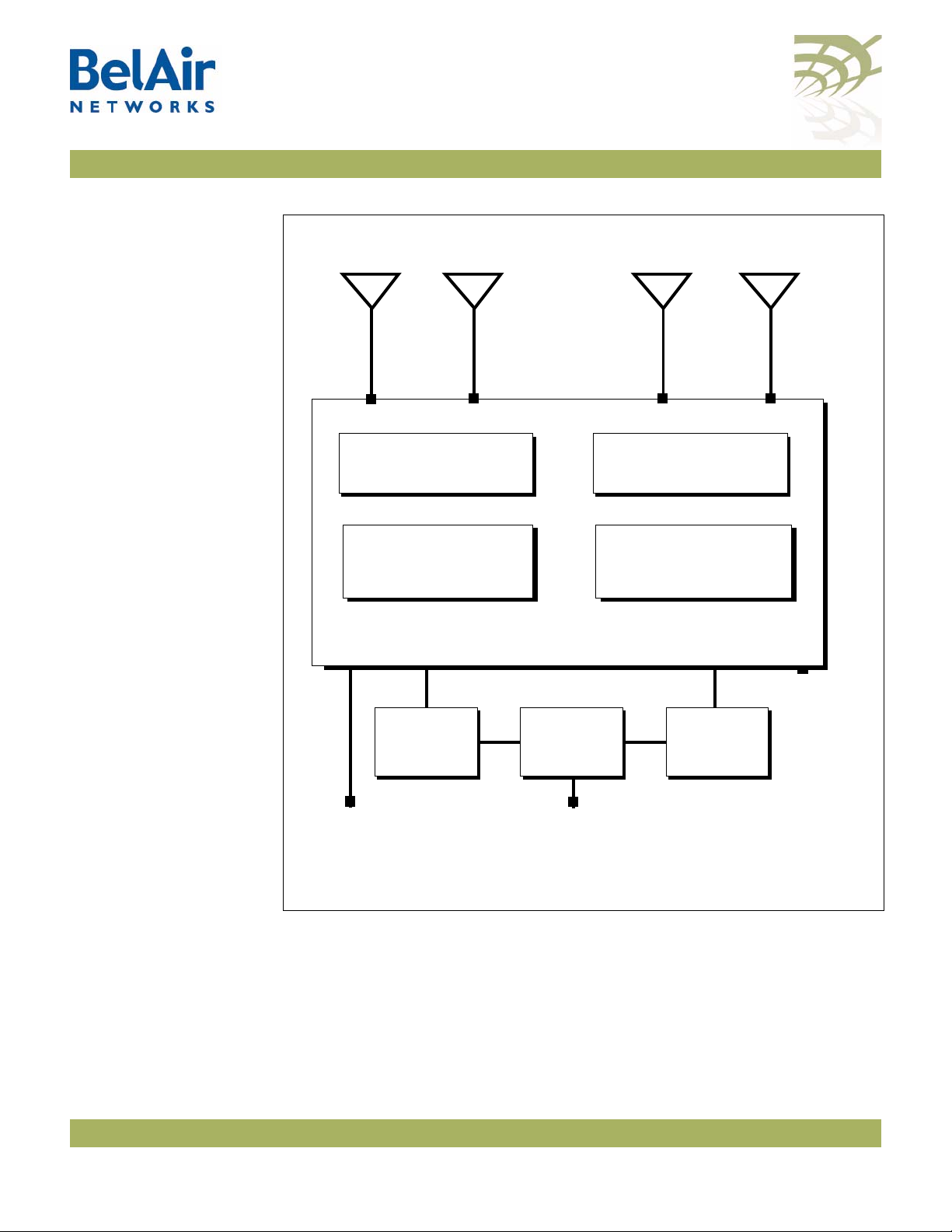
BelAir100SN User Guide System Overview
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 5 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Figure 1: BelAir100SN Hardware Module Block Diagram
Ethernet
10Base-TX
100Base-TX
1000Base-TX
DOCSIS
40 to 87 V
DRU
5 GHz
Radio
Antenna 1 Antenna 3 Antenna 2
2.4 GHz
Radio
Diplexer
Cable
Modem Power
Supply
Unit
Power
Protection
Module
Reset
Antenna 4
Diplexer

BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 6 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
The BelAir100SN can be accessed and configured using the following
configuration interfaces:
• the command line interface (CLI)
• the SNMP interface
• the Web interface (using either HTTPS or HTTP)
All three interfaces (CLI, SNMP and Web) have the same public IP address. All
three also access the same BelAir100SN node database. That means that
changes made with one interface are seen immediately through the other
interfaces.
Command Line
Interface
The CLI allows you to configure and display all the parameters of a
BelAir100SN unit, including:
• system parameters
• system configuration and status
• radio module configuration and status
• user accounts
• BelAir100SN traffic statistics
• layer 2 functionality, such as those related to bridging and VLANs
• Quality of Service parameters
• alarm system configuration and alarms history
Each unit can have up to nine simultaneous CLI sessions (Telnet or SSH). For a
description of basic CLI commands and tasks see “Command Line Interface
Basics” on page 12.
SNMP Interface The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a means of
communication between SNMP managers and SNMP agents. The SNMP
manager is typically a part of a network management system (NMS) such as HP
OpenView, while the BelAir100SN provides the services of an SNMP agent.
Configuring the BelAir100SN SNMP agent means configuring the SNMP
parameters to establish a relationship between the manager and the agent.
BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 7 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
The BelAir100SN SNMP agent contains Management Information Base (MIB)
variables. A manager can query an agent for the value of MIB variables, or
request the agent to change the value of a MIB variable.
Refer to the following sections:
•“SNMP Configuration Guidelines” on page 27
•“SNMP Command Reference” on page 28
Integrating the
BelAir100SN with a
Pre-deployed NMS
In addition to providing support for the SNMP MIBs described in Table 2 , BelAir
Networks provides a number of enterprise MIB definitions that you can
integrate with your Network Management System (NMS). Table 3 on page 8
describes the BelAir100SN SNMP MIBs. A copy of the BelAir100SN SNMP
MIBs is available from the BelAir Networks online support center at:
www.belairnetworks.com/support/index.cfm.
Table 2: Standard SNMP MIBs
File Name Description
BRIDGE-MIB.mib implements RFC1493
IANAifType-MIB.mib defines standard interface types assigned by the Internet
Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
IEEE802dot11-MIB.mib IEEE MIB to manage 802.11 devices
IF-MIB.mib implements RFC2863
IP-MIB.mib defines IP and ICMO data types
PerfHist-TC-MIB.mib defines data types to support 15-minute performance history
counts
RADIUS-ACC-CLIENT-MIB.mib implements RFC2620
RADIUS-AUTH-CLIENT-MIB.mib implements RFC2618
RSTP-MIB.mib implements 802.1w RSTP
SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB.mib defines data types to support co-existence between SNMP
versions
SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB.mib implements RFC3411
SNMP-MPD-MIB.mib implements RFC3412
BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 8 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB.mib implements RFC3413
SNMP-TARGET-MIB.mib implements RFC3413
SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB.mib implements RFC3414
SNMPv2-CONF.mib implements RFC1450
SNMPv2-MIB.mib implements RFC1907
SNMPv2-SMI.mib implements RFC1450
SNMPv2-TC.mib implements RFC1450
SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM-MIB.mib implements RFC3415
Table 3: BelAir Enterprise MIBs
File Name Description
BELAIR-CABLE-MODEM.mib
BELAIR-CM-OEM.mib
defines DOCSIS cable modem data types
BELAIR-IEEE802DOT11-CLIENT.mib
BELAIR-IEEE802DOT11.mib
defines features that are not supported by the standard
IEEE802.11 MIB
BELAIR-IP.mib defines BelAir IP data types
BELAIR-MESH.mib defines BelAir multipoint-to-multipoint data types
BELAIR-MOBILITY.mib defines data types to support mobile backhaul mesh and
point-to-point links
BELAIR-PHYIF-MAPPING.mib defines data types to support universal slots
BELAIR-PRODUCTS.mib defines product object IDs
BELAIR-RSTP.mib defines RSTP data types
BELAIR-SMI.mib defines BelAir top level OID tree
BELAIR-SYSTEM.mib defines basic OAM features such as software download,
temperature and BelAir alarms
Table 2: Standard SNMP MIBs (Continued)
File Name Description

BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 9 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
The procedure for importing the SNMP MIB definition files depends on the
deployed NMS platform. Refer to your NMS platform documentation for
details.
Web Interface BelAir Networks has verified that the BelAir100SN Web interface operates
correctly with the following web browsers:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0, service pack 2
• Mozilla Firefox version 1.5, or later
Accessing the Web
Interface You can access the Web interface using either secure HTTP (HTTPS) or HTTP.
Both HTTP and HTTPS are enabled when each BelAir100SN node is shipped.
Each unit can have up to five simultaneous CLI sessions (HTTP or HTTPS).
By default, the BelAir100SN Web interface has an associated time-out value. If
the interface is inactive for 9 minutes, then you are disconnected from the
interface. To reconnect to the interface, you need to log in again.
Accessing the System
Page with Secure HTTP
or with HTTP
To log in to the BelAir100SN Web interface and access the main page using
HTTPS or HTTP, do the following steps:
1 Open your Web browser and specify the IP address of the BelAir100SN
node you want to access.
The default IP address of each BelAir100SN node is: 10.1.1.10.
Figure 2 shows the resulting Login page.
BELAIR-TC.mib defines BelAir data types
BELAIR-TUNNEL.mib defines L2TP data types
BELAIR-WRM.mib defines BelAir WiMAX data types
Table 3: BelAir Enterprise MIBs (Continued)
File Name Description

BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 10 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Figure 2: Typical Login Page
2 Enter a valid user name, such as root, and a valid password.
Note:The specified password is case sensitive.
Figure 3 on page 10 shows a typical resulting main page for the Web
interface.
Figure 3: Typical Web Interface Main Page

BelAir100SN User Guide BelAir100SN Configuration Interfaces
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 11 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Stopping a Session To stop a Web interface session, click on the Logout button located in the top
right corner each page. See Figure 3.
Additional
Troubleshooting Tools The Web interface provides the following tools to display radio performance
metrics:
• a throughput meter
• histogram display of various performance metrics
These tools are only available with the Web interface. For full details, see the
BelAir100SN Troubleshooting Guide
.

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 12 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Command Line Interface Basics
Use this chapter to familiarize yourself with basic CLI tasks, including:
•“Connecting to the BelAir100SN” on page 12
•“Starting a CLI Session” on page 13
•“Command Modes” on page 14
•“Abbreviating Commands ” on page 18
•“Command History” on page 18
•“Special CLI Keys ” on page 18
•“Help Command” on page 19
•“Common CLI Commands” on page 22
In addition, “Saving and Restoring the BelAir100SN Configuration” on page 53
contains a detailed procedure on how to do that task.
Connecting to the
BelAir100SN
You can connect to the BelAir100SN default address using one of the following
methods:
• through the BelAir100SN radio interface
• by connecting directly to the Ethernet port on the BelAir100SN
• by connecting through the cable modem
CAUTION! Do not connect the BelAir100SN to an operational data network before you
configure its desired IP network parameters. This may cause traffic disruptions
due to potentially duplicated IP addresses.
The BelAir100SN unit must connect to an isolated LAN, or to a desktop or
laptop PC configured to communicate on the same IP sub-network as the
BelAir100SN.
Using the Radio Interface
Use a desktop or laptop PC equipped with a wireless 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g
or 802.11n compliant interface as required, configured with a static IP address
on the same subnet as the default OAM IP address (for example, 10.1.1.1/24).
For the required configuration procedure, refer to your PC and wireless
interface configuration manuals or contact your network administrator. The PC
will connect to the BelAir100SN through the radio interface.
Connecting to the Ethernet Port
Use a cross-connect RJ45 cable to connect the Ethernet port of the unit.

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 13 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Using the Cable Modem
The MAC address for the unit’s cable modem should have been supplied to
your System Administrator when the unit was installed so that an IP address
could be assigned to it. Contact your system administrator to determine the IP
address to use.
For a detailed procedure, refer to the
BelAir100SN Installation Guide
.
Starting a CLI
Session
Start a Telnet or secure shell (SSH) client and connect to the BelAir100SN IP
address. If you are configuring the BelAir100SN for the first time, you must use
the BelAir100SN default IP address (10.1.1.10). The BelAir100SN prompts you
for your user name and password.
The default super-user account is “root”. The default password is “admin123”.
If the login is successful, the BelAir100SN prompt is displayed. The default
prompt is “#”, if you login as root. Otherwise, the default prompt string is “>”.
Note 1: The terminal session locks after four unsuccessful login attempts. To
unlock the terminal session, you must enter the super-user password.
Note 2: BelAir100SN CLI commands are not case sensitive (uppercase and
lowercase characters are equivalent). However, some command
parameters are case sensitive. For example, passwords and any Service
Set Identifier (SSID) supplied with the
radio
commands are case
sensitive. Also, all parameters of the
syscmd
commands are case
sensitive.
Note 3: Later, you will see that you can configure the BelAir100SN to have
more than one interface with an IP address. For example, you can
configure Virtual LANs and management interfaces each with their
own IP address. If you do this, make sure your Telnet or secure shell
(SSH) connections are to a management interface. This ensures
maximum responsiveness for your session by keeping higher priority
management IP traffic separate from other IP traffic.

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 14 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
SSH Session Example of Initial Login
With secure shell, the system prompts you twice for your password.
ssh -l root 10.1.1.10
BelAir Backhaul and Access Wireless Router
BelAir User: root
Password:
/#
Telnet Session Example of Initial Login
With Telnet, the system prompts you only once for your password.
telnet 10.1.1.10
BelAir Backhaul and Access Wireless Router
BelAir User: root
Password:
/#
Command Modes The BelAir100SN CLI has different configuration “modes”. Different commands
are available to you, depending on the selected mode.
Each card in the BelAir100SN has at least one associated physical interface.
Some examples of physical interfaces are a Wi-Fi radio or an Ethernet interface.
Use the
mode
command to display the modes that are available. Because each
physical interface and each card in the BelAir100SN has its own mode,
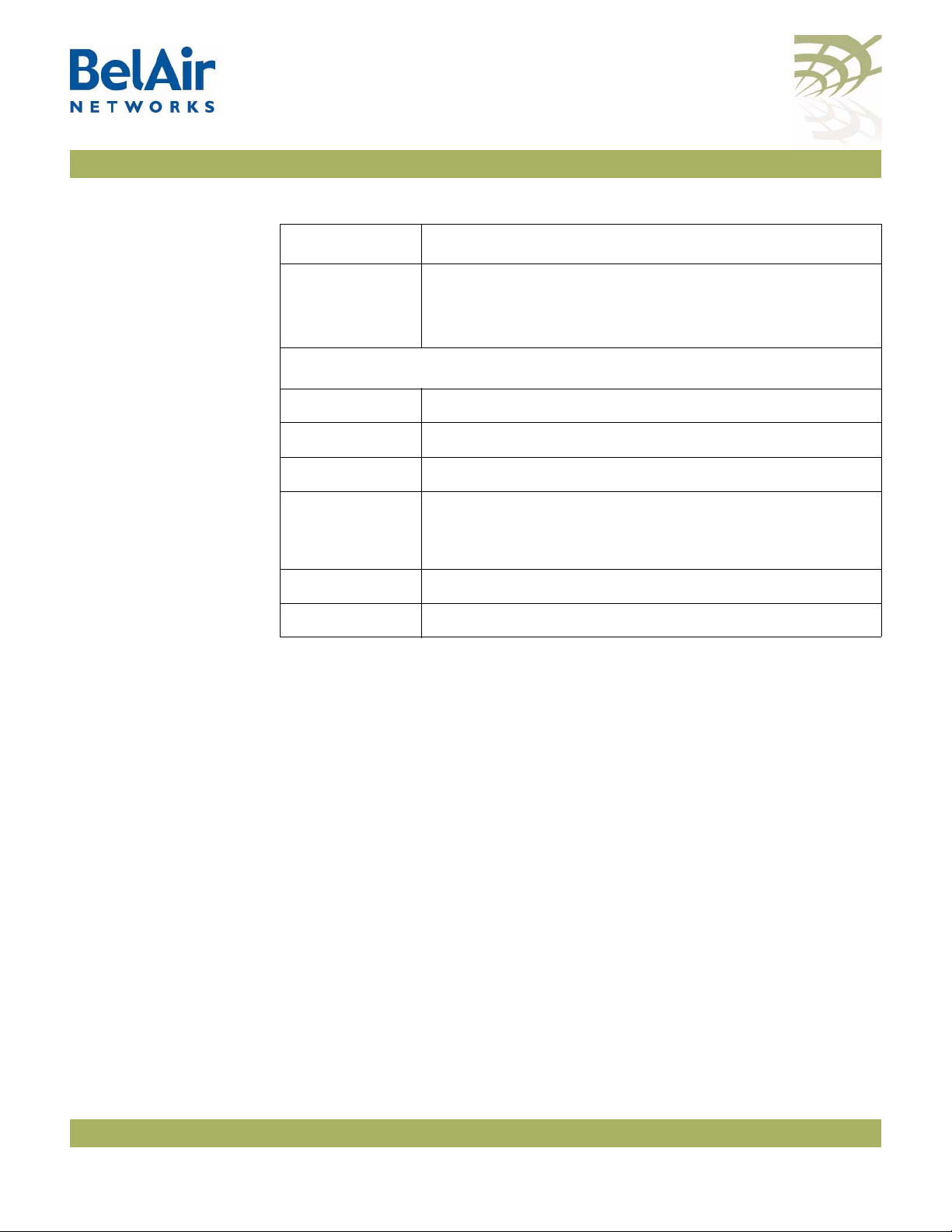
displaying the modes also displays a profile summary of the BelAir100SN. See
Figure 4.
BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 15 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Figure 4: Sample Output of mode Command
Table 4 describes the modes that are supported.
/# mode
/card
/dru-1
/cm-9
/interface
/wifi-1-1 (DRUv1 2.4GHz 802.11n)
/wifi-2-1 (DRUv1 5GHz 802.11n)
/eth-1-1 (1x1000baseTx [Electrical: Single])
/mgmt
/protocol
/ip
/radius
/rstp
/snmp
/sntp
/te-syst (tunnel)
/qos
/services
/auto-conn
/mobility
/ssh
/ssl
/syslog
/system
/diagnostics
• The node has two cards. The DRU
card is in slot 1. The Cable Modem
(CM) is in slot 9.
• The node has three physical
interfaces:
—Interface
wifi-1-1
is associated
with the DRU 2.4 GHz radio.
—Interface
wifi-2-1
is associated
with the DRU 5 GHz radio.
—Interface
eth-1-1
is associated the
DRU card’s Ethernet interface.
• The
mgmt
mode allows you to
control user accounts, which
authentication to use, and whether
you can access the node with Telnet.
• You can control the IP, RADIUS,
RSTP, SNMP, SNTP and L2TP
protocols through the
protocol
mode and its submodes.
• You can control auto-connect and
backhaul mobility through the
services
mode and its submodes.
• These modes allow you to control
SSH, SSL, Syslog and system settings.
You can also run diagnostics.
Table 4: Command Line Interface Modes
Mode Description
“root” mode (/) The top or root level of the CLI commands.
Card Management: /card/<card_type>-<n>

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 16 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
one of:
•dru-<n>
•cm-<n>
Configure hardware:
•
dru
is Dual Radio Unit
•
cm
is Cable Modem
•<n>isslotnumber
Physical Interfaces: /interface/<iface>-<n>-<m>
one of:
• wifi-<n>-<m>
• eth-<n>-<m>
Configure the BelAir100SN physical interfaces:
• <iface> is the type of physical interface. One of:
—
wifi
: 802.11a/b/g/n, DRU, radios
—
eth
: 1000Base-TX DRU electrical Ethernet
•<n>istheslotnumberwhere the interface is located
in the BelAir platform
• <m> is port number. <m> is 1 for most interfaces.The
DRU card can have multiple ports representing
multiple Wi-Fi radios operating different frequencies.
Some configurations may have multiple Ethernet ports.
Node Management
mgmt • Configure user accounts, user authentication and
Te l n e t a c c e s s
Protocol Management: /protocol/<protocol>
one of:
•ip
•nat
•radius
•rstp
• snmp
• sntp
• te-<eng>
Configure the following protocols:
• IP parameters for node and VLANs
•NAT
• RADIUS for user sessions
•RSTP
• SNMP
•SNTP
• L2TP tunnel engine (te). BelAir platforms can have one
tunnel engine per system (syst).
Services: /services/<service>
Table 4: Command Line Interface Modes (Continued)
Mode Description
BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 17 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
You can move between modes with the
cd
command. For instance, you can
move from
root
mode to
system
mode using the command:
/# cd /system
/system#
Note 1: The prompt changes to match the current mode. You can further
customize the prompt to show the switch name or a 20-character
string that you define.
Note 2: Access to a mode is only allowed if the user has sufficient privileges to
execute commands in that mode.
When you access a given mode, only the commands pertaining to that mode
are available. For example, accessing
snmp
mode provides access to SNMP
commands. For a physical interface, this means that only the commands that
apply to that specific type and version of interface are available when you access
a particular physical interface. For example, if you access an DRU interface, only
the commands that apply to an DRU Wi-Fi radio are available.
Entering
?
displays the commands that apply to the currently accessed mode.
Entering
??
or
help
displays the commands that apply to the currently accessed
mode plus common commands that are available in all modes.
one of:
• auto-conn
• mobility
Configure the following services:
• Auto-configuration
•Backhaulmobility
Administration
qos Configure Quality of Service (QoS) parameters
ssh Configure Secure Shell (SSH) parameters
ssl Configure Secure Socket Layer (SSL) parameters
syslog Configure the destination of SYSLOG messages
See the
BelAir100SN Troubleshooting Guide
for details.
system System and node configuration and administration
diagnostics Run link diagnostics.
Table 4: Command Line Interface Modes (Continued)
Mode Description

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 18 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
Users may execute commands from other modes than the current one, by
prefixing the desired command with the slash character ‘/’ followed by the
mode’s name. For instance, entering:
/system# /protocol/snmp/show community
executes a command from
snmp
mode while in
system
mode.
Abbreviating
Commands
You must enter only enough characters for the CLI to recognize the command
as unique.
The following example shows how to enter the
mgmt
mode command
show
telnet status
:
/mgmt# sh t s
Command
History
You can use the
history
command to display a list of the last commands that
you have typed.
Example
/# history
8 h
9 hi
10 ?
11 show user
12 cd /system
13 show loads
14 show sessions
15 cd /
16 cd interface/wifi-1-1/
17 ?
18 show
19 show ssid table
20 show statistics
21 history
Special CLI Keys Command Completion
You can ask the CLI to complete a partially typed command or mode name by
pressing the
tab
key. If the command or mode name cannot be completed
unambiguously, the CLI presents you with a list of possible completions. For
instance, entering:
/system# show co{tab}
produces the following output:
Available commands :
show communications
show config-download status

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 19 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
show coordinates
show country [detail]
Execution of the Last Typed Command
You may repeat the last command, by entering the
!
key twice, followed by
carriage return.
Executing the Previous Commands
You may browse through the command history by using the up and down arrow
keys of a VT100 or compatible terminal. You can also execute a certain
command from the command history by entering the
!
key, followed by the
command number (as displayed in the
history
command output) and carriage
return.
Help Command ?
?? [<command>]
help [<command>]
These commands display:
• a list of commands available in the current mode
• help on a particular command available in the current mode
• help on commands starting with the given keyword in the current mode
Entering "??" is equivalent to entering "help".
Available Commands
Entering
?
displays the commands that apply to the currently accessed mode.
For example:
/mgmt# ?
Available commands :
adduser <user-name> -p <passwd> [ -d <default-mode>] [-g <grp-name>]
deluser <user-name>
moduser <user-name> [ -p <passwd>] [ -d <default-mode>] [-g <grp-name>]
set authentication-login {local | radius <list>}
set telnet {enabled|disabled}
show authentication-login
show telnet status
show user
Entering
??
or
help
displays the commands that apply to the currently accessed
mode plus common commands that are available in all modes. For example:
/mgmt# ??
Available commands :

BelAir100SN User Guide Command Line Interface Basics
May 31, 2010 Confidential Page 20 of 212
Document Number BDTM11001-A01 Released
adduser <user-name> -p <passwd> [ -d <default-mode>] [-g <grp-name>]
deluser <user-name>
moduser <user-name> [ -p <passwd>] [ -d <default-mode>] [-g <grp-name>]
set authentication-login {local | radius <list>}
set telnet {enabled|disabled}
show authentication-login
show telnet status
show user
alias [<replacement string> <token to be replaced>]
cd <path>
clear-screen
console lock
exit
help [ command ]
history
mode [<mode_name>]
passwd
ping <ip addr> [-l <size>]
run script <script file> [<output file>]
version
whoami
config-save [{active|backup} remoteip <server> remotefile <filename>
[{tftp | ftp [user <username> password <password>]}]]
config-restore remoteip <ipaddress> remotefile <filename> [{tftp | ftp
[user <username> password <password>]}] [force]
show date
su <username>
Keyword Help
Entering
??
or
help
followed by a keyword displays all possible commands
starting with that keyword. For example:
/mgmt# ?? show
Available commands :
show authentication-login
Description : show authentication login status and RADIUS servers
configuration
show telnet status
Description : shows the status of the telnet.
show user
Description : List all valid users, along with their permissible mode.
show date
Description : show current system date and time
Help for a Specific Command
When help is needed for a specific command, enter
??
or
help
followed by the
command within quotes. For example:
/mgmt# help "adduser"
Available commands :
adduser <user-name> -p <passwd> [ -d <default-mode>] [-g <grp-name>]
Description : Create a user.
Table of contents
Popular Wireless Access Point manuals by other brands

Cisco
Cisco Aironet 1250 Series Hardware installation guide

H3C
H3C WA2110-AG installation guide

D-Link
D-Link DWL-7130AP - xStack - Wireless Access Point Quick installation guide
NETGEAR
NETGEAR WAX220 user manual

Cisco
Cisco AIR-LMC352 Ordering guide

Alcatel-Lucent
Alcatel-Lucent OAW-AP120 Series installation guide