BOSSCO TIG 200HF User manual

MODEL
•BOSS TIG 160HF
•BOSS TIG 200HF
Operating Manual
(Owner’s Manual)
IMPORTANT: Read these instructions before installing, operating, or servicing this system.
First Edition
September, 2008Manual No. B0807
-1 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
CONTENTS
SYMBOL LEGEND---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2
STATEMENT OF WARRANTY------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION-------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
1.01 Notes, Cautions and Warnings------------------------------------------------------------------------4
1.02 Important Safety Precautions--------------------------------------------------------------------------4
1.03 Transporting methods-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------6
2.0 INSTALLATION RECOMMENDATION----------------------------------------------------------------7
2.01 Electrical Input Connections---------------------------------------------------------------------------8
2.02 Specifications--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
2.03 Duty cycle-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
3.0 OPERATOR CONTROLS-------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
3.01 TIG HF Series controls--------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
3.02 Weld parameter description--------------------------------------------------------------------------13
3.03 Weld parameters for TIG HF series----------------------------------------------------------------13
4.0 SET-UP FOR MMA(STICK) AND GTAW (TIG)----------------------------------------------------14
4.01 Stick welding---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15
4.02 DC TIG welding-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15
4.03 DC pulse TIG welding---------------------------------------------------------------------------------15
5.0 POWER SUPPLY CONTROLS INDICATORS AND REATURES-----------------------------16
6.0 BASIC TIG WELDING GUIDE--------------------------------------------------------------------------17
6.01 Electrode Polarity---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------17
6.02 Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges---------------------------------------------------------------17
6.03 Tungsten Electrode Types----------------------------------------------------------------------------17
6.04 Guide for Selecting Filler Wire Diameter----------------------------------------------------------17
6.05 Shielding gas selection--------------------------------------------------------------------------------18
6.06 TIG welding parameters for low carbon & low alloy steel pipe-------------------------------18
6.07 Welding parameters for steel------------------------------------------------------------------------18
7.0 BASIC ARC WELDING GUIDE------------------------------------------------------------------------19
7.01 Electrode polarity---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
7.02 Effects of stick welding various materials---------------------------------------------------------19
8.0 MAINTENANCE--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------20
9.0 BASIC TROUBLESHOOTING-------------------------------------------------------------------------20
9.01 Check the item and excrescent phenomenon exclusion method---------------------------20
9.02 TIG welding problems---------------------------------------------------------------------------------22
9.03 Stick welding problems--------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
9.04 Power source problems-------------------------------------------------------------------------------24
10.0 PARTS LIST-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------25
11.0 REMARK-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
-2 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
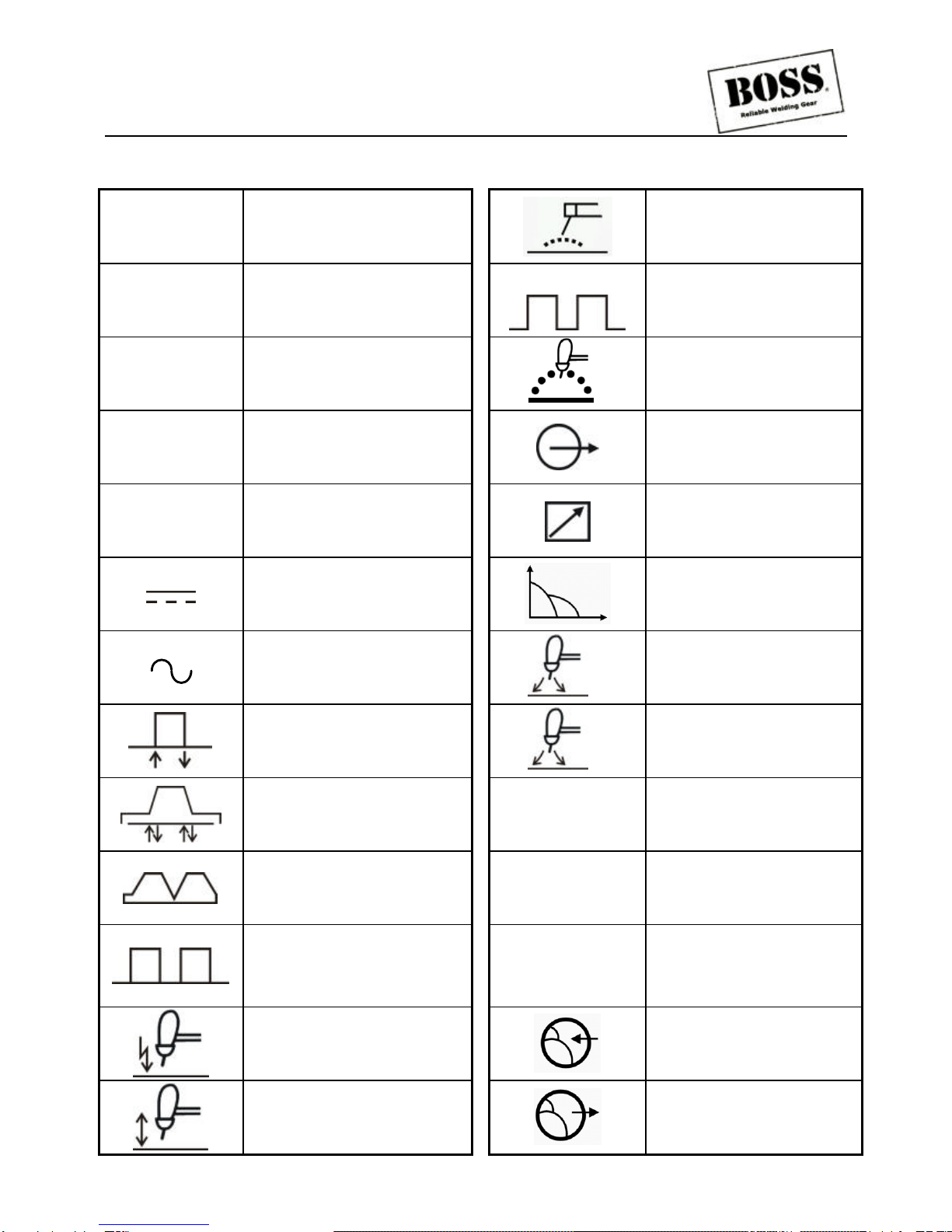
SYMBOL LEGEND
AAmperage
Stick (SMAW)
VVoltage
Pulse Current Function
(GTAW)
Hz Hertz (frequency)
tSpot Time (GTAW)
SEC Seconds
Remote outputs control
(Panel/Remote)
%Percent
Remote Function
DC (Direct Current)
Arc Control (SMAW)
AC (Alternating Current)
t
2Gas Post-Flow Time
2T (GTAW)
t1Gas Pre-Flow Time
4T (GTAW)
VRD Voltage Reduction
Device Circuit
Repeat Function (GTAW)
—Negative
Spot Function (GTAW)
+Positive
High Frequency Starting
(GTAW)
Gas Input
Lift Start (GTAW)
Gas Output

-3 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
STATEMENT OF WARRANTY
LIMITED WARRANTY: "BOSS" warrants to customers of its authorized distributors hereafter "BOSS" that its products will be
free of defects in workmanship or material. Should any failure to conform to this warranty appear within the time period
applicable to theBOSS products as stated below, BOSS shall, upon notification thereof and substantiation that the product has
been stored, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance withBOSS’sspecifications,instructions, recommendations and
recognized standard industry practice, and not subject to misuse, repair, neglect, alteration, or accident, correct such defects by
suitable repair or replacement, at BOSS ‘s sole option, of any components or parts of the product determined by BOSS to be
defective.
The BOSS COMPANY MAKESNO OTHER WARRANTY,EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND
IN LIEU OF ALL OTHERS, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY ORFITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULARPURPOSE.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: BOSS shall not under any circumstances be liable for special, indirect or consequential damages,
such as, but not limited to, lost profits and business interruption. The remedies of the Purchaser set forth herein are exclusive
and the liability of BOSS with respect to any contract, or anything done in connection therewith such as the performance or
breach thereof, or from the manufacture, sale, delivery, resale, or use of any goods covered by or furnished by BOSS whether
arising out of contract, negligence, strict tort, or under any warranty, or otherwise, shall not, except as expressly provided herein,
exceed the price of the goods upon which such liability is based. No employee, agent, or representative of BOSS is authorized
to change this warranty in any way or grant any other warranty.
PURCHASER'S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF REPLACEMENT PARTS OR ACCESSORIES ARE USED
WHICH IN BOSS’S SOLE JUDGEMENT MAY IMPAIR THE SAFETY OR PERFORMANCE OF ANY BOSS PRODUCT.
PURCHASER'S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF THE PRODUCT IS SOLD TO PURCHASER BY
NON-AUTHORIZED PERSONS.
The warranty is effective for the time stated below beginning on the date that the authorized distributor delivers the products to
the Purchaser. Notwith standing the foregoing, in no event shall the warranty period extend more than the time stated plus one
year from the dateBOSS delivered the product to the authorized distributor.
POWER SUPPLIES POWER SUPPLIES & WIRE FEEDERS
MAIN POWER MAGNETICS (STATIC& ROTATING) 1YEAR
ORIGINAL MAIN POWER RECTIFIER 1YEAR
POWER SWITCHING SEMI-CONDUCTORS & CONTROL PC BOARD 1YEAR
ALL OTHER CIRCUITS AND COMPONENTS INCLUDING 1YEAR
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, CONTACTORS, RELAYS,
SOLENOIDS, PUMPS, SWITCHES, MOTORS
Warranty repairs or replacement claims under this limited warranty must be submitted toBOSS by an authorizedBOSS repair
facility within thirty (30) days of purchaser’s notice of any Warranty Claim. No transportation costs of any kind willbe paid under
this warranty. Transportation charges to send products to an authorized warranty repair facility shall be the responsibility of the
Purchaser. All returned goods shall be at the Purchaser’s risk and expense. This warranty supersedes all previous BOSS
warranties.

-4 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
1.0 GENERAL INFORMATION
1.01 Notes,Cautions and Warnings
Throughout this manual, notes, cautions, and warnings are used to highlight important information. These
highlights are categorized as follows:
NOTE
An operation, procedure, or background information which requires additional emphasis or is helpful in
efficient operation of the system.
CAUTION
A procedure which, if not properly followed, may cause damage to the equipment.
WARNING
A procedure which, if not properly followed, may cause injury to the operator or others in the operating area.
1.02 Important Safety Precautions
WARNING
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE OF ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT CAN BE DANGEROUS AND
HAZARDOUS TO YOUR HEALTH.
To prevent possible injury, read, understand and follow all warnings, safety precautions and instructions
before using the equipment. Call your local distributor if you have any questions.
GASES AND FUMES
Gases and fumes produced during the Arc welding or cutting process can be dangerous and hazardous to
your health.
lKeep all fumes and gases from the breathing area. Keep your head out of the welding fume plume.
lUse an air-supplied respirator if ventilation is not adequate to remove all fumes and gases.
lThe kinds of fumes and gases from the arc welding/cutting depend on the kind of metal being used,
coatings on the metal, and the different processes. You must be very careful when cutting or welding
any metals which may contain one or more of the following:
Antimony Arsenic Barium Beryllium Cadmium ChromiumCobalt Copper Lead
ManganeseMercury Nickel Selenium Silver Vanadium
lAlways read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) that should be supplied with the material you
are using. These MSDSs will give you the information regarding the kind and amount of fumes and
gases that may be dangerous to your health.
lUse special equipment, such as water or down draft welding/cutting tables, to capture fumes and
gases.
lDo not use the welding torch in an area where combustible or explosive gases or materials are
located.
lPhosgene, a toxic gas, is generated from the vapors of chlorinated solvents and cleansers. Remove
all sources of these vapors.

-5 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
ELECTRIC SHOCK
Electric Shock can injure or kill. The arc welding process uses and produces high voltage electrical energy.
This electric energy can cause severe or fatal shock to the operator or others in the workplace.
lNever touch any parts that are electrically “live” or “hot.”
lWear dry gloves and clothing. Insulate yourself from the work piece or other parts of the welding
circuit.
lRepair or replace all worn or damaged parts.
lExtra care must be taken when the workplace is moist or damp.
lInstall and maintain equipment according to NEC code, refer to relative standards
lDisconnect power source before performing any service or repairs.
lRead and follow all the instructions in the Operating Manual.
FIRE AND EXPLOSION
Fire and explosion can be caused by hot slag, sparks, or the arc weld.
lBe sure there is no combustible or flammable material in the workplace. Any material that cannot be
removed must be protected.
lVentilate all flammable or explosive vapors from the workplace.
lDo not cut or weld on containers that may have held combustibles.
lProvide a fire watch when working in an area where fire hazards may exist.
lHydrogen gas may be formed and trapped under aluminum workpieces when they are cut
underwater, or while using a water table. Donot cut aluminum alloys underwater or on a water table
unless the hydrogen gas can be eliminated or dissipated. Trapped hydrogen gas that is ignited will
cause an explosion.
NOISE
Noise can cause permanent hearing loss. Arc welding/cutting processes can cause noise levels to exceed
safe limits. You must protect your ears from loud noise to prevent permanent loss of hearing.
lTo protect your hearing from loud noise, wear protective ear plugs and/ or ear muffs. Protect others
in the workplace.
lNoise levels should be measured to be sure the decibels (sound) do not exceed safe levels.
ARC WELDING RAYS
Arc Welding/ Cutting Rays can injure your eyes and burn your skin. The arc welding/cutting process produces
very bright ultra violet and infra red light. These arc rays will damage your eyes and burn your skin if you are
not properly protected.
lTo protect your eyes, always wear a welding helmet or shield. Also always wear safety glasses with
side shields, goggles or other protective eye wear.
lWear welding gloves and suitable clothing to protect your skin from the arc rays and sparks.
lKeep helmet and safety glasses in good condition. Replace lenses when cracked, chipped or dirty.
lProtect others in the work area from the arc rays. Use protective booths, screens or shields.

-6 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
1.03 Transporting methods
These units are equipped with a handle for carrying purposes.
WARNING: ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
DO NOT TOUCHlive electrical parts. Disconnect input power conductors from de-energized supply
line before moving the welding power source.
WARNING: FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause serious personal injury and
equipment damage.
lLift unit with handle on top of case.
lUse handcart or similar device of adequate capacity.
lIf using a fork lift vehicle, place and secure unit on a proper skid before transporting.

-7 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
2.0 INSTALLATION RECOMMENDATION
Installation Environment
TIG HF Series is designed for use in hazardous environments.
Examples of environments with increased hazardous environments are-
In locations in which freedom of movement is restricted, so that the operator is forced to perform the work
in a cramped (kneeling, sitting or lying) position with physical contact with conductive parts; In locations which
are fully or partially limited by conductive elements, and in which there is a high risk of unavoidable or
accidental contact by the operator, or in wet or damp hot locations where humidity or perspiration
considerable reduces the skin resistance of the human body and the insulation properties of accessories.
Environments with hazardous environments do not include places where electrically conductive parts in
the near vicinity of the operator, which can cause increased hazard, have been insulated.
Installation Location
Be sure to locate the welder according to the following guidelines:
lIn areas, free from moisture and dust.
lIn areas, free from oil, steam and corrosive
gases.
lIn areas, not exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
lAmbient temperature: between -10 degrees C
to 40 degrees C.
lIn areas, not subjected to abnormal vibration or
shock.
lPlace at a distance of 304.79mm or more from
walls or similar that could restrict natural airflow
for cooling.
WARNING 1
BOSS advises that this equipment be electrically connected by a qualified electrician.
The following Primary Current recommendations are required to obtain the maximum welding current and
duty cycle from this Power Supply:
Minimum primary current
circuit size Current & Duty Cycle
Model Primary supply
lead size TIG STICK TIG STICK
TIG 160HF Minimum 4mm2220V/22A
240V/20.2A
220V/24.5A
240V/22.5A
160A/16.4V@60%
125A/15V@100%
140A/25.6V@60%
125A/25V@100%
TIG 200HF Minimum 6mm2220V/32A
240V/29.3A
220V/33.5A
240/30.7A 200A/18V@60%
160A/16.4V@100%
160A/26.4V@60%
140A/25.6V@100%
Table 1Primary current circuit sizes to achieve maximum current
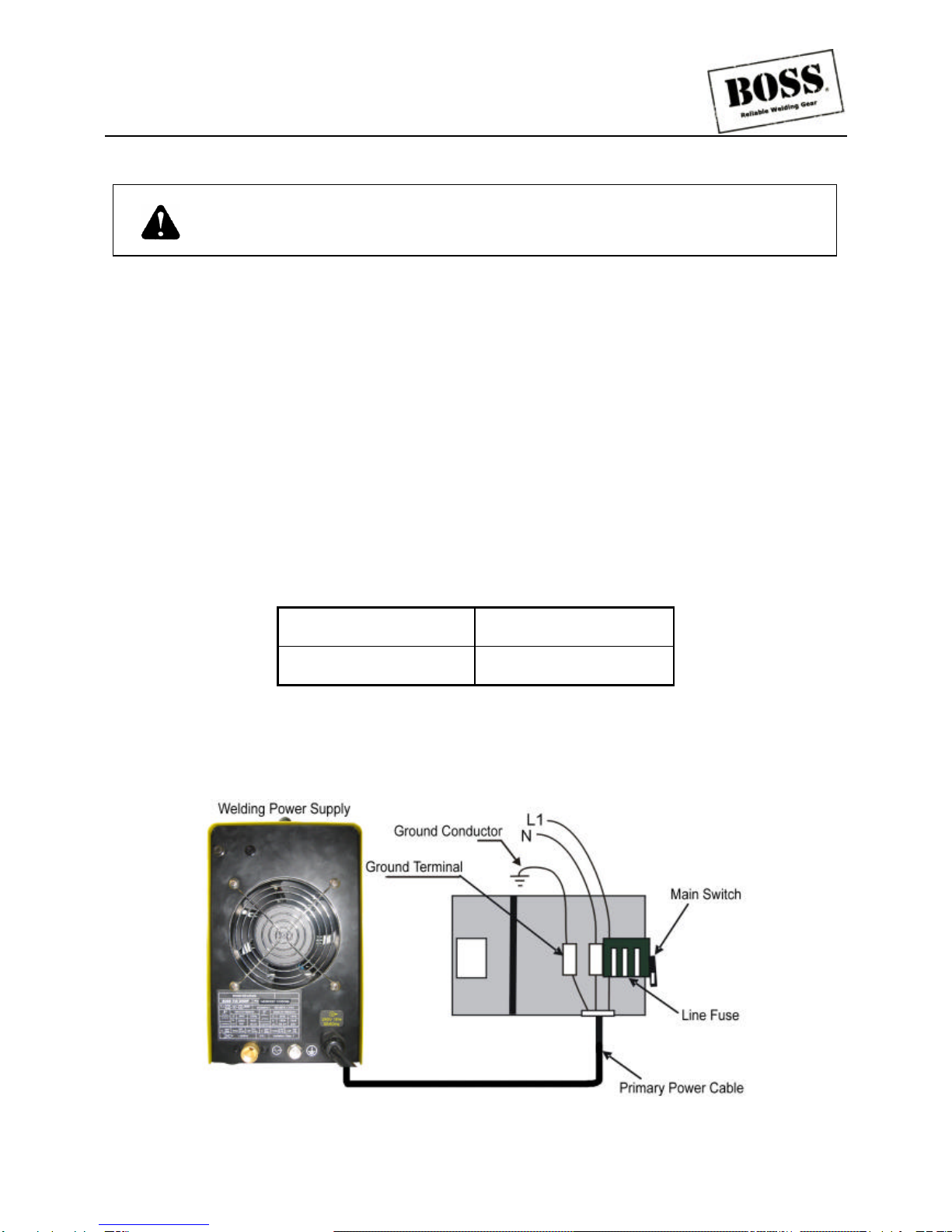
-8 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
2.01 Electrical Input Connections
WARNING: ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill;SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE is
present after removal of input power.
DO NOT TOUCH live electrical parts
SHUT DOWN welding power source, disconnect input power employing lockout/ tagging procedures.
Lockout/ tagging procedures consist of padlocking line disconnect switch in open position, removing fuses
from fuse box, or shutting off and red-tagging circuit breaker or other disconnecting device.
Electrical Input Requirements
Operate the welding power source from a single phase 50/ 60 Hz, AC power supply. The input voltage must
match one of the electrical input voltages shown on the input data label on the unit nameplate. Contact the
local electric utility for information about the type of electrical service available, how proper connections
should be made, and inspection required.
The line disconnect switch provides a safe and convenient means to completely remove all electrical power
from the welding power supply whenever necessary to inspect or service the unit.
According to Table 1 and below as a guide to select line fuses for the disconnect switch.
Input Voltage Fuse Size
220/240VAC 50 Amps
Table 2
Notice: Fuse size is based on not more than 200 percent of the rated input amperage of the
welding power source (Based on Article 630, National Electrical Code).
Figure 1 Electrical input connections

-9 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
Input Power
Each unit incorporates an INRUSH circuit and input voltage sensing circuit. When the MAIN CIRCUIT
SWITCHis turned on, the inrush circuit provides a pre-charging of the input capacitors. The welding machine
will turn on after the input capacitors have charged to full operating voltage (after approximately 1.5 seconds).
Introduction
The importance of correct installation of high frequency welding equipment cannot be overemphasized.
Interference due to high frequency initiated or stabilized arc is almost invariably traced to improper installation.
The following information is intended as a guide for personnel installing high frequency welding machine.
Warning
Explosives
The high frequency section of this machine has an output similar to a radio transmitter.The machine
should NOT be used in the vicinity of blasting operations due to the danger of premature firing.
Computers
It is also possible that operation close to computer installations may cause computer malfunction.
High Frequency Interference
Interference may be transmitted by a high frequency initiated or stabilized arc welding machine in the
following ways:
Direct Radiation
Radiation from the machine can occur if the case is metal and is not properly grounded. It can occur
through apertures such as open access panels. The shielding of the high frequency unit in the
Power Source will prevent direct radiation if the equipment is properly grounded.
Transmission via the Supply Lead
Without adequate shielding and filtering, high frequency energy may be fed to the wiring within the
installation (mains) by direct coupling. The energy is then transmitted by both radiation and
conduction. Adequate shielding and filtering is provided in the Power Source.
Radiation from Welding Leads
Radiated interference from welding leads, although pronounced in the vicinity of the leads,
diminishes rapidly with distance. Keeping leads as short as possible will minimize this type of
interference. Looping and suspending of leads should be avoided where possible.
Re-radiation from Unearthed Metallic Objects
A major factor contributing to interference is re-radiation from unearthed metallic objects close to the
welding leads .Effective grounding of such objects will prevent re-radiation in most cases.

-10 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
2.02Specifications
MODEL TIG 160HF TIG 200HF
Input voltage and frequency and phases
220/240V50/60Hz 220/240V50/60Hz
TIG 4.8kVA 7.0kVA
KVA @ max output MMA 5.4kVA 7.4kVA
TIG 160A 200A
Max current MMA 140A 160A
TIG 10~160A 10~200A
Output current range MMA 10~140A 10~160A
Open circuit voltage 56/61V56/61V
Pulse frequency 2Hz/250Hz 2Hz/250Hz
Down slope time 0-5S 0-5S
Post flow time 5S 5S
Duty cycle at 40℃60% 60%
Weight 9kg 12kg
Dimensions 370×150×245 420×160×265
Table 3
2.03Duty cycle
The duty cycle of a welding power source is the percentage of a ten (10) minute period that it can be
operated at a given output without causing overheating and damage to the unit. If the welding amperes
decrease, the duty cycle increases. If the welding amperes are increased beyond the rated output, the duty
cycle will decrease.
WARNING: Exceeding the duty cycle ratings will cause the thermal overload
protection circuit to become energized and shut down the output until has
cooled to normal operating temperature
Continually exceeding the duty cycle ratings
can cause damage to the welding power source.
NOTICE:
Due to variations that can occur in manufacture products, claimed performance, voltages, ratings, all
capacities, measurements, dimensions and weights quoted are approximate only. Achievable capacities and
ratings in use and operation will depend upon correct installation, use, applications, maintenance and service.
-11 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
3.0 OPERATOR CONTROLS
3.01 TIG HF Series Controls
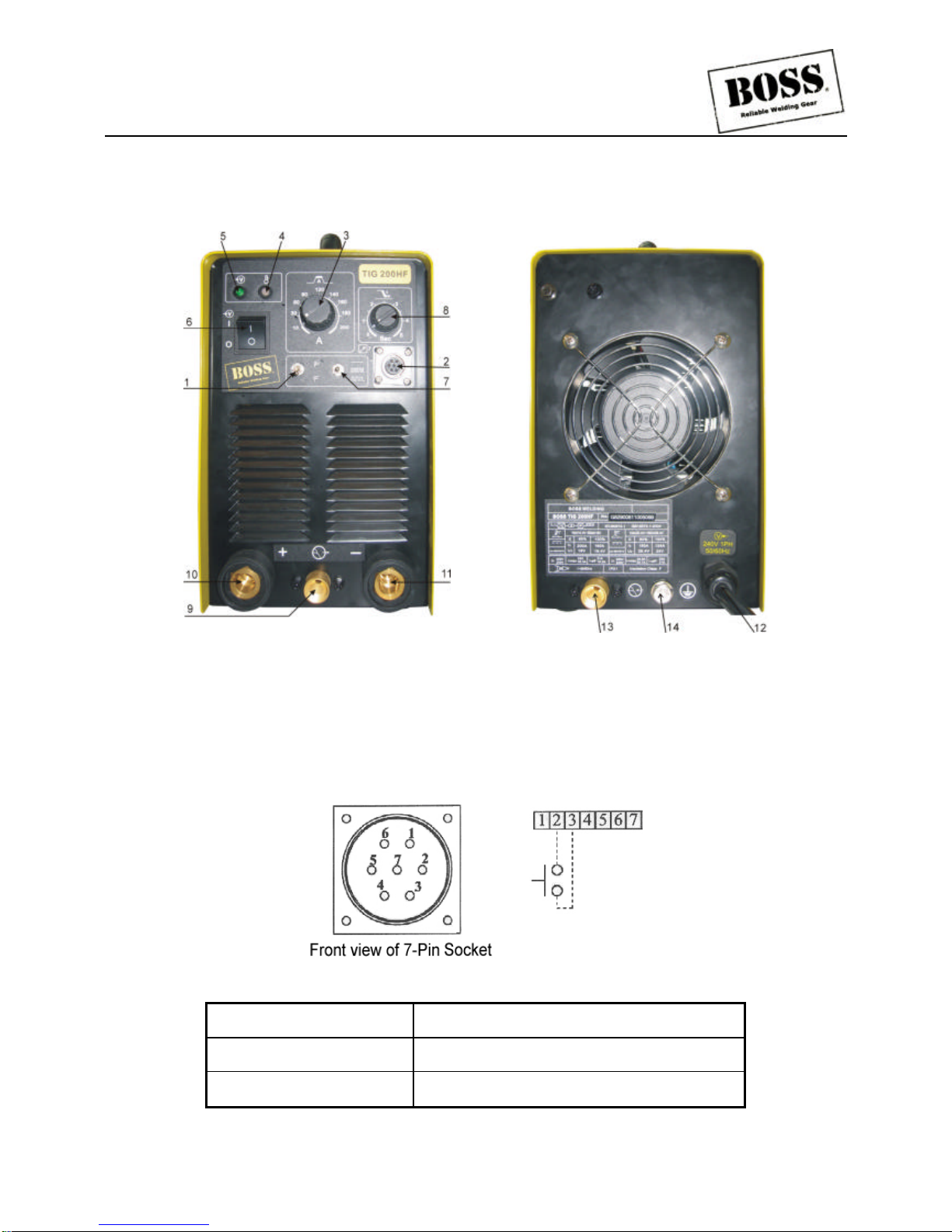
Figure 2
1. The function switch:
TIG mode
MMAmode
2. 7-Pin Socket——Used for the TIG torch switch only.
Figure 3
Pin Function
2TIG torch switch
3TIG torch switch
Table 4

-12 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
3. Welding Current Control——Used for regulating to welding current.
4. Warning Indicator
5. AC Power Indicator
6. Main Power Switch
7. Pulse Switch
DC only (no pulse).
High frequency pulse: the pulse frequency can output 250Hz.
Low frequency pulse: the pulse frequency can output 2Hz.
8. Down Slope Time and Post Flow Time
9. Gas Outlet
10. Positive (+) Socket——TIG connect the work lead/ MMA connect the electrode holder.
11. Negative (-) Socket——TIG connect the TIG torch/MMA connect the work lead.
12. Input Power Cable
13. Gas Inlet
14. Ground Screw
WARNING
When the welder is connected to the primary supply voltage, the internal electrical
components maybe at primary potential with respect to earth.

-13 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
3.02Weld parameters description
Figure 4 TIG HF seriesfront panel with parameter description
Parameter Description
Peak Current This parameter sets the peak current when in pulse mode.
Welding Current This parameter sets the welding current when pulse is off.
Base Current When choice pulse mode this base current by the welding machine in the automatic
hypothesis is 10A.
Pulse Width When choice pulse mode this pulse width is fixed.
Pulse Freq. When choice pulse mode this pulse frequency from 2Hz to 250Hz depend on peak
current.
Down Slope Time
This parameter operates in TIG modes only and is used to set the time for the welding
current to ramp down, this control is used to eliminate the crater that can form at the
completion of a weld.
Post-Flow
t2
This parameter operates in TIG modes only and is used to adjust the post gas flow
time once the arc has extinguished. This control is used to dramatically reduce
oxidation of the tungsten electrode.
t2= 5S
Table 5Weld parameter description for TIG HF series
3.03Weld parameter for TIG HF series
ModelTIG 160HF TIG 200HF
Peak Current 10~160A 10~200A
TIG 10~160A 10~200A
Welding Current STICK 10~140A 10~160A
Pulse Frequency 2Hz/250Hz/OFF 2Hz/250Hz/OFF
Down Slope Time 0~5S 0~5S
Post-Flow Time 5S 5S
Table 6Weld parameters for TIG HF series
-14 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
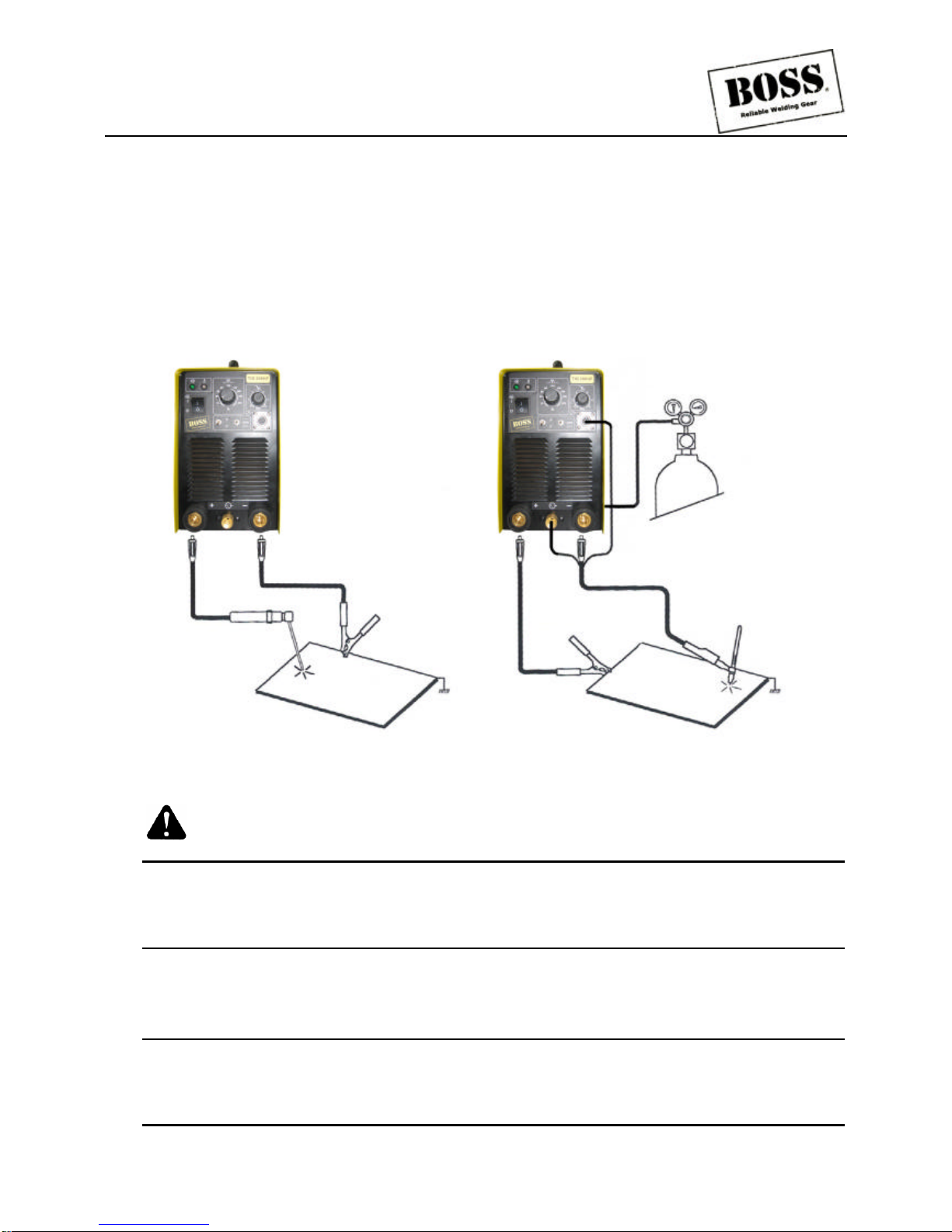
4.0 SET-UP FOR MMA (STICK) AND GTAW (TIG)
Conventional operating procedures apply when using the welding power source, i.e. connect work lead
directly to work piece and welding cable is used to electrode holder. Wide safety margins provided by the coil
design ensure that the welding power source will withstand short-term overload without adverse effects. The
welding current range values should be used as a guide only. Current delivered to the arc is dependent on the
welding arc voltage, and as welding arc voltage varies between different classes of electrodes, welding
current at any one setting would vary according to the type of electrode in use. The operator should use the
welding current range values as a guide, and then finally adjust the current setting to suit the application.
Figure 5 Set up for TIG HF series
WARNING:
Before connecting the work clamp to the work and inserting the electrode in the electrode holder
make sure the Primary power supply is switched off.
CAUTION 2:
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the
Welding Power Source.

-15 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
4.01 Stick welding
lConnect work lead to negative terminal.
lConnect electrode lead to positive terminal.
lSwitch machine on.
lSet MMA mode.
lSet welding current control (see table 7).
Workpiece thickness mm
0.5-2.0 2.0-5.0 5.0-7.0
Electrode diameter mm 1.0-2.0 2.0-3.2 3.2-4.0
Welding current(A)10-50 50-150 150-250
Table 7
4.02 DC TIG welding
lConnect work lead to positive terminal.
lConnect TIG torch to negative terminal.
lSwitch machine on.
lSet DC TIG mode.
lSet welding current control (see table 8).
4.03 DC pulse TIG welding
lConnect work lead to positive terminal.
lConnect TIG torch to negative terminal.
lSwitch machine on.
lSet pulse high/ pulse low position.
lSet welding current control (see table 8).
Workpiece
thickness (mm)
Tungsten
diameter (mm)Welding current
(A)Filler wire
diameter (mm)Argon Gas flow
(L/min)
0.3-0.5 1-1.6 5-30 3-8
0.5-1.2 1.6-210-50 1.2-1.6 4-8
1.2-21.6-210-50 1.2-1.6 4-8
1.2-21.6-230-70 1.6-2.0 6-9
2-42-460-100 1.6-2.0 7-10
4-63-4100-200 2.0-2.5 1-15
Table 8
-16 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
5.0 POWER SUPPLY CONTROLS INDICATORS AND REATURES
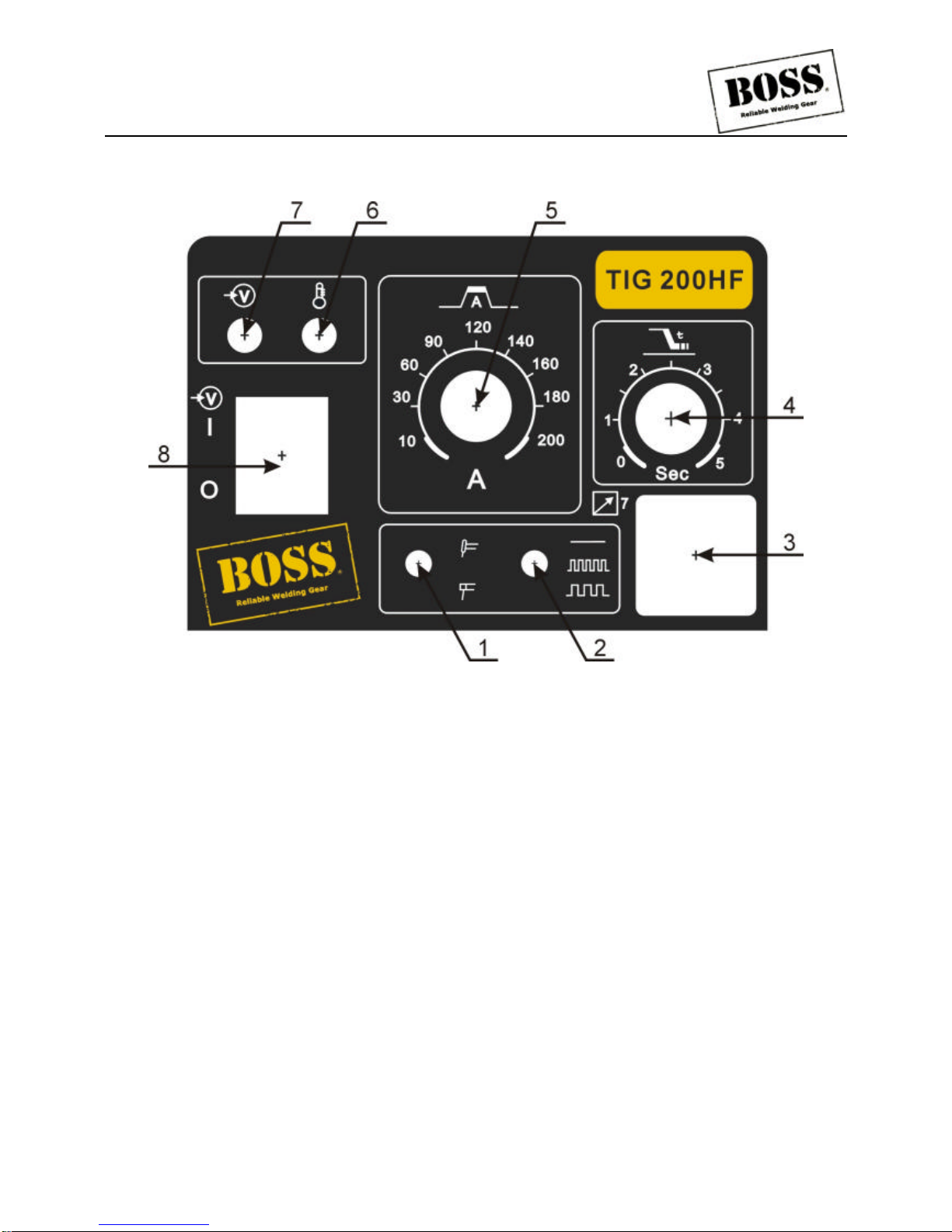
Figure 6 TIG HF seriesfront panel
1. Function switch——Two kind of functions choices, from the top down in turn is:
TIG
STICK
2. Pulse switch——-Three kind of choices,from the top down in turn is:
DC only
High frequency pulse TIG welding: The pulse frequency may output the 250Hz.
Low frequency pulse TIG welding: The pulse frequency may output the 2Hz.
3. 7-Pin socket.
4. Down slope time and post flow time control——Uses in adjusts when the welding receiving arc the output
current automatic weaken to the zero needing the time, the knob shows is the actual hour, the unit for the
second; and post flow time is fixed 5s.
5. Welding currents control——Uses in adjusting the welding current.
6. Warning indicator——Red colored light instruction welding machine overload.
7. AC power indicator——Green colored light instruction power source is normal.
8. Main Power switch.

-17 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
6.0 BASIC TIG WELDING GUIDE
6.01 Electrode Polarity
Connect the TIG torch to the -/ torch terminal and the work lead to the + / work terminal for direct current
straight polarity. Direct current straight polarity is the most widely used polarity for DC TIG welding. It allows
limited wear of the electrode since 70% of the heat is concentrated at the work piece.
6.02 Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Electrode Diameter(mm)DC current (A)
1.0 30—60
1.6 60—115
2.4 100—165
3.2 135—200
4.0 190—280
4.8 250—340
Table 9Current ranges for varies tungsten electrode sizes
6.03 Tungsten Electrode Types
Tungsten type
(Ground finish)
Welding Application Features Color
code
Thoriated 2% DC welding of mild steel, stainless
steel and copper Excellent arc starting, Long life, high
current carrying capacity Red
Ceriated 2% DC welding of mild steel, stainless
steel, copper, aluminium, magnesium
and their alloys
Longer Life, More stable arc, Easier
starting, Wider current range,
Narrower more concentrated arc Grey
Table 10 Tungsten electrode types
6.04 Guide for Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler wire diameter DC current range (Amps)
1.6 20—90
2.4 65—115
3.2 100—165
4.8 200—350
Table 11Filler wire selection guide
Notice:
The filler wire diameter specified in Table 11is a guide only, other diameter wires may be used
according to the welding application.

-18 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
6.05 Shielding gas selection
Alloy Shielding gas
Aluminium & alloys Argon
Carbon steel Argon
Stainless steel Argon
Nickel alloy Argon
Copper Argon
Titanium Argon
Table 12 Shield gas selection
6.06 TIG welding parameters for low carbon & low alloy steel pipe
Tungsten type &
diameter Current range DC
(Amperes)Filler rod for root pass
Joint preparation
Thoriated 2%
3/32”(2.4mm) 120—170 Yes
Thoriated 2%
3/32” (2.4mm) 100—160 Yes
Thoriated 2%
3/32” (2.4mm) 90—130 No
Table 13 TIG welding parameters for low carbon & low alloy steel pipe
6.07 Welding parameters for steel
Base metal
thickness
(mm)
DC current
for mild
steel(A)
DC current
for stainless
steel(A)
Tungsten
diameter
(mm)
Filler rod
diameter (if
require) (mm)
Argon gas
flow rate
(litres/min)
Joint type
1.035—45
40—50 20—30
25—35 1.0 1.6 5—7butt/corner
lap/fillet
1.2 45—55
50—60 30—45
35—50 1.0 1.6 5—7butt/ corner
lap/ fillet
1.6 60—70
70—90 40—60
50—70 1.6 1.6 7butt/ corner
lap/ fillet
3.2 80—100
90—115 65—85
90—110 1.6 2.4 7butt/ corner
lap/ fillet
4.8 115—135
140—165 100—125
125—150 2.4 3.2 10 butt/ corner
lap/ fillet
6.4 160—175
170—200 135—160
160—180 3.2 4.0 10 butt/ corner
lap/ fillet
Table 14 DC TIG welding parameters
-19 -
BOSS TIG 160HF、200HFOperating Manual
7.0 BASIC ARC WELDING GUIDE
7.01 Electrode polarity
Stick electrodes are generally connected to the “+”terminal and the work lend to the “-“terminal but if in
doubt consult the electrode manufacturers literature.
7.02 Effects of stick welding various materials
High tensile and alloy steels
The two most prominent effects of welding these steels are the formation of a hardened zone in the weld
area, if suitable precautions are not taken, the occurrence in this zone of under-bead cracks. Hardened zone
and under-bead cracks in the weld area may be reduced by using the correct electrodes, preheating, using
higher current settings, using larger electrodes size, short runs for larger electrode deposits or tempering in a
furnace.
Manganese steels
The effect on manganese steel slow of cooling from high temperature is to embrittle it.For this reason it
is absolutely essential to keep manganese steel cool during welding by quenching after each weld or skip
welding to distribute the heat.
Cast iron
Most types of cast iron, expect white iron, are weldable. White iron, because of its extreme brittleness,
generally cracks when attempts are made to weld it. Trouble may also be experienced when welding
white-heart malleable, due to the porosity caused by gas held in this type of iron.
Copper and alloys
The most important factor is the high rate of heat conductivity of copper, so making preheating of heavy
sections necessary to give proper fusion of weld and base metal.
Types of Electrodes
Arc welding electrodes are classified into a number of groups depending on their applications. There are
a great number of electrodes used for specialized industrial purposes, which are not of particular interest for
everyday general work. These include some low hydrogen types for high tensile steel, cellulose types for
welding large diameter pipes, etc. The range of electrodes dealt with in this publication will cover the vast
majority of applications likely to be encountered; areall easy to use and all will work on even the most basic of
welding machines.
Metals being joined Electrode Comments
mild steel 6013 Ideal electrodes for all general purpose work. Features
include out standing operator appeal, easy arc starting and
low spatter.
mild steel 7014 All positional electrodes for use on mild and galvanized
steel furniture, plates, fences, gates, pipes and tanks etc.
Especially suitable for vertical-down welding.
cast iron nickel 99% Suitable for joining all cast irons except white cast iron.
stainless steel 318L-16 High corrosion resistance. Ideal for dairy work, etc.On
stainless steels.
copper, bronze,brass etc. bronze
5.7ERCUSI-A
Easy to use electrode for marine fittings, water taps and
valves, water trough float arms, etc. Also for joining copper
to steel and for bronze overlays on steel shafts.
high alloy steels, dissimilar
metals, crack resistance,all
hard-to-weld jobs 312-16 It will weld most problematical jobs such as springs, shafts,
broken joins mild steel to stainless and alloy steels. Not
suitable for Aluminum.
Table 15 Types of Electrodes
Table of contents
Other BOSSCO Welding System manuals
Popular Welding System manuals by other brands

REHM
REHM TIGER DIGITAL 230 AC/DC ULTRA operating instructions

Helvi
Helvi COMPACT 400 instruction manual

Lincoln Electric
Lincoln Electric Precision TIG 375 Service manual

EWM
EWM alpha Q 330 Progress puls MM TKM operating instructions

Craftsman
Craftsman 196.205690 owner's manual

Spartus
Spartus MasterARC 250C user manual