Table of contents YHC 700
Table of contents
Warnings.....................................................................................................................4
1. General characteristics ..........................................................................................5
2. Technical specifications ........................................................................................5
2.1 Hardware..................................................................................................................................5
2.2 Mechanical features.................................................................................................................5
2.3 Electrical features.....................................................................................................................5
2.4 Supported devices ...................................................................................................................6
2.4.1 Devices on bus RS485 #1 (remote control)..........................................................................6
2.4.2 Devices on bus RS485 #2 (monitoring)................................................................................6
2.5 Accessories..............................................................................................................................6
3. Electrical installation..............................................................................................7
3.1 Electrical connections ..............................................................................................................7
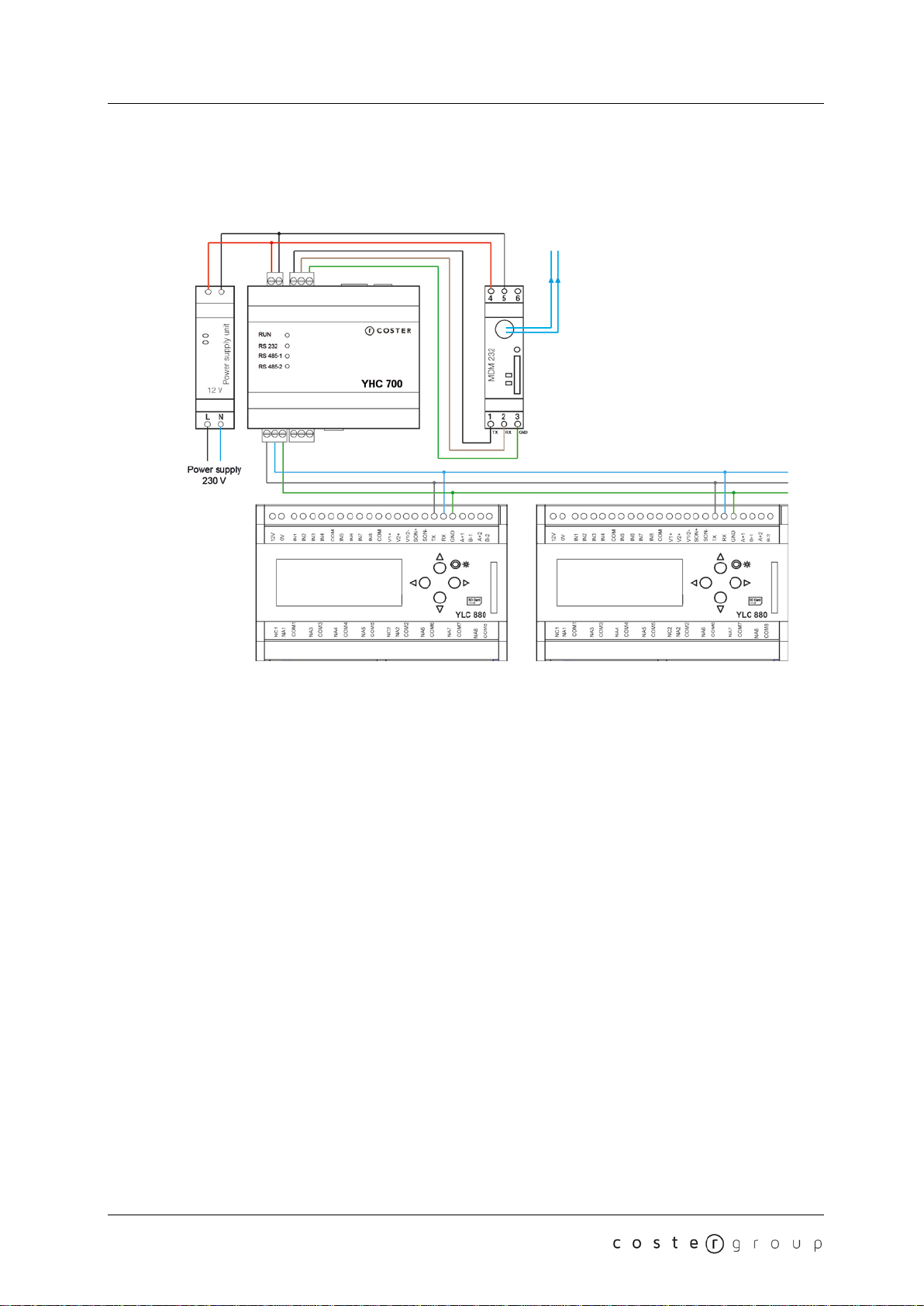
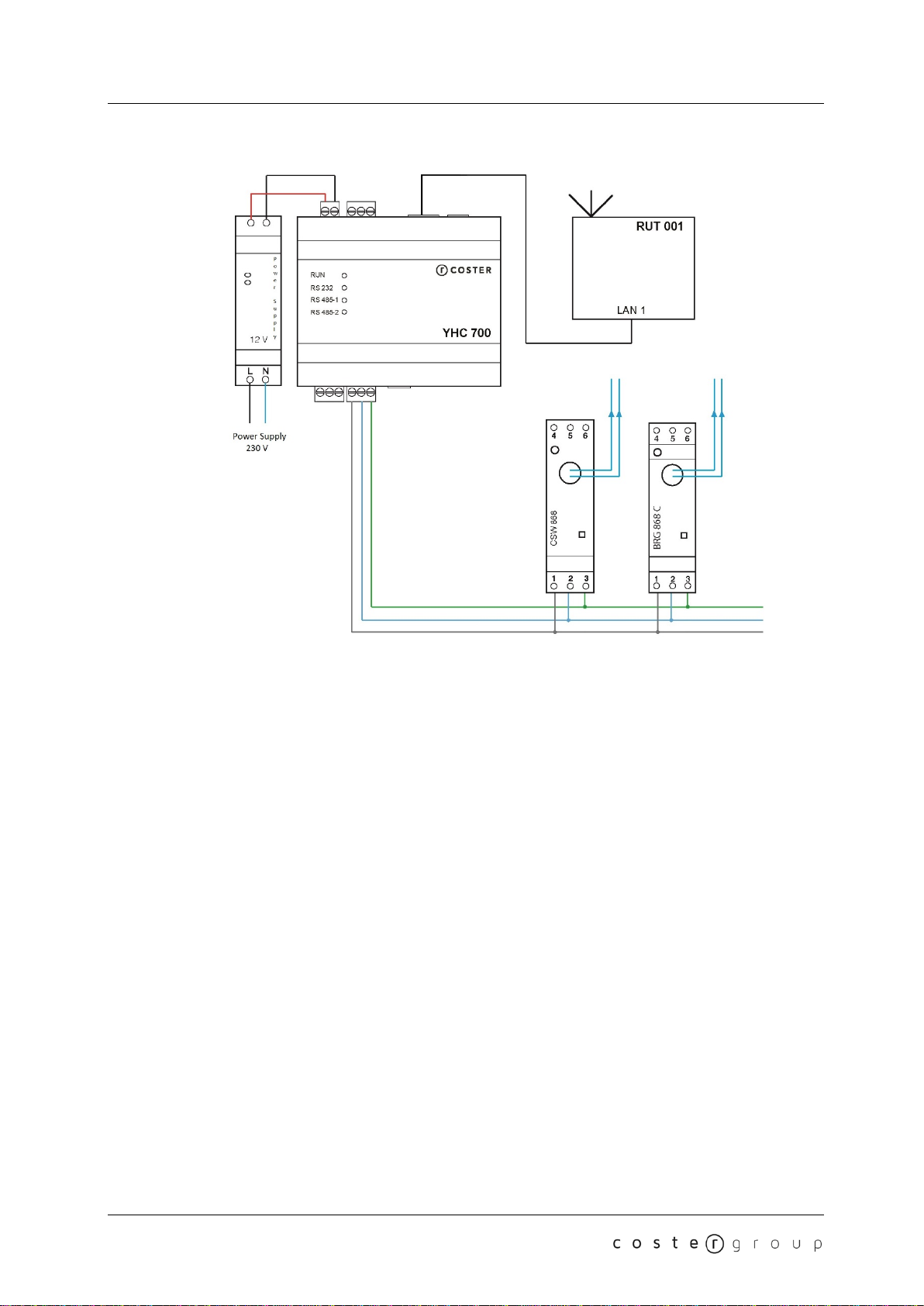
3.2 Connection examples...............................................................................................................8
4. LEDs......................................................................................................................12
5. Main features.........................................................................................................13
5.1 Communication with a supervisor..........................................................................................13
5.2 Communication with field devices..........................................................................................13
5.3 Bridging between YLC controllers..........................................................................................14
5.4 Data logging (instantaneous data logger)..............................................................................14
5.5 YLC data caching...................................................................................................................14
5.6 Sending alarms......................................................................................................................14
5.6.1 Sending alarms via e-mail...................................................................................................14
5.6.2 Sending alarms via HTTP/HTTPs.......................................................................................14
5.6.3 Sending alarms using the MDM 232 modem......................................................................15
5.7 Monitoring data reading .........................................................................................................15
5.8 Datalogging dei dati di monitoraggio......................................................................................15
5.9 M-BUS devices integration.....................................................................................................15
5.10 Sending data to the Cloud ...................................................................................................16
5.10.1 Sending data via the Ethernet port ...................................................................................16
5.10.2 Sending data to the cloud using the MDM 232 modem....................................................16
5.11 Sending date and time.........................................................................................................16
5.12 Software reset......................................................................................................................17
6. Remote management............................................................................................17
7. YHC Configuration................................................................................................17
7.1 Connecting to YHC ................................................................................................................17
2