–The Heat-sink Fins (Fig. 1.5a) are used to evacuate heat from the light source, allowing stable output power.
Ensure the fins are not blocked to allow proper cooling.
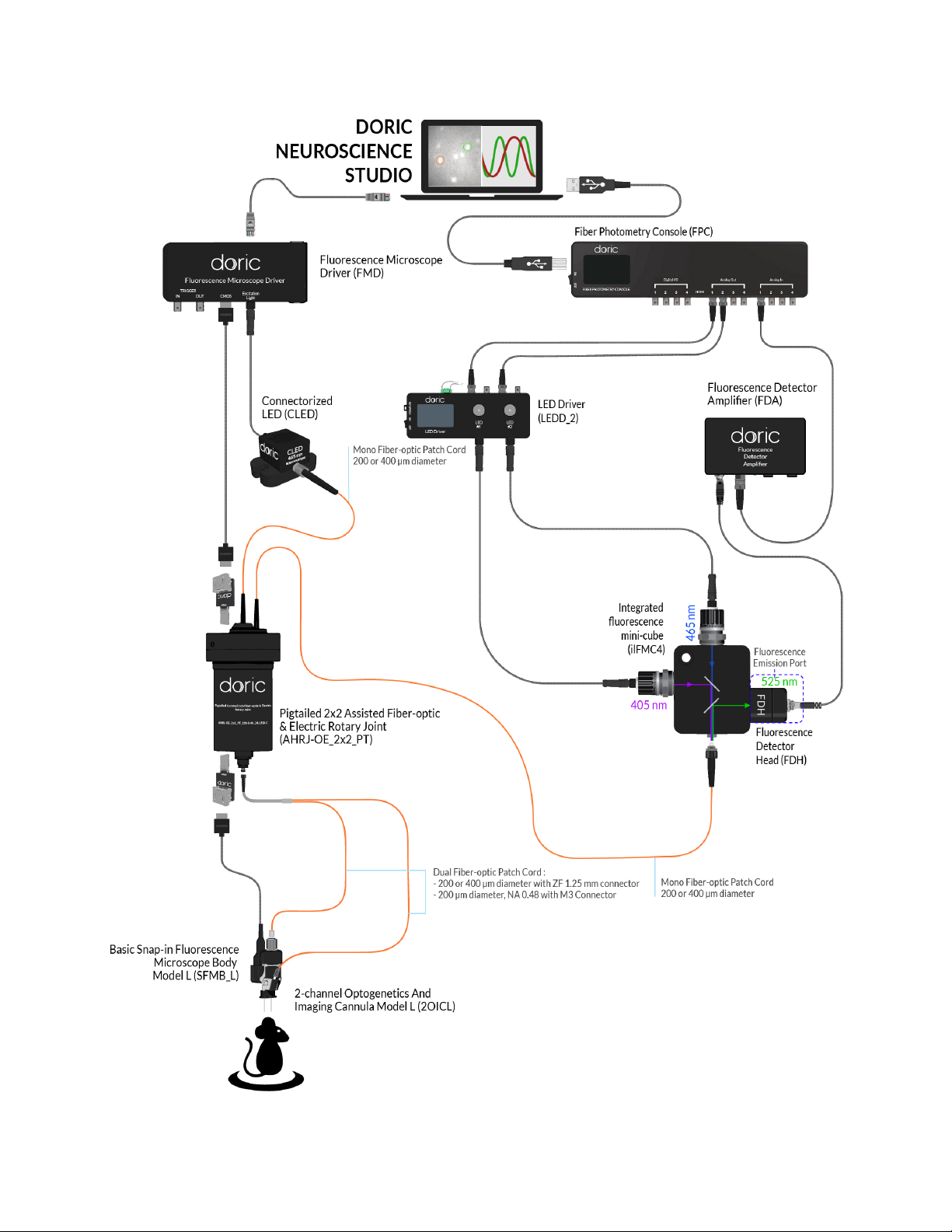
•F(Fig. 1.4) represents ports for fluorescence emission light. Each port of this type comes with a Built-in Doric
Fluorescence Detector Head.
–The M5 Connector (Fig. 1.5b) allows the Fluorescence Detector Head to be connected to the Fluorescence
Detector Amplifier using an M5 male/male connection cable.
–For extremely low light level applications, the fluorescence ports (F, F1, etc.) can have a Built-in Photomultiplier
Tube rather than a Built-in Fluorescence Detector Head.
•O(Fig. 1.4) represents optogenetic activation or silencing ports. These are always FC receptacles to allow connec-
tion to laser or fluorescence light sources.
•S(Fig. 1.4) represents the exit port to the sample. These are always FC receptacles to allow connection to an ex-
perimental subject.
(a) Built-in LED Optical Head (b) Built-in Fluorescence Detector Head
Figure 1.5: ilFMC Built-in components
1.4 Light Sources
1.4.1 LED Driver
Doric LED Drivers can be used as a stand-alone device or controlled via USB port. Each channel connects to a single
Connectorized LED which can be controlled manually or via the Doric Neuroscience Studio Software.
The LEDs drivers can be used as a stand alone device. During stand-alone operation, it is possible to change the operating
mode (CW or external analog mode) and the current sent to the Connectorized LED. These changes can be done directly
on the device with the control knobs and the LCD display.
Connecting the LED drivers to a computer provides the user with more options. Doric Neuroscience Studio Software
allows the access to more operating modes like CW, external TTL, external analog, internal TTL and internal Complex
modes. Doric Neuroscience Studio Software enables the creation of different sequences of light source activation. It
also provides the possibility to let these sequences be triggered or paused by an external signal. If more power is needed,
it is possible to overdrive the LED driver with the software. Our LED driver has a live pulse capability allowing the
visualization of the signal modulation on the input BNC in a scope-like manner.
• The LCD display (Fig. 1.7) allows easy operation and monitoring. For each channel, the LCD displays the type of
light source (LED), the operating mode, the center wavelength in nm and the current setting.
Chapter 1. Fiber Photometry Systems at a Glance 7