Elpro Technologies 905U-E User manual
ELPRO Technologies Pty Ltd, 9/12 Billabong Street, Stafford Q 4053, Australia.
Web: www.elprotech.com
User Manual
905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 2
Thank you for your selection of the 905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge. We trust it will
give you many years of valuable service.
ATTENTION!
Incorrect termination of supply wires may
cause internal damage and will void warranty.
To ensure your 905U-E enjoys a long life,
double check ALL your connections with
the user’s manual
before turning the power on.
Caution!
For continued protection against risk of fire, replace the internal module fuse only with the same type
and rating.
CAUTION:
To comply with FCC RF Exposure requirements in section 1.1310 of the FCC Rules, antennas used
with this device must be installed to provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons
to satisfy RF exposure compliance.
DO NOT:
operate the transmitter when someone is within 20 cm of the antenna
operate the transmitter unless all RF connectors are secure and any open connectors are properly
terminated.
operate the equipment near electrical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere
All equipment must be properly grounded for safe operations. All equipment should be serviced only
by a qualified technician.
Important Notices
Page 3 © February 2005
FCC Notice:
This user’s manual is for the ELPRO 905U-E Wireless Ethernet bridge. This device
complies with Part 15.247 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference and
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This device must be operated as supplied by ELPRO Technologies Pty Ltd. Any changes or
modifications made to the device without the written consent of ELPRO Technologies Pty.
Ltd. May void the user’s authority to operate the device.
This device may only be used with ELPRO antenna / cable combinations as specified
below.
Cable OptionsELPRO
Antenna
Part #
Antenna
Gain No Cable CC10/900 CC20/900
WH900 -2dBi OK N/A N/A
DG900 -2dBi OK N/A N/A
CFD890EL 0dBi OK N/A N/A
SG900EL +5dBi N/A OK OK
SG900-6 +8dBi N/A OK OK
YU6/900 +10dBi N/A NOT
Permitted
OK
End user products that have this device embedded must be supplied with non-standard
antenna connectors, and antennas available from vendors specified by ELPRO
Technologies. Please contact ELPRO Technologies for end user antenna and connector
recommendations.
Notices:
Safety
Exposure to RF energy is an important safety consideration. The FCC has adopted a safety standard
for human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC regulated equipment
as a result of its actions in Docket 93-62 and OET Bulletin 65 Edition 97-01.
Limited Warranty, Disclaimer and Limitation of Remedies
ELPRO products are warranted to be free from manufacturing defects for a period of 24 months from

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 4
the effective date of purchase by the end user. The effective date of purchase is decided solely by
ELPRO Technologies.
This warranty does not extend to:
- failures caused by the operation of the equipment outside the particular product's specification,
or
- use of the module not in accordance with this User Manual, or
- abuse, misuse, neglect or damage by external causes, or
-repairs, alterations, or modifications undertaken other than by an authorized Service Agent.
ELPRO’s liability under this warranty is limited to the replacement or repair of the product. This
warranty is in lieu of and exclusive of all other warranties. This warranty does not indemnify the
purchaser of products for any consequential claim for damages or loss of operations or profits and
ELPRO is not liable for any consequential damages or loss of operations or profits resulting from the
use of these products. ELPRO is not liable for damages, losses, costs, injury or harm incurred as a
consequence of any representations, warranties or conditions made by ELPRO or its representatives or
by any other party, except as expressed solely in this document.
CONTENTS
2.3 P
OWER
S
UPPLY
...............................................................................................................6
2.4 E
THERNET
C
ONNECTIONS
...............................................................................................6
2.4 S
ERIAL
C
ONNECTIONS
....................................................................................................6
2.4.1 RS232 Serial Port.......................................................................................................... 6
2.4.2 RS485 Serial Port.......................................................................................................... 7
2.4 D
IGITAL
I
NPUT
/O
UTPUT
..................................................................................................8
CHAPTER THREE.................................................................................... OPERATION 9
3.1 P
OWER
-
UP AND
N
ORMAL
O
PERATION
.............................................................................9
3.2 S
ERIAL AND
R
ADIO
D
ATA
...............................................................................................9
3.3 A
DDRESSING
.................................................................................................................10
3.3 B
RIDGE
M
ODE
..............................................................................................................10
3.3 R
OUTER
M
ODE
.............................................................................................................10
3.3 A
CCESS
P
OINT
..............................................................................................................11
3.3 C
LIENT
..........................................................................................................................11
3.3 F
ILTER
..........................................................................................................................11
3.3 R
ADIO
R
ATES
................................................................................................................12
3.8 R
ADIO
I
NTERFERENCE
...................................................................................................12
CHAPTER FOUR................................................................................... CONFIGURATION 13

Important Notices
Page 5 © February 2005
4.1 B
EFORE
C
ONFIGURING
..................................................................................................13
4.2 A
DDRESSING
.................................................................................................................13
4.3 D
EFAULT
C
ONFIGURATION
...........................................................................................13
4.4 C
ONFIGURATION
P
ROGRAM
..........................................................................................14
4.6 C
ONFIGURATION
E
XAMPLES
.........................................................................................25
CHAPTER SIX .................................................................................TROUBLESHOOTING 31
6.1 D
IAGNOSTICS
C
HART
....................................................................................................31
6.1 C
ONNECTIVITY
..............................................................................................................31
6.1 M
ONITOR
C
OMMUNICATIONS
.......................................................................................31
6.1 S
TATISTICS
....................................................................................................................32
6.1 PING ............................................................................................................................32
6.1 IPCONFIG ................................................................................................................... 32
6.1 ARP..............................................................................................................................32
6.1 ROUTE........................................................................................................................32
Accessing Configuration inside a module for the first time ................................................14
Modifying an existing configuration.................................................................................... 19
Remote modification of an existing configuration ..............................................................19
Setting a 905U-E to Factory Default Settings...................................................................... 25
Extending a wired network..................................................................................................26
Connecting two separate networks together........................................................................28

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 6
2.3 Power Supply
The 905U-E module is powered by a 10 - 30VDC
supply. The power supply should be rated at 1 Amp and
be CSA Certified Class 2.
The negative side of the supply is connected to "COM"
and may be connected to “ground”. The supply negative
is connected to the “GND” terminal internally. The
positive side of the supply must not be connected to earth. The supply may be a floating supply
or negatively grounded.
The power requirements of the 905U-E units is 700mA at 12VDC or 450mA at 24VDC.
2.4 Ethernet Connections
HUB NIC
2.4 Serial Connections
2.4.1 RS232 Serial Port
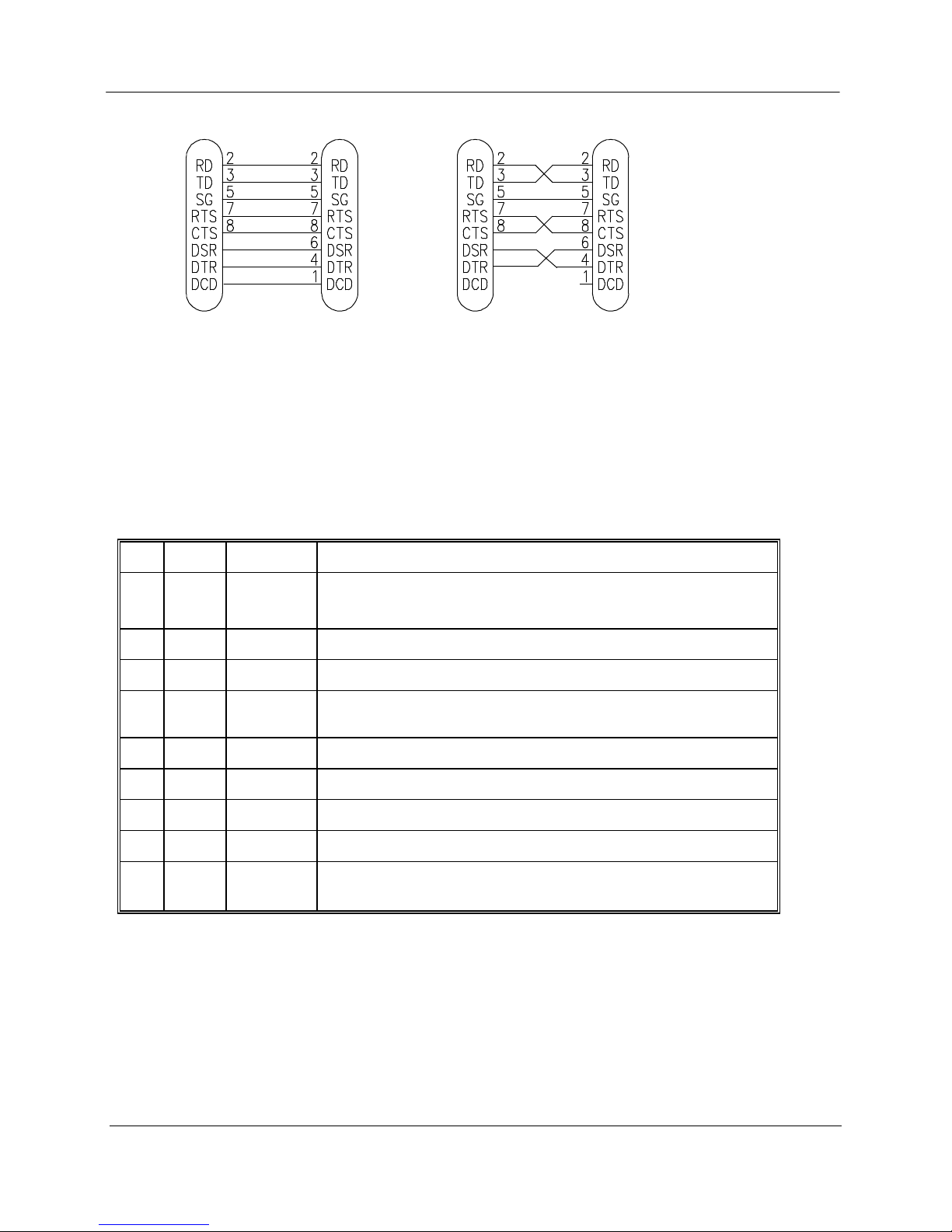
The serial port is a 9 pin DB9 female and provides for connection to a host device. This
port is independent of the RS485 port. Communication is via standard RS232 signals.
The 905U-E is configured as DCE equipment with the pinout detailed below.
905U-E
10 – 30 +
VDC -
+
-
Chapter Two Installation
Page 7 © February 2005
905U-D
DB9
MALE
DTE HOST
DB9
FEMALE
905U-D
DB9
MALE
DCE HOST
DB9
MALE
Hardware handshaking using the CTS/RTS lines is provided. The CTS/RTS lines may be used to
reflect the status of the local unit’s input buffer, or may be configured to reflect the status of
CTS/RTS lines at the remote site. The 905U-D does not support XON/XOFF.
Example cable drawings for connection to a DTE host (a PC) or another DCE host (or modem) are
detailed above.
DB9 Connector Pinout
Pin Name Direction Function
1 DCD Out Data carrier detect –
- on when link is established in controlled mode
- on always in transparent mode
2 RD Out Transmit Data – Serial Data Output
3 TD In Receive Data – Serial Data Input
4 DTR In Data Terminal Ready - DTR can be configured to initiate low power
mode, or to force a link disconnection (“hang up” in controlled mode.
5 SG Signal Ground
6 DSR Out Data Set Ready - always high when unit is powered on.
7 RTS In Request to Send - hardware flow control configurable
8 CTS Out Clear to send - hardware flow control configurable
9 RI Ring indicator - indicates another module is attempting to connect in
controlled mode.
2.4.2 RS485 Serial Port
The RS485 port provides for communication between the 905U-E unit and its host device using a
multi-drop cable. Up to 32 devices may be connected in each multi-drop network.

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 8
As the RS485 communication medium is shared, only one of the units on the RS485 cable may
send data at any one time. Thus communication protocols based on the RS-485 standard require
some type of arbitration.
RS485 is a balanced, differential standard but it is recommended that shielded, twisted pair cable
be used to interconnect modules to reduce potential RFI. It is important to maintain the polarity
of the two RS485 wires. An RS485 network should be wired as indicated in the diagram below
and terminated at each end of the network with a 120 ohm resistor. On-board 120 ohm resistors
are provided and may be engaged by operating the single DIP switch in the end plate next to the
RS485 terminals. The DIP switch should be in the “1” or “on” position to connect the resistor. If
the module is not at one end of the RS485 cable, the switch should be off.
HOST
905U-D
HOST
RS485 CONNECTIONS
120
Ω
RS485
SUPPLY
RS232
DIP SWITCH
FOR 120Ω
120
Ω
HOST HOST
905U-E
+
-
+
-
+
-
RS485 CONNECTION USING TERMINATING RESISTOR
ETHERNET
DIO
DEFAULTS DIP SWITCH
2.4 Digital Input/Output
Chapter Three Operation
Page 9 © February 2005
Chapter Three OPERATION
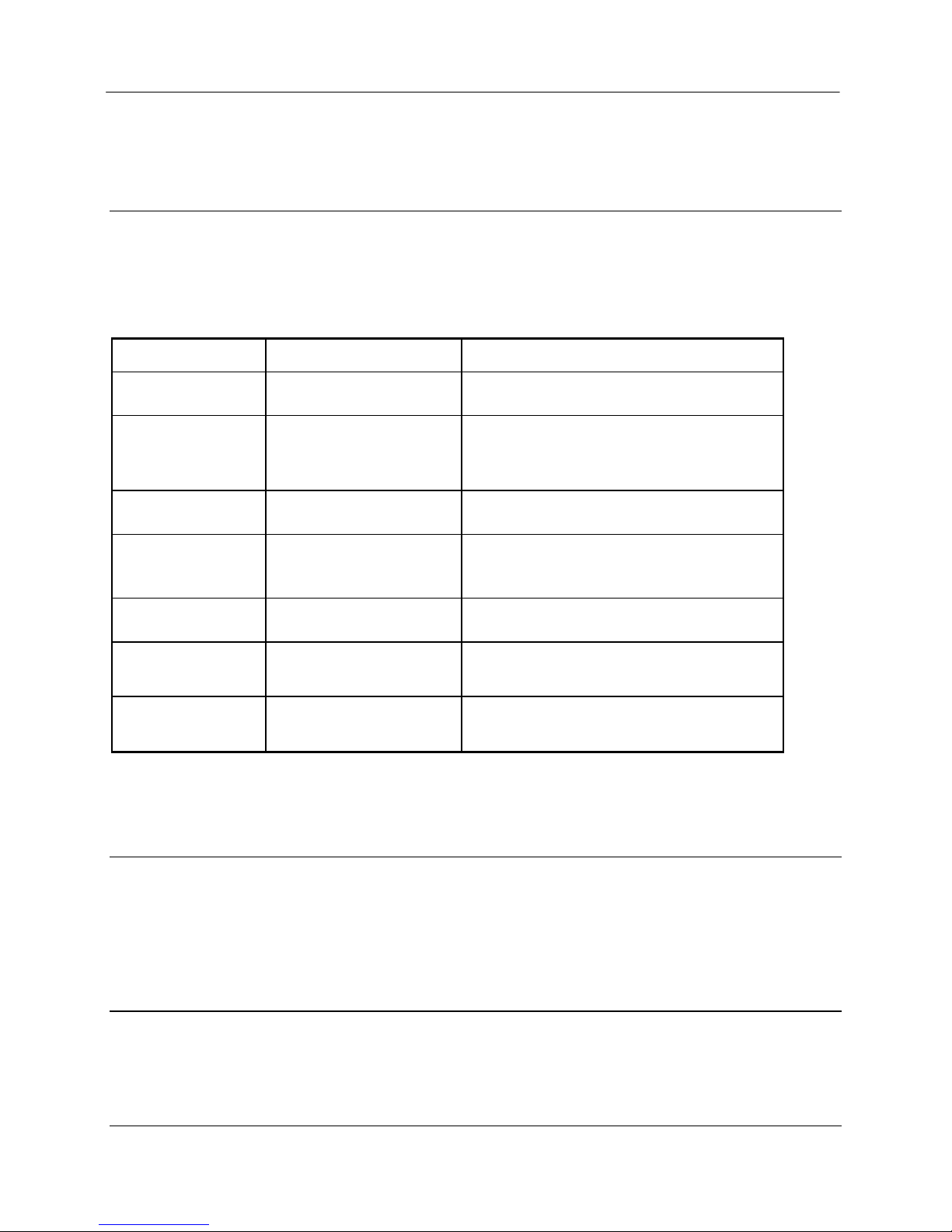
3.1 Power-up and Normal Operation
When power is initially connected to the 905U-E module, the module will perform internal
diagnostics to check its functions. The following table details the status of the indicating LEDs
on the front panel under normal operating conditions.
LED Indicator Condition Meaning
OK On Normal Operation
Radio RX GREEN flash
RED flash
Radio receiving data
Weak radio signal
Radio TX Flash Radio Transmitting
Serial RX GREEN flash
RED flash
Serial Port Receiving
CTS low
Serial TX GREEN flash Serial Port Transmitting
LINK On On when a radio communications link is
established
LINK Off Communications failure or radio link
not established
Other conditions indicating a fault are described in Chapter Six Troubleshooting.
3.2 Ethernet Data
3.2 Serial Data
The 905U-E module provides a full-duplex RS232 serial port and half-duplex RS485 serial port.
The radio communications is half-duplex - this means that the 905U-E operates at half duplex.
Many applications use full duplex RS232 communications but do not require full duplex - the

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 10
protocol used operates at half-duplex and will operate with the 905U-E without problems. If an
application really requires full duplex communications, then the 905U-E should not be used.
3.2 Radio Data
3.3 Addressing
A 905U-E network comprises modules with the same "system" address. Only modules with the
same system address will communicate with each other. This feature allows more than one
system to operate in the same area on the same radio channel.
3.3 Bridge Mode
Joins sections of the same network.
Work at the MAC Layer.
Filter may be used to minimize traffic
Learns where to send data
Initially Broadcast, listen, then limit
3.3 Router Mode
Joins separate networks
Useful for minimizing traffic between networks
Work at the Internet Layer
Knows where to send data based on IP address and routing rules.
905U-E at present only implements only 1 routing rule – default gateway

Chapter Three Operation
Page 11 © February 2005
3.3 Access Point
Access Points (AP)??.
Alternatively, Access Points may be used as a single hop repeater.
All radio traffic with the radio cell is controlled by the Access Point, and must pass through the
Access Point. Ideally the Access Point is placed at the wired location where the majority of data
traffic will flow. This will reduce quantity of data transmitted over the radio.
Access Points periodically sent out Beacon messages. These messages are used by Clients to
synchronise their link with an individual AP.
3.3 Client
A Client is a How is a Connection Established
Client Scanning - RX LED flicker. Select best RSSI
Joining, Timer Synchronisation, Leadin short
Authentication Request
Encryption Requested -> Challenge and Response
Acceptance
Association LINK LED on
Monitor RSSI and Fade Margin
Short vs Long Beacon Interval
How is a Connection Lost
Retry 3 times, allow other data through, backoff, then disassociation
Client hears misses several beacons
Client periodically reassociates
Access Point doesn’t hear any reassociating or data from a Client
All related to Beacon Interval configured.
3.3 Filter
need to add other bridges mac addresses when in bridge mode?

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 12
3.3 Radio Rates
The 905U-E is capable of using several radio transmission rates. A reduction in speed will
increase the range.
3.8 Radio Interference
The 905U-E operates on the 902-928MHz license-free radio band (restricted to 915 – 928 MHz
in Australia and 921 – 928MHz in New Zealand). Devices on this radio band must use a spread
spectrum technique to allow multiple users to share the band with minimal interference.
The 905U-E uses a frequency-hopping spread spectrum technique. The 905U-E will not interfere,
or be interfered by, radio devices on other bands, such as two way radios or wireless telephones.
There can be interference from other devices on the same band. As the “hopping sequence” used
by the 905U-E is different to other devices on this band, the probability of two devices using the
same channel is small, and if this does occur, the probability of sharing the same channel on a
re-transmission is even smaller.
In countries which allow the full 902-928MHz band (such as USA and Canada), there are eight
hopping sequences, and the first four do not use the same frequency channels as the last four -
this can give isolation between two systems. That is, a system with hopping sequence 1 will
hear messages from another system using hopping sequence 3, but will not if the other system
used hopping sequence 5. The hopping sequence may be configured under the Radio Settings
Configuration menu. In countries which only allow half the band (such as Australia and New
Zealand), it is not possible to separate systems in this way because the band is smaller and all
hopping sequences use all channels available.

Chapter Five Specifications
Page 13 © February 2005
Chapter Four CONFIGURATION
4.1 Before Configuring
Configuration comprises selecting parameter values for the operation of the 905U-E unit. Before
you start configuration, parameter settings must be decided. The main parameters are:-
•Addressing – System address, IP address, Network mask, Gateway IP address.
•Device Mode – Bridge or Router
•Operating Mode – Access Point or Client.
•Encryption
The other configuration parameters do not need to be selected, and are provided as a means of
"fine tuning" the operation of the 905U-E units.
Configuration may be achieved using only Windows Internet Explorer ®.
4.2 Addressing
A 905U-E network comprises modules with the same "system" address. The system address is
text string 1 to 31 characters in length. Only modules with the same system address will
communicate with each other. If you are adding another module to an existing system, use the
same value as the existing modules. If you are starting a new system, select random values and
use the same value for each module.
The Device Mode must also be selected. If you wish to link a single network together, then set
Device Mode to Bridge. If two separate networks are to be joined then Device Mode should be
set to Router.
IP addresses and netmasks must be set to reflect the Device Mode configured. If the unit is
configured as a Router, then the 905U-E requires an IP address and netmask to be set for within
each of the networks it is joining. When configured as a Bridge, the 905U-E requires only one IP
address.
4.3 Default Configuration
The default configuration of the 905U-E is a Bridge, Client, IP address 192.168.123.123,
netmask 255.255.255.0, gateway IP address 192.168.123.1. Default username is “user” and the
default password is “user” for configuration.
The module may be forced to factory default setting by using the default configuration dipswitch
or via the System Tools menu via Internet Explorer.

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 14
4.4 Factory Default Switch
When powered up with the Factory Default switch on, the 905U-E will start with temporary
settings of ethernet IP address 192.168.123.123, subnet mask 255.255.255.0, gateway IP
192.168.123.1, username and password “user” and the radio disabled. This allows easy access to
configuration when configuration detail has been forgotten. The existing configuration is not
modified, unless the user makes changes.
Do not forget to set the switch back to the OFF position and cycle power at the conclusion of
configuration for resumption of normal operation.
4.4 Configuration Program
The 905U-E has a built-in webserver, containing webpages for analysis and modification of
configuration. The configuration must be accessed using Microsoft® Internet Explorer. This
program is shipped with Microsoft Windows or may be obtained freely via the Microsoft®
website on the internet.
Serial configuration for IP address, gateway address and subnet mask may be accessed via the
RS-232 serial port.
Accessing Configuration inside a module for the first time
There are two methods for accessing the configuration inside a 905U-E. The first method
requires changing your computer settings so that the configuring PC is on the same network as
the 905U-E with factory default settings.The second method requires setting an IP address so the
905U-E is accessable on your network.
You will need a straight through ethernet cable between the PC ethernet card and the 905U-E.
The factory default ethernet address for the 905U-E is 192.168.123.123.
Consult your network administrator for an IP address on your network, the gateway IP address,
and network mask.
Adjust PC or 905U-E network settings so that both are on the same network. This may achieved
two ways as outlined below.
Option 1 – Set PC to same network as 905U-E
Connect ethernet cable between unit and the PC configuring the module.
Set the Factory Default Switch to the ON (SETUP) position. This will always start the
905U-E with ethernet IP address 192.168.123.123, subnet mask 255.255.255.0,
gateway IP 192.168.123.1 and the radio disabled. Do not forget to set the switch
back to the OFF position and cycle power at the conclusion of configuration for
resumption of normal operation.
Power up module.
Open Network Settings on PC under Control Panel.
Open Properties of Local Area Connection.
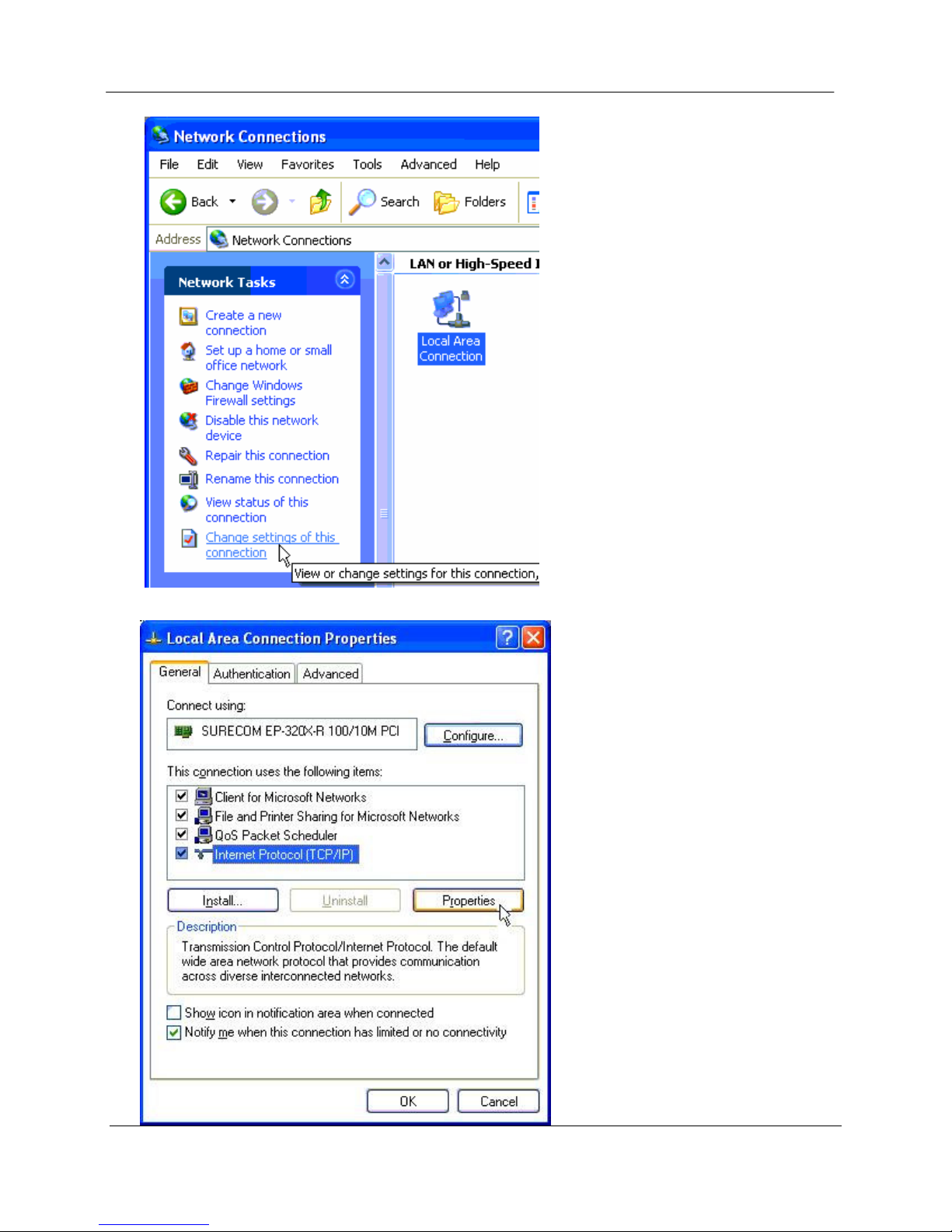
Chapter Five Specifications
Page 15 © February 2005
Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click on Properties.

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 16
On the General tab enter IP address 192.168.123.1, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0,
and default gateway 192.168.123.1.
Open Internet Explorer and ensure that settings will allow you to connect to the IP
address selected. If the PC uses a proxy server, ensure that Internet Explorer will
bypass the Proxy Server for local addresses. This option may be modified by
opening Tools -> Internet Options -> Connections Tab -> LAN Settings->Proxy
Server -> bypass proxy for local addresses.
Enter the webpage http://192.168.123.123/ A welcome webpage should be
displayed as illustrated below.

Chapter Five Specifications
Page 17 © February 2005
Configuration and Diagnostics may be opened by clicking on any of the menu items,
and entering the default username “user” and password “user”.
Switch dip-switch on 905U-E to RUN (OFF) position, and cycle power to resume
normal configured operation.
Option 2 – Set 905UE to same network as PC
a) Switch dip-switch on 905U-E to SETUP (ON) position.
b) Open a terminal package with 19200bps data rate, 8 data bit, 1 stop and no parity.
c) Power up 905U-E. Basic network settings will be displayed on the terminal as illustrated
below. When prompted, hit enter key to stop automatic boot process.

905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 18
My Right Boot 2.1
Copyright 1999-2004 Cybertec Pty Ltd, All rights reserved.
This software is provided by Cybertec ``as is'' and with NO WARRANTY.
http://www.cybertec.com.au/
ROM : 256KB @ 0xffe00000
RAM : 8192KB @ 0x00000000 (140KB / 0x00023214)
ROM Configuration table ... PASSED.
RAM address pattern check . PASSED.
RAM address bus check ..... PASSED.
Product : E900P
Variant : default-variant
Serial No. : default-serial
Release : default-release
Released date :
Released host :
Build date : Oct 12 2004, 17:27:32
Build host :
Boot Flags : no RAM test, no ROM test, bus timer on, wdog on
static IP, auto-boot, net-boot, reset on
local file, no binary load
Boot delay : 1
Boot Filename : /memory/0xffe40000,0x50000
Boot Address : 169.254.101.93
Boot Netmask : 255.255.255.0
Boot Gateway : 169.254.101.1
Boot Host : 169.254.101.1
Boot Mac 0 : 00:12:af:00:00:04
RTE data store .... no error
Setting bus timer (on) and watchdog (on) ... PASSED
eip: mount point /memory
fec0: connected at 10M Half Duplex.
fec0: local ip = 169.254.101.93, server ip = 169.254.101.1
Press ENTER to abort automatic booting ... 30
d) Check values for Boot Address, Boot Netmask, and Boot Gateway. These values should
be set to reflect those of the PC you are using to configure the unit. If these are correct
skip to step (h). You may check settings again with the rct command. For further help,
type the help command.
e) Set Boot Netmask to the same settings as the computer you have the ethernet cable
connected to. This may be performed with the command: bnm <Type the netmask>
f) Set Boot Gateway to the same settings as the computer you have the ethernet cable
connected to. This may be performed with the command: bgw <Type the gateway IP
address>
g) Choose an IP address for the 905U-E being upgraded. This IP address must be on the
same network as the computer you have connected the ethernet cable to. This may be
performed with the command: bip <Type the IP address>
h) Set boot delay to 1 second with the command bdelay 1
i) Switch dip-switch on 905U-E to RUN (OFF) position.
j) Type the command reset. The 905UE will reset and start with the network settings you
have entered.
Chapter Five Specifications
Page 19 © February 2005
k) Open Internet Explorer and ensure that settings will allow you to connect to the IP
address selected. If the PC uses a proxy server, ensure that Internet Explorer will bypass
the Proxy Server for local addresses. This option may be modified by opening Tools ->
Internet Options -> Connections Tab -> LAN Settings->Proxy Server -> bypass proxy for
local addresses.
l) Enter the webpage http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/ where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address selected
for the module. A welcome webpage should be displayed as illustrated.
m) Clicking on any of the menu items, and entering the default username “user” and
password “user” may open Configuration and Diagnostics. If the password has previously
been configured other than the default password, then enter this instead.
Modifying an existing configuration
Open Internet Explorer to the IP address set for the module (ie http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/ where
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address set on the 905U-E.), and use menu system to open the item
you wish to modify. When prompted for username and password, enter “user” as the username,
and the previously configured password in the password field.
If IP address or password has been forgotten, the Factory Default switch may be used to access
the existing configuration. Refer to Option 1 Accessing Configuration inside a module for the
first time.
Remote modification of an existing configuration
Care must be taken if modifying the configuration of a module remotely. If the network link is
via a radio link, some changes made may cause loss of the radio link, and therefore the network
connection.
It is advisable to determine path of the links to the modules you wish to modify, and draw a tree
diagram if necessary. Modify the modules at the “leaves” of your tree diagram. These will be the
furtherest away from your connection point in terms of the number of radio or ethernet links.
In a simple system, this usually means modifying the Client modules first and the Access Point
last.
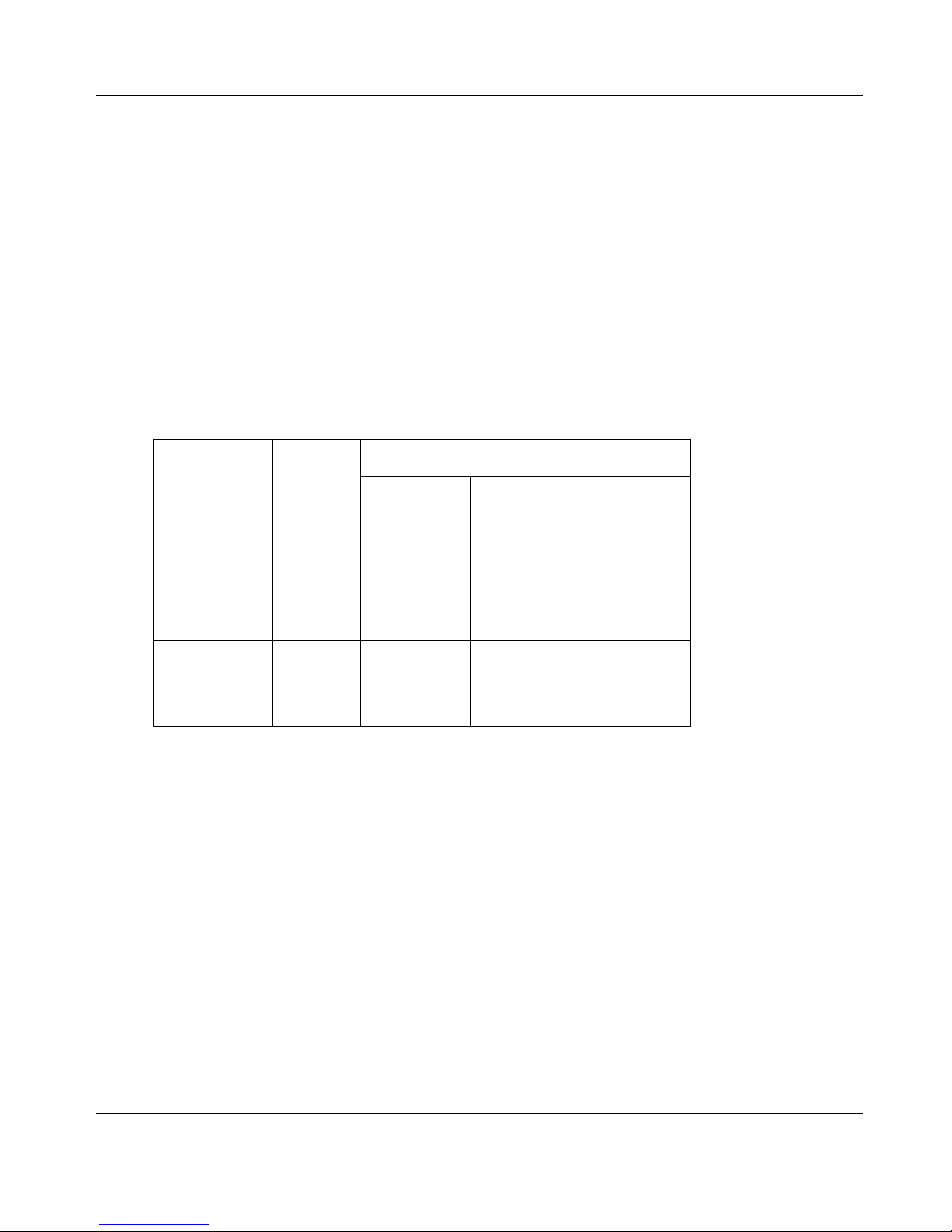
Network Settings Webpage Fields
Device Mode Used to select Bridge or Router mode.
By default this is set to Bridge.
Operating Mode Used to select Access Point or Client mode.
By default this is set to Client.
Bridge Priority The priority of the 905U-E, if configured as a bridge, in the Bridge
Spanning Tree algorithm.
By default this is set to the lowest priority at 255.
FTP Enabled Check this item to enable the FTP server on the 905U-E. The FTP
905U-E Wireless Ethernet Bridge User Manual
Man_905U-E Rev 1.0 Page 20
server is not secure, and should be disabled for normal operation of
the unit.
By default this is enabled.
MAC Address This is the unique hardware address of the 905U-E. This item is for
information purposes only.
This unique identifier is assigned to the 905U-E when built in the
factory.
Gateway IP Address The IP address of the default gateway.
By default this is set to 192.168.123.1.
Ethernet IP Address The IP address of the 905U-E on the RJ-45 ethernet port.
By default this is set to 192.168.123.123.
Ethernet IP Subnet Mask The IP network mask of the 905U-E on the RJ-45 ethernet port.
By default this is set to 255.255.255.0.
Wireless IP Address The IP address of the 905U-E on the radio port. If the unit is
configured as a bridge this address must be the same as the ethernet
IP address. If configured as a router, the IP address must be different
from the Ethernet IP Address.
By default this is set to 192.168.123.123.
Wireless IP Subnet Mask The network mask of the 905U-E on the radio port. If configured as
a Bridge, this must be the same as the Ethernet IP Subnet Mask.
By default this is set to 255.255.255.0.
System Address This field must be the same value for all 905U-E intended to interact
with each other using the radio. All units intended to operate within
the same radio cell must have the same system address configured.
By default System Address is set to “905E”.
Radio Encryption
Enabled Check this field to enable encryption of data transmitted over the
radio.
By default Radio Encryption is disabled.
Encryption Keys 1 to 4 These are the keys used to encrypt radio data to protect data from
unwanted eavesdroppers. These keys must be set the same for all
905U-E intended to operate in the radio cell. Each of the fields are 5
bytes in length, and must be entered as hexidecimal numbers
separated by colons. Eg 12:AB:EF:00:56
Encryption keys must not be all zeros, ie 00:00:00:00:00
Save and Reboot. Save settings to non-volatile memory, and reboot 905U-E.
Table of contents
Other Elpro Technologies Network Router manuals