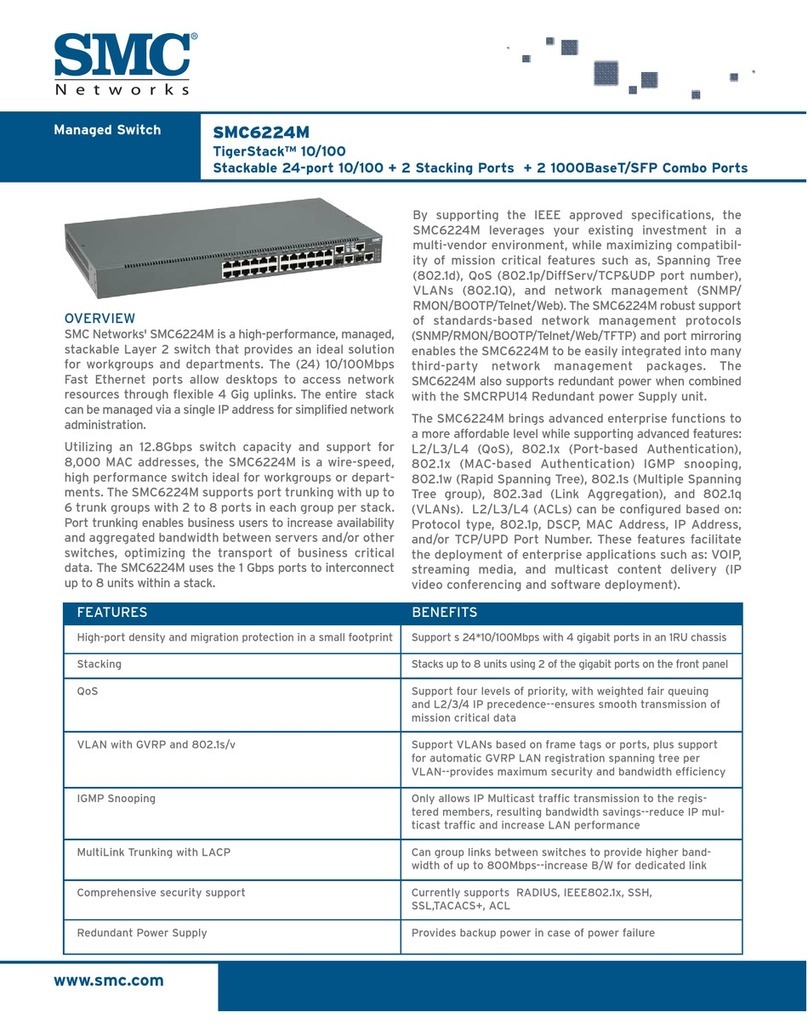
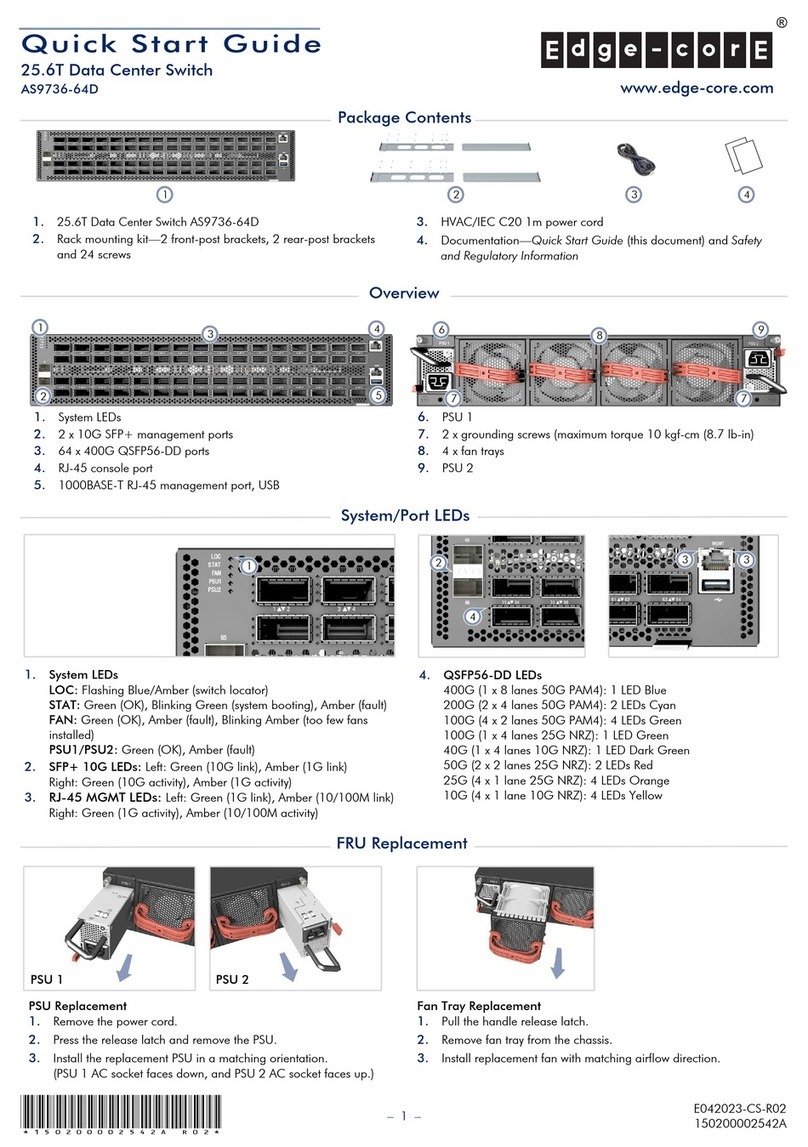
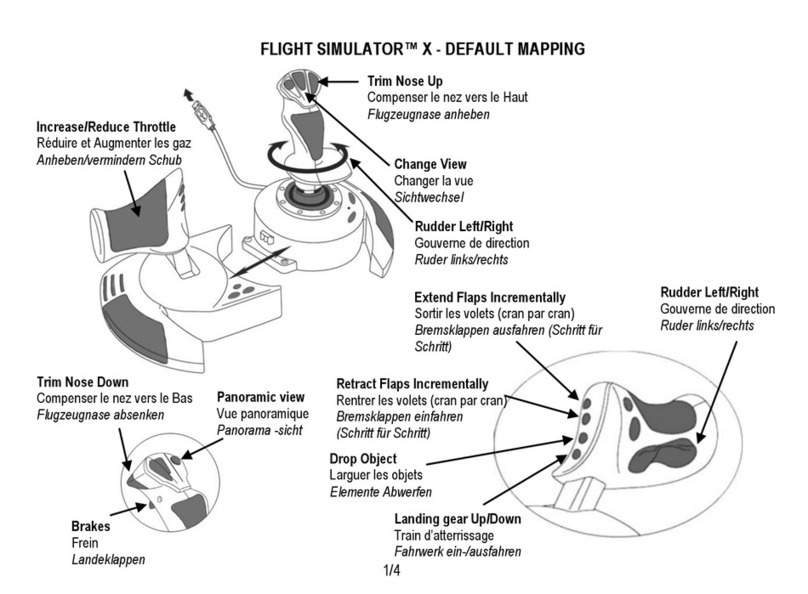
MES3000 Ethernet switch series 7
5.8.4 IP interface configuration ........................................................................................................73
5.9 Selective Q-in-Q.................................................................................................................................73
5.10 Storm control.....................................................................................................................................75
5.11 Link Aggregation Groups (LAG) .........................................................................................................76
5.11.1 Static link aggregation groups ..............................................................................................77
5.11.2 Link aggregation Control Protocol........................................................................................78
5.12 IPv4 addressing configuration ...........................................................................................................79
5.13 Green Ethernet configuration ...........................................................................................................81
5.14 IPv6 addressing configuration ...........................................................................................................82
5.14.1 IPv6 protocol.........................................................................................................................82
5.14.2 IPv6 protocol tunnelling (ISATAP).........................................................................................85
5.14.3 IPv6 RA guard configuration .................................................................................................87
5.14.4 DHCPv6 guard configuration ................................................................................................87
5.15 Protocol configuration.......................................................................................................................88
5.15.1 DNS protocol configuration ..................................................................................................88
5.15.2 ARP configuration .................................................................................................................89
5.15.3 GVRP protocol configuration................................................................................................91
5.15.4 Loopback detection mechanism (loopback-detection)........................................................93
5.15.5 STP family (STP, RSTP, MSTP) ...............................................................................................94
5.15.6 Flex-link configuration ........................................................................................................100
5.15.7 EAPS protocol .....................................................................................................................101
5.15.8 G.8032v2 (ERPS) protocol configuration ............................................................................102
5.15.9 LLDP protocol configuration ...............................................................................................103
5.15.10OAM protocol configuration...............................................................................................108
5.15.11CFM protocol configuration................................................................................................111
5.15.12Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT) function configuration.................................................114
5.16 Voice VLAN ......................................................................................................................................117
5.17 Multicast addressing .......................................................................................................................118
5.17.1 Multicast addressing rules..................................................................................................118
5.17.2 IGMP snooping ...................................................................................................................124
5.17.3 MLD Snooping—multicast traffic control protocol for IPv6 networks...............................127
5.17.4 Multicast traffic restriction functions.................................................................................129
5.17.5 IGMP Proxy multicast routing.............................................................................................131
5.18 Control functions.............................................................................................................................133
5.18.1 AAA mechanism..................................................................................................................133
5.18.2 RADIUS protocol .................................................................................................................137
5.18.3 TACACS+ protocol...............................................................................................................139
5.18.4 Simple network management protocol (SNMP) ................................................................140
5.18.5 Remote network monitoring protocol (RMON) .................................................................144
5.18.6 Access Lists (ACL) for device management.........................................................................150
5.18.7 Access configuration...........................................................................................................152
5.19 Alarm log, SYSLOG protocol.............................................................................................................155
5.20 Port mirroring (monitoring).............................................................................................................157
5.21 SFlow function .................................................................................................................................159
5.22 Physical layer diagnostics functions ................................................................................................160
5.22.1 Copper-wire cable diagnostics............................................................................................160
5.22.2 Optical transceiver diagnostics...........................................................................................162
5.23 IP Service Level Agreements (IP SLA)...............................................................................................165
5.23.1 ICMP Echo operation..........................................................................................................166
5.23.2 UDP Jitter operation ...........................................................................................................167
5.24 Security functions............................................................................................................................170
5.24.1 Port security functions........................................................................................................170
5.24.2 Port-based client authentication (IEEE 802.1x standard)...................................................171
5.24.3 DHCP protocol management and Option 82......................................................................179