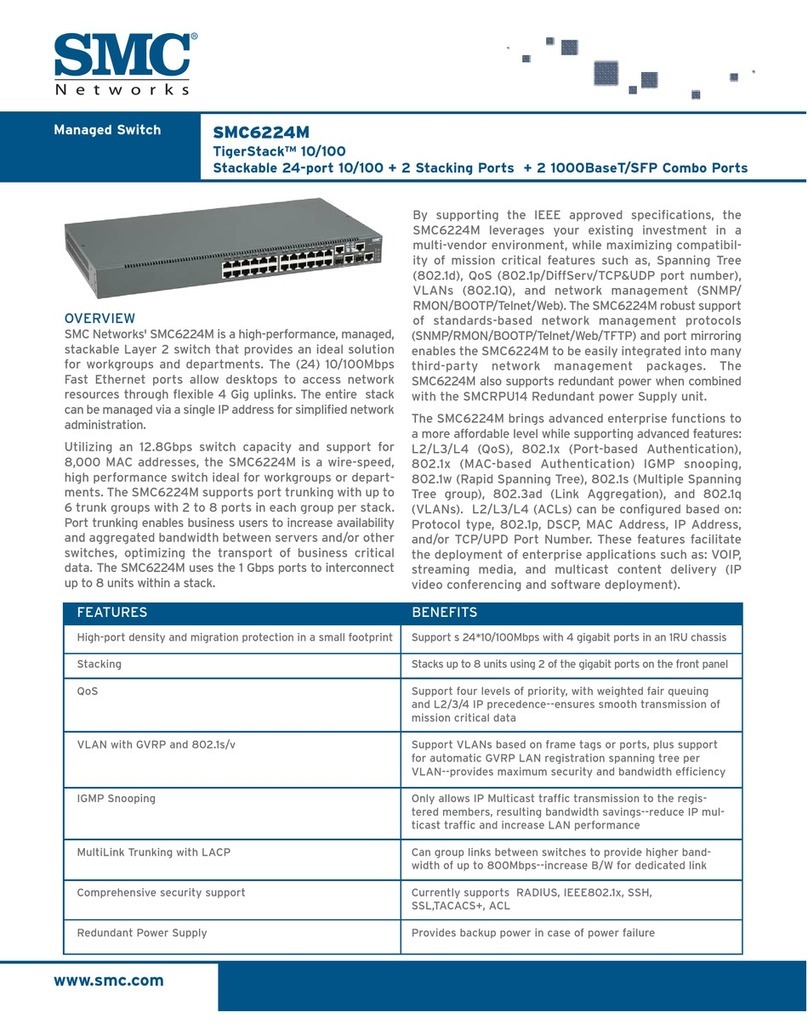
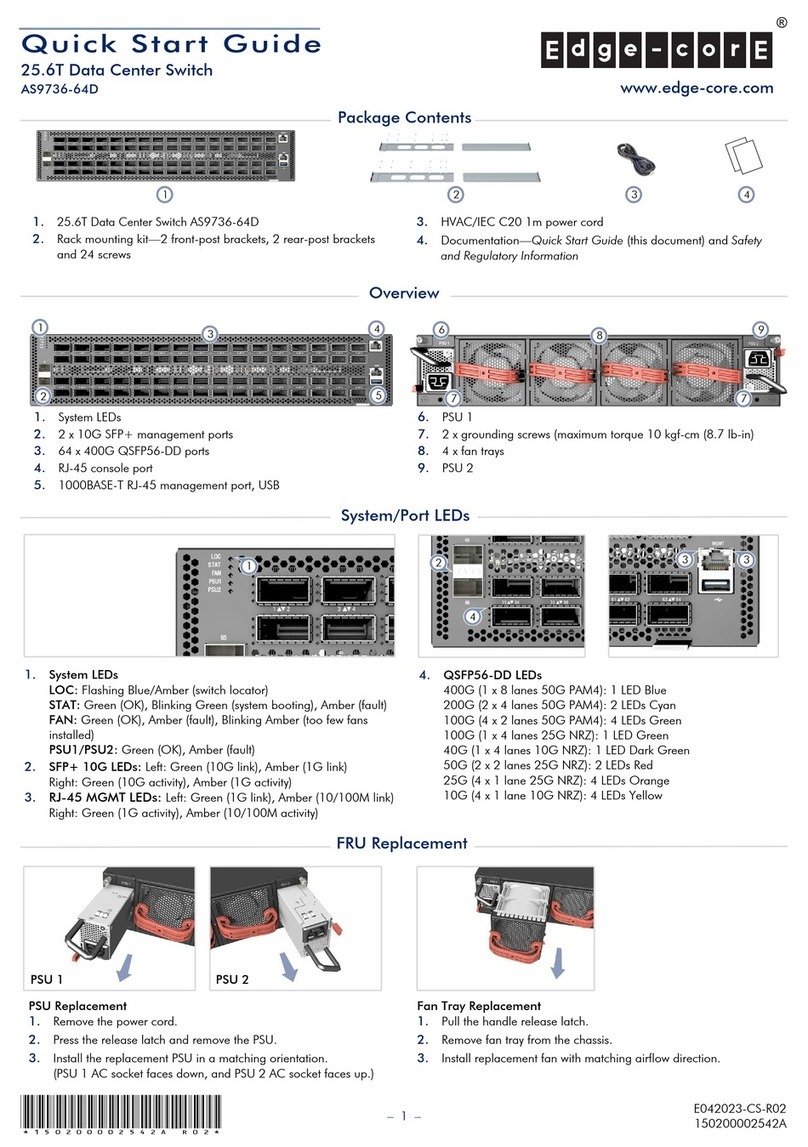
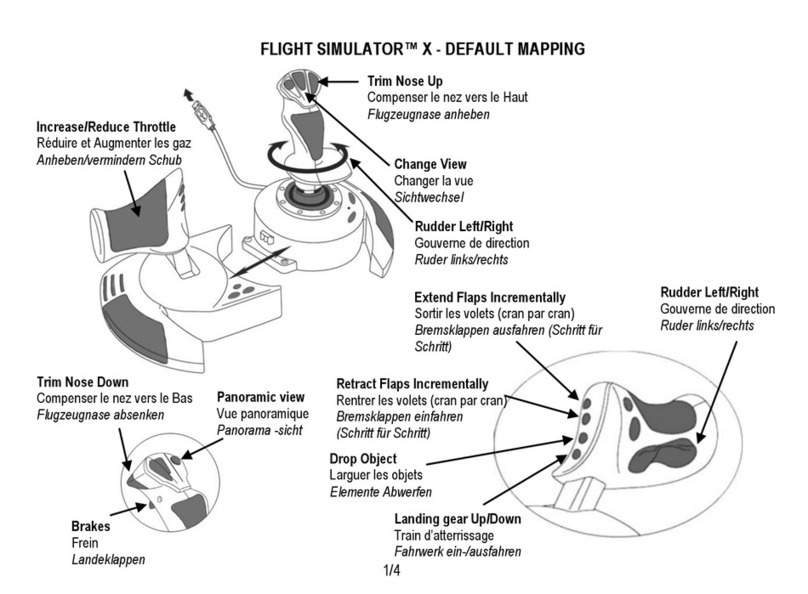
6MES1000, MES2000 Ethernet Switches
5.11 Selective Q-in-Q ................................................................................................................................ 75
5.12 Broadcast storm control ................................................................................................................... 76
5.13 Link Aggregation Groups (LAG)......................................................................................................... 77
5.13.1 Static link aggregation groups.............................................................................................. 78
5.13.2 LACP link aggregation protocol............................................................................................ 79
5.14 IPv4 addressing configuration .......................................................................................................... 80
5.15 IPv6 addressing configuration .......................................................................................................... 81
5.15.1 IPv6 protocol........................................................................................................................ 81
5.15.2 IPv6 protocol tunnelling (ISATAP)........................................................................................ 84
5.15.3 IPv6 RA guard function configuration.................................................................................. 86
5.15.4 DHCPv6 guard function configuration ................................................................................. 87
5.16 Protocol configuration...................................................................................................................... 88
5.16.1 DNS protocol configuration—domain name system........................................................... 88
5.16.2 ARP protocol configuration.................................................................................................. 89
5.16.3 GVRP protocol configuration ............................................................................................... 90
5.16.4 Loopback detection mechanism (loopback-detection) ....................................................... 92
5.16.5 STP protocol family (STP, RSTP, MSTP)................................................................................ 93
5.16.6 Flex-link function configuration........................................................................................... 99
5.16.7 EAPS protocol..................................................................................................................... 100
5.16.8 G.8032v2 (ERPS) protocol configuration ........................................................................... 101
5.16.9 LLDP protocol configuration .............................................................................................. 103
5.16.10OAM protocol configuration.............................................................................................. 108
5.16.11CFM protocol configuration............................................................................................... 110
5.17 Voice VLAN...................................................................................................................................... 113
5.18 Multicast addressing....................................................................................................................... 115
5.18.1 Multicast addressing rules................................................................................................. 115
5.18.2 IGMP snooping function .................................................................................................... 120
5.18.3 MLD snooping—multicast traffic control protocol for IPv6 networks .............................. 124
5.18.4 Multicast traffic restriction functions................................................................................ 126
5.18.5 RADIUS Authorization of IGMP Queries ............................................................................ 127
5.19 Control functions ............................................................................................................................ 129
5.19.1 AAA mechanism................................................................................................................. 129
5.19.2 RADIUS protocol ................................................................................................................ 133
5.19.3 TACACS+ protocol .............................................................................................................. 135
5.19.4 Simple network management protocol (SNMP)................................................................ 136
5.19.5 Remote network monitoring protocol (RMON) ................................................................ 140
5.19.6 ACL access lists for device management ........................................................................... 146
5.19.7 Access configuration.......................................................................................................... 147
5.20 Alarm log, SYSLOG protocol............................................................................................................ 151
5.21 Port mirroring (monitoring)............................................................................................................ 153
5.22 sFlow function................................................................................................................................. 155
5.23 Physical layer diagnostics functions ............................................................................................... 156
5.23.1 Copper-wire cable diagnostics........................................................................................... 156
5.23.2 Optical transceiver diagnostics .......................................................................................... 158
5.24 IP Service Level Agreements (IP SLA).............................................................................................. 160
5.24.1 ICMP Echo operation ......................................................................................................... 161
5.24.2 UDP Jitter operation .......................................................................................................... 163
5.25 Green Ethernet configuration......................................................................................................... 165
5.26 Power over Ethernet (PoE) ............................................................................................................. 167
5.27 Security functions ........................................................................................................................... 171
5.27.1 Port security functions....................................................................................................... 171
5.27.2 Port-based client authentication (802.1x standard).......................................................... 172
5.27.3 DHCP protocol management and Option 82 ..................................................................... 179
5.27.4 Client IP address protection (IP-source Guard) ................................................................. 183