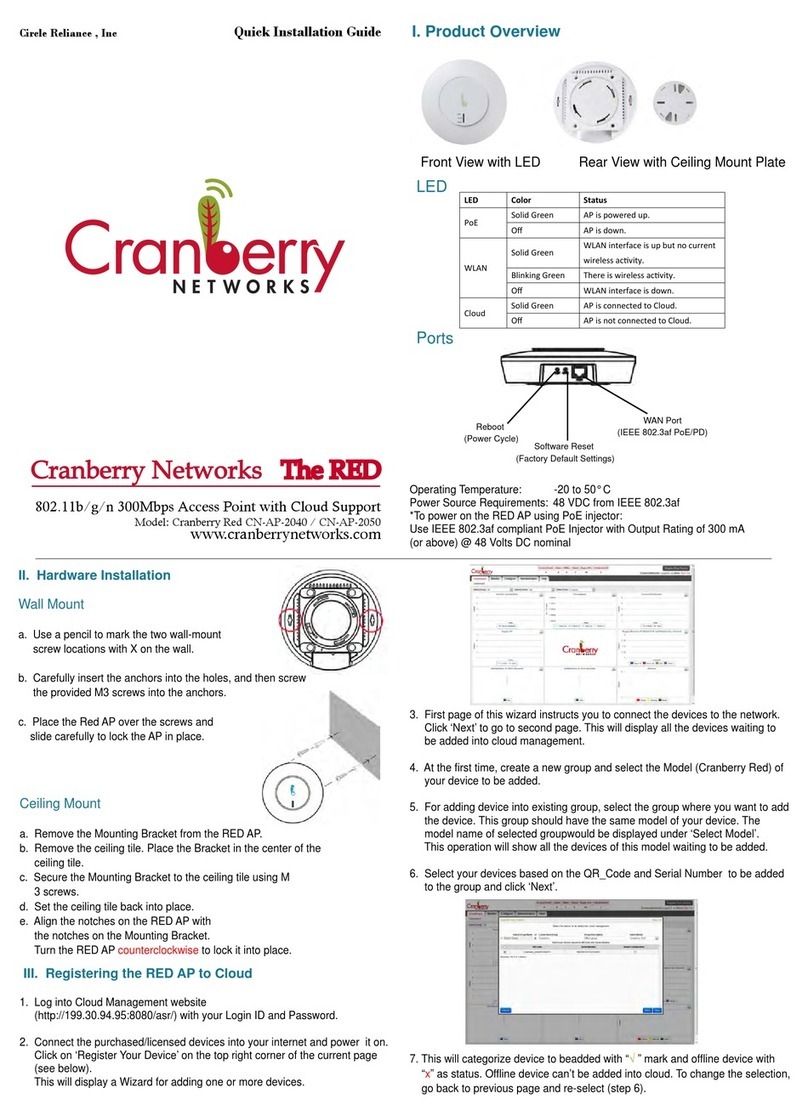
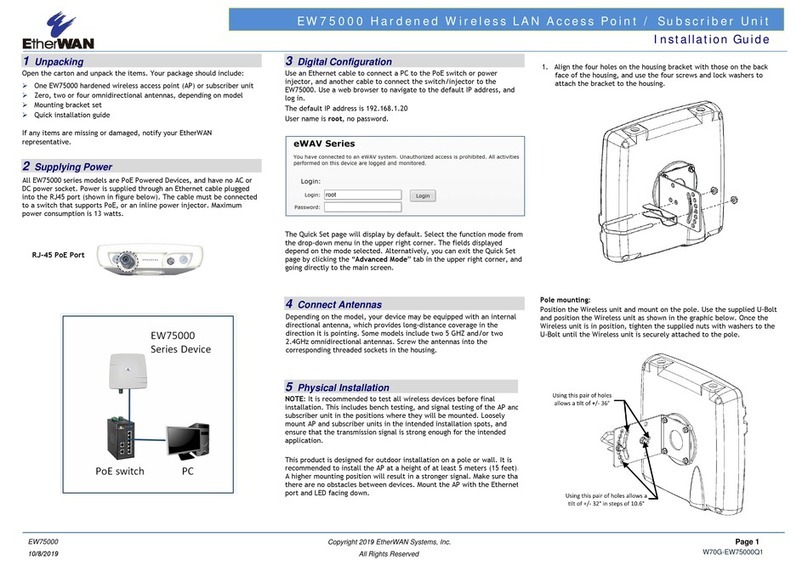
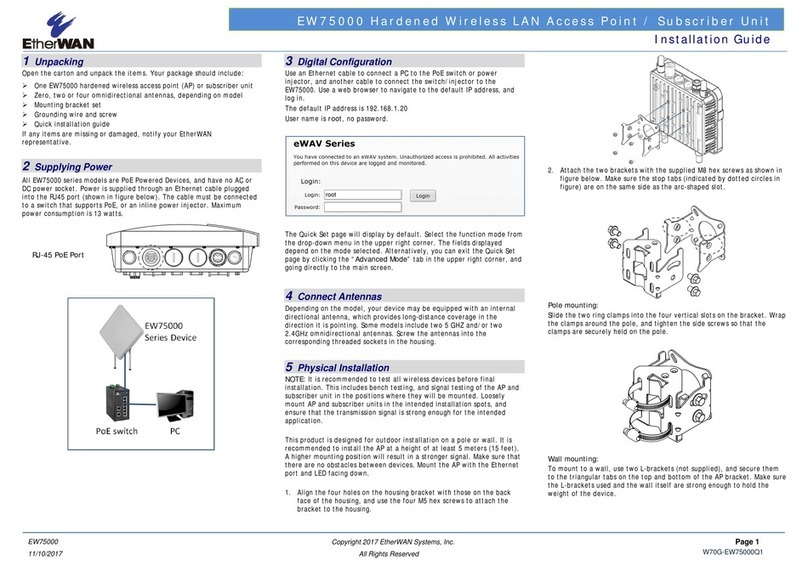
18
EW75000 Hardened Wireless LAN Access Point
Interface – Shows current interfaces. Clicking on an item in the table opens the detail page
for that interface.
Interface List – Allows for the defining of interface sets for easier interface management in
firewalls.
Ethernet – Click an Ethernet connection shown in the table to view or modify its
parameters.
VLAN – Add new and view existing VLANs. 802.1Q VLANs and Q-in-Q are supported.
Bridge
Ethernet-like networks (Ethernet, Ethernet over IP, IEEE802.11 in ap-bridge or bridge
mode, WDS, VLAN) can be connected together using MAC bridges. The bridge feature
allows the interconnection of hosts connected to separate LANs (using EoIP,
geographically distributed networks can be bridged as well if any kind of IP network
interconnection exists between them) as if they were attached to a single LAN. As bridges
are transparent, they do not appear in traceroute list, and no utility can make a distinction
between a host working in one LAN and a host working in another LAN if these LANs are
bridged (depending on the way the LANs are interconnected, latency and data rate
between hosts may vary).
Bridge – In the Bridge sub-tab, new bridges can be created, and existing bridges can be
managed.
Ports – This page shows which ports are assigned to which bridges. Click Add New to
add a new port to a bridge (Bridge must have already been created).
Filters – The bridge firewall implements packet filtering and thereby provides security
functions that are used to manage data flow to, from and through bridge. Filters can be
configured with one of three predefined chains:
input: filters packets, where the destination is the bridge (including those packets that
will be routed, as they are destined to the bridge MAC address anyway)
output: filters packets, which come from the bridge (including those packets that has
been routed normally)
forward: filters packets, which are to be bridged (note: this chain is not applied to the
packets that should be routed through the router, just to those that are traversing
between the ports of the same bridge)
NAT – Bridge network address translation provides ways for changing source/destination
MAC addresses of the packets traversing a bridge. It has two built-in chains:
srcnat: used for "hiding" a host or a network behind a different MAC address. This
chain is applied to the packets leaving the router through a bridged interface
dstnat: used for redirecting some packets to other destinations
Hosts – This is a read-only page that shows list of hosts connected to a bridge and their
corresponding MAC addresses.