Introduction 1
Introduction
Overview
This guide provides a quick introduction to the operations of your new
D/ESAM 8000 audio mixer. You will be up and running very quickly if
you follow the steps outlined in this guide. Several sections have step-
by-step examples after the general discussion of the operation or
feature.
The following information is covered in this QuickStart Guide:
Define Virtual Machines (page 4)
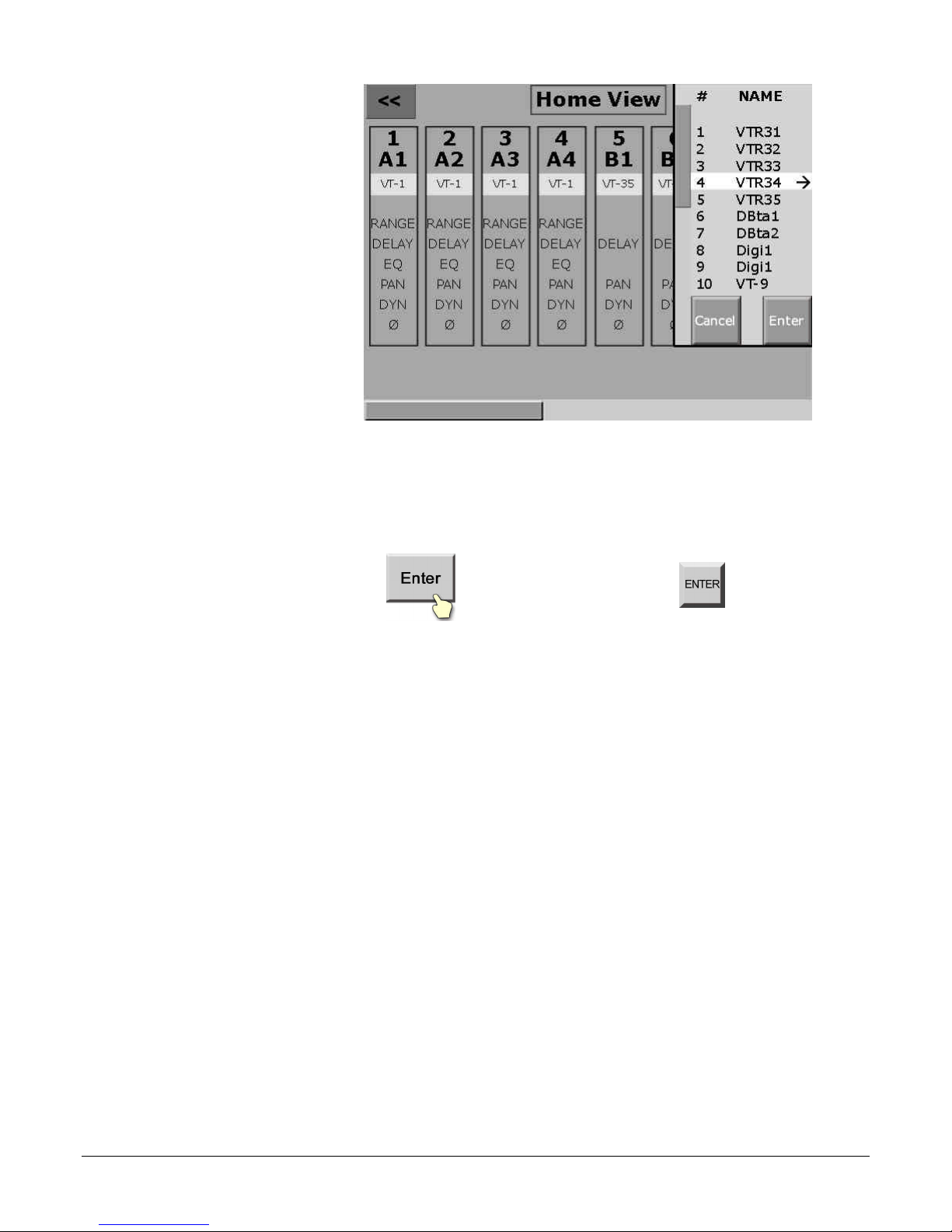
A virtual machine provides the unique ability to
group physical inputs and maintain this grouping
throughout the system via a name and/or number.
Assign Virtual Machines to Logical Machines (page 4)
Edit systems use the traditional Logical Machine
method of identifying sources. The 12 logical
machines (R, A, B, C, etc.) on the D/ESAM 8000 can
be reassigned at any time to a different virtual
machine. In this way, you are not limited by your
edit system’s logical machine sources.
Assign Logical Machines to Faders (page 6)
Once you have defined Virtual Machines and
assigned them to a Logical Machine, this step places
the logical machine on physical faders.
Configure Bus Assignment (page 10)
This section covers how to put a source on the
program and/or preview bus and allows you to re-
route source audio for recording and/or monitoring.
Monitoring Setup (page 12)
The monitoring section of the D/ESAM 8000 is
explained and diagramed. The Monitor Matrix allows
you to re-route monitor inputs to the speaker
outputs and adjust the level to provide a monitor
sub-mix.
Edit Interface Configuration (page 14)
The D/ESAM 8000 is fully controllable by a number
of edit systems and gives you options on the level of
control you would like.