1
Content
I. Technical indicators and specifications of products................................................................................................2
II. Inverter Installation and Wiring............................................................................................................................. 4
2.1 Matters needing attention for Installation.....................................................................................................4
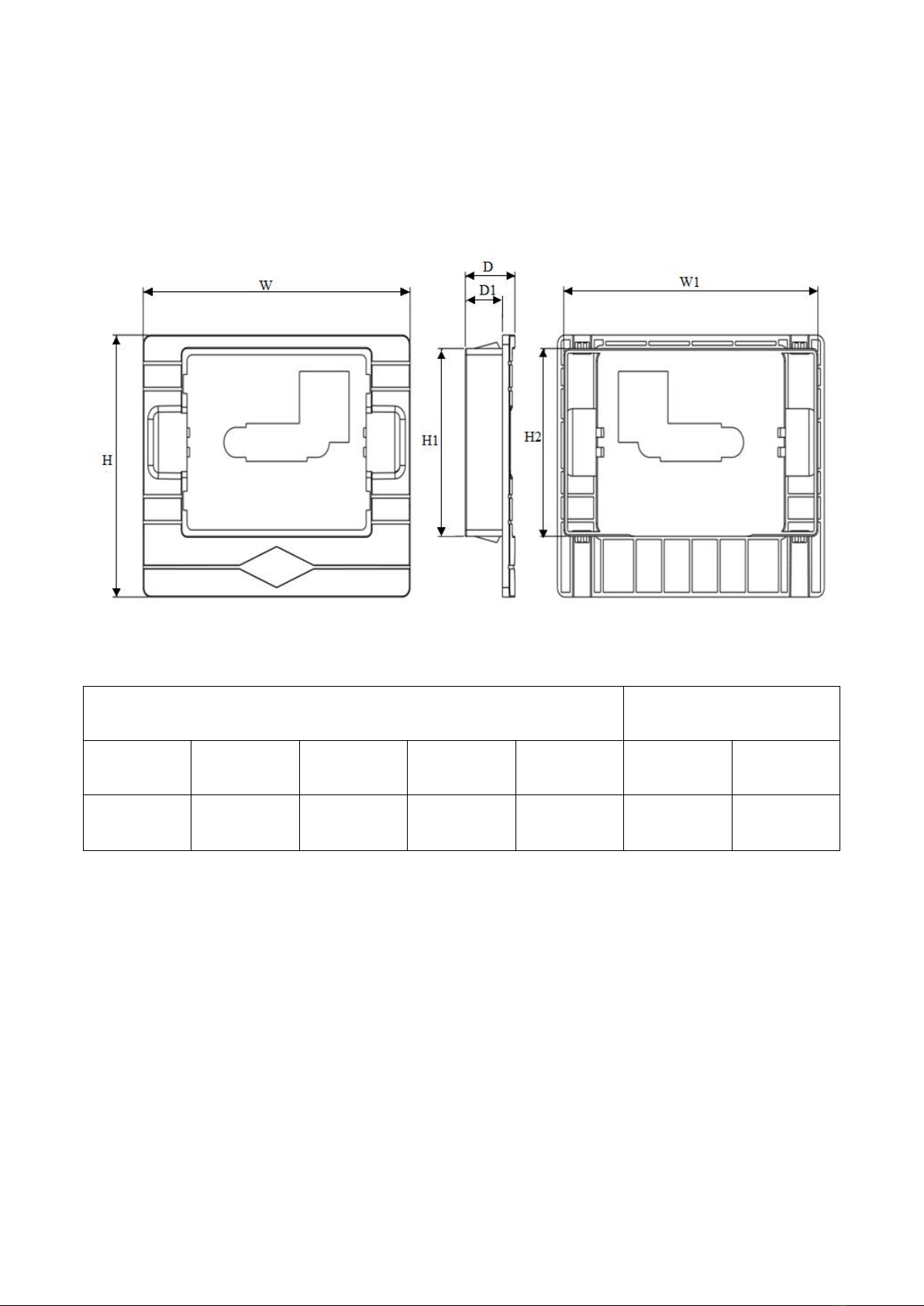
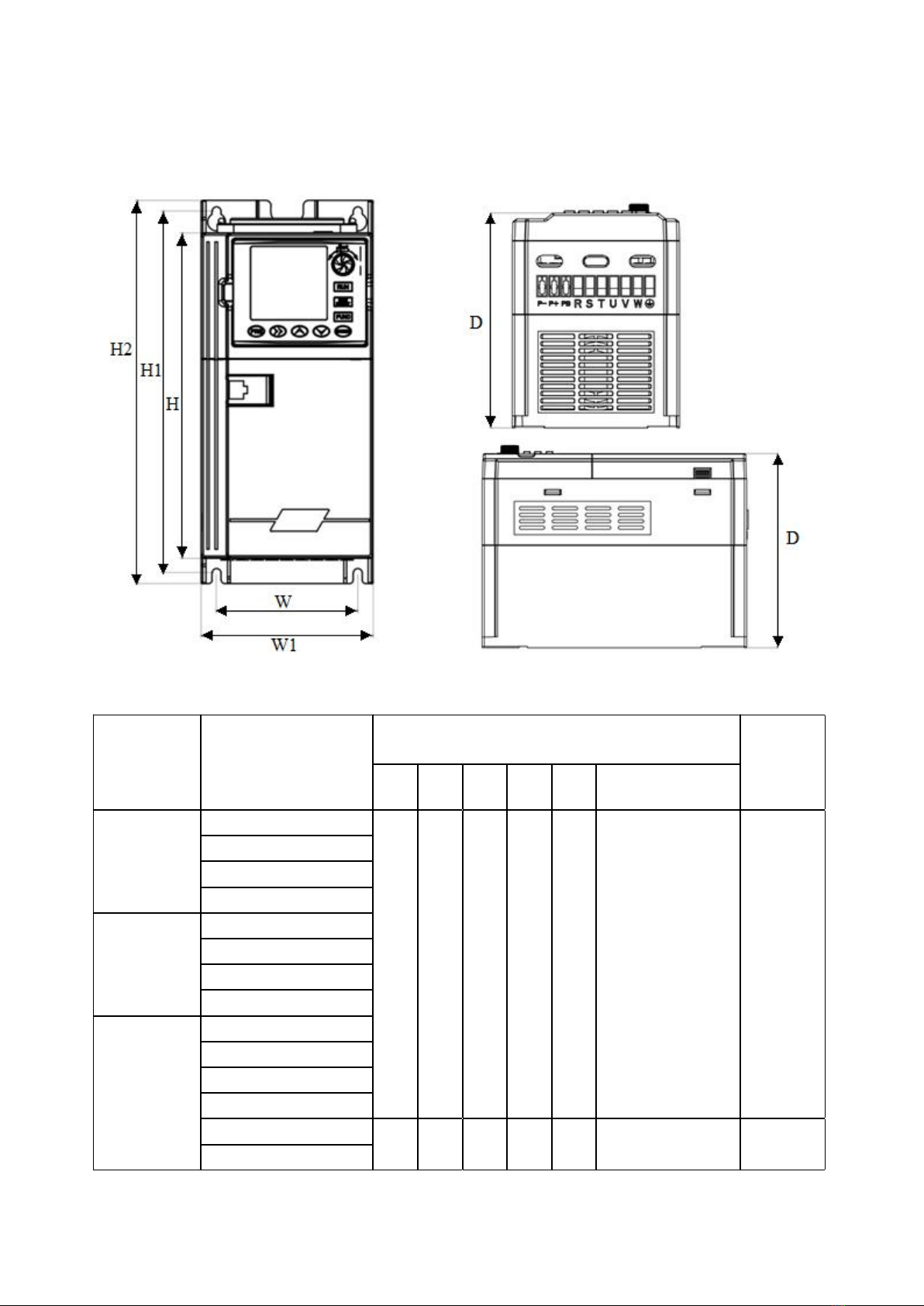
2.2 Outline drawing.............................................................................................................................................5
a. Overall dimensions of keypad base........................................................................................................ 5
b. Overall dimensions of the whole machine..............................................................................................6
2.3 Basic operation wiring.................................................................................................................................. 7
2.4 terminal for controlling loop.........................................................................................................................7
2.5 Matters needing attention for Wiring............................................................................................................9
III Communication protocol......................................................................................................................................10
1.RTU mode and format....................................................................................................................................10
2.Description of reading and writing function code:........................................................................................10
3.Register address............................................................................................................................................10
4.Description of parameter address of communication protocol:.................................................................... 10
5. 03H Reading function mode:........................................................................................................................ 12
6. 06H write function mode.............................................................................................................................. 13
IV. Exceptions and Handling.....................................................................................................................................15
V. Parameters instructions.........................................................................................................................................16
VI. Parameter description......................................................................................................................................... 31
00 group-basic operating parameters................................................................................................................31
01 group-auxiliary operating parameters..........................................................................................................36
02 group-analog and digital input and output parameters................................................................................ 42
03 group -PID parameters.................................................................................................................................49
04 group -advanced functions parameters........................................................................................................ 53
05 group- Protective Function parameters........................................................................................................56
06 group: communication parameters...............................................................................................................59
07 group- supplementary Function parameters................................................................................................ 61
08 group-manage and display parameters........................................................................................................ 63
Warranty agreement.................................................................................................................................................. 65