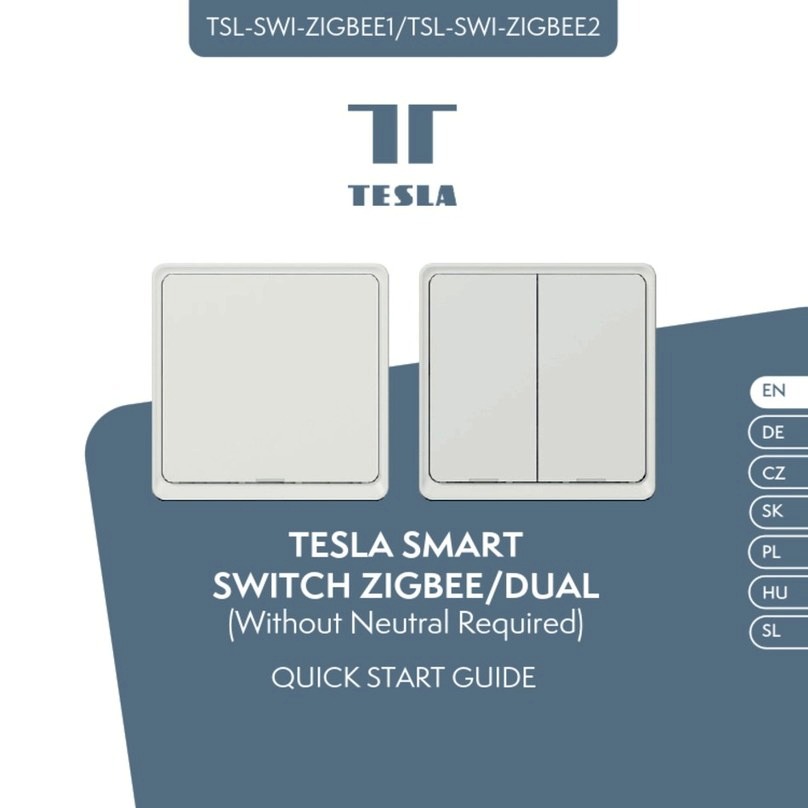
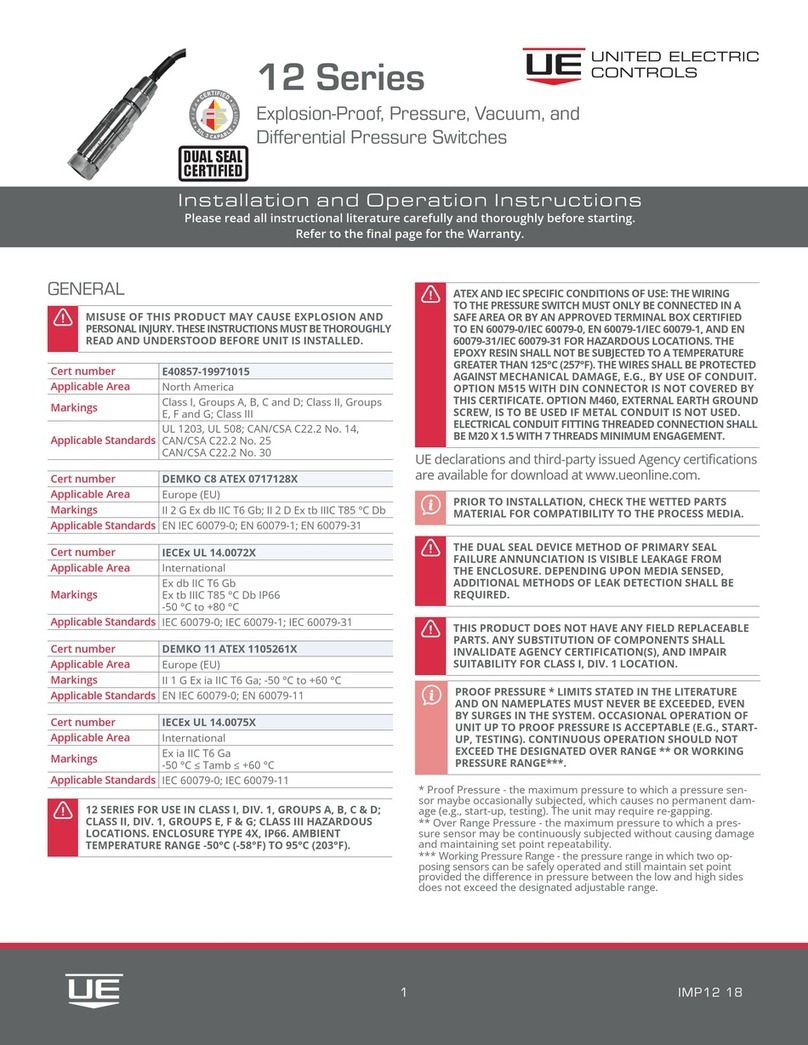
The information contained in this document supersedes all similar information that
may be found elsewhere in this manual.
Service –Due to the sophisticated
nature of the sensors and associated
instrumentation provided by PCB
Piezotronics, user servicing or repair is
not recommended and, if attempted,
may void the factory warranty. Routine
maintenance, such as the cleaning of
electrical connectors, housings, and
mounting surfaces with solutions and
techniques that will not harm the
physical material of construction, is
acceptable. Caution should be observed
to ensure that liquids are not permitted
to migrate into devices that are not
hermetically sealed. Such devices
should only be wiped with a dampened
cloth and never submerged or have
liquids poured upon them.
Repair –In the event that equipment
becomes damaged or ceases to
operate, arrangements should be made
to return the equipment to PCB
Piezotronics for repair. User servicing or
repair is not recommended and, if
attempted, may void the factory
warranty.
Calibration –Routine calibration of
sensors and associated instrumentation
is recommended as this helps build
confidence in measurement accuracy
and acquired data. Equipment
calibration cycles are typically
established by the users own quality
regimen. When in doubt about a
calibration cycle, a good “rule of thumb”
is to recalibrate on an annual basis. It is
also good practice to recalibrate after
exposure to any severe temperature
extreme, shock, load, or other
environmental influence, or prior to any
critical test.
PCB Piezotronics maintains an ISO-
9001 certified metrology laboratory and
offers calibration services, which are
accredited by A2LA to ISO/IEC 17025,
with full traceability to SI through
N.I.S.T. In addition to the normally
supplied calibration, special testing is
also available, such as: sensitivity at
elevated or cryogenic temperatures,
phase response, extended high or low
frequency response, extended range,
leak testing, hydrostatic pressure
testing, and others. For information on
standard recalibration services or
special testing, contact your local PCB
Piezotronics distributor, sales
representative, or factory customer
service representative.
Returning Equipment –Following
these procedures will ensure that your
returned materials are handled in the
most expedient manner. Before
returning any equipment to PCB
Piezotronics, contact your local
distributor, sales representative, or
factory customer service representative
to obtain a Return Warranty, Service,
Repair, and Return Policies and
Instructions Materials Authorization
(RMA) Number. This RMA number
should be clearly marked on the outside
of all package(s) and on the packing
Service, Repair, and Return
Policies and Instructions