Contents
1 Overview .................................................................................................................................. 1
2 Installation and Setting........................................................................................................... 2
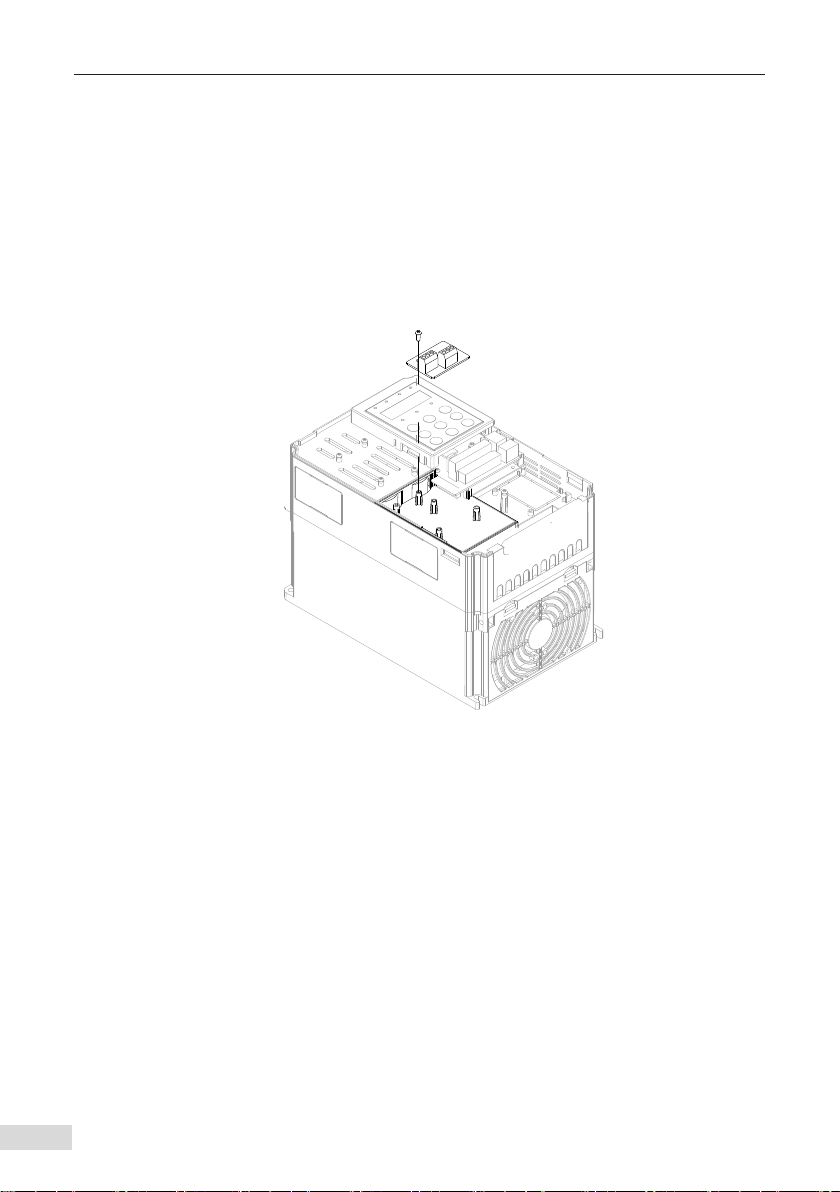
2.1 Installation of MD380CAN2 ........................................................................................... 2
2.2 Hardware Layout ........................................................................................................... 2
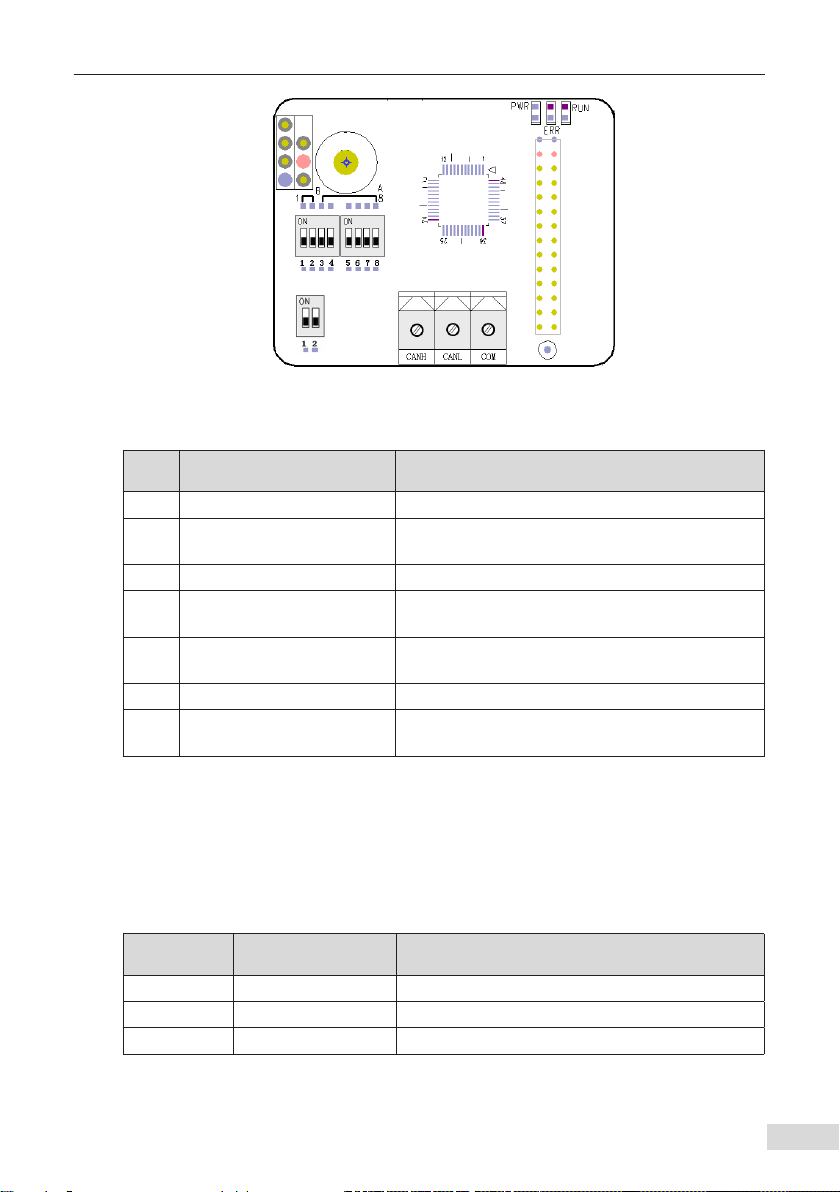
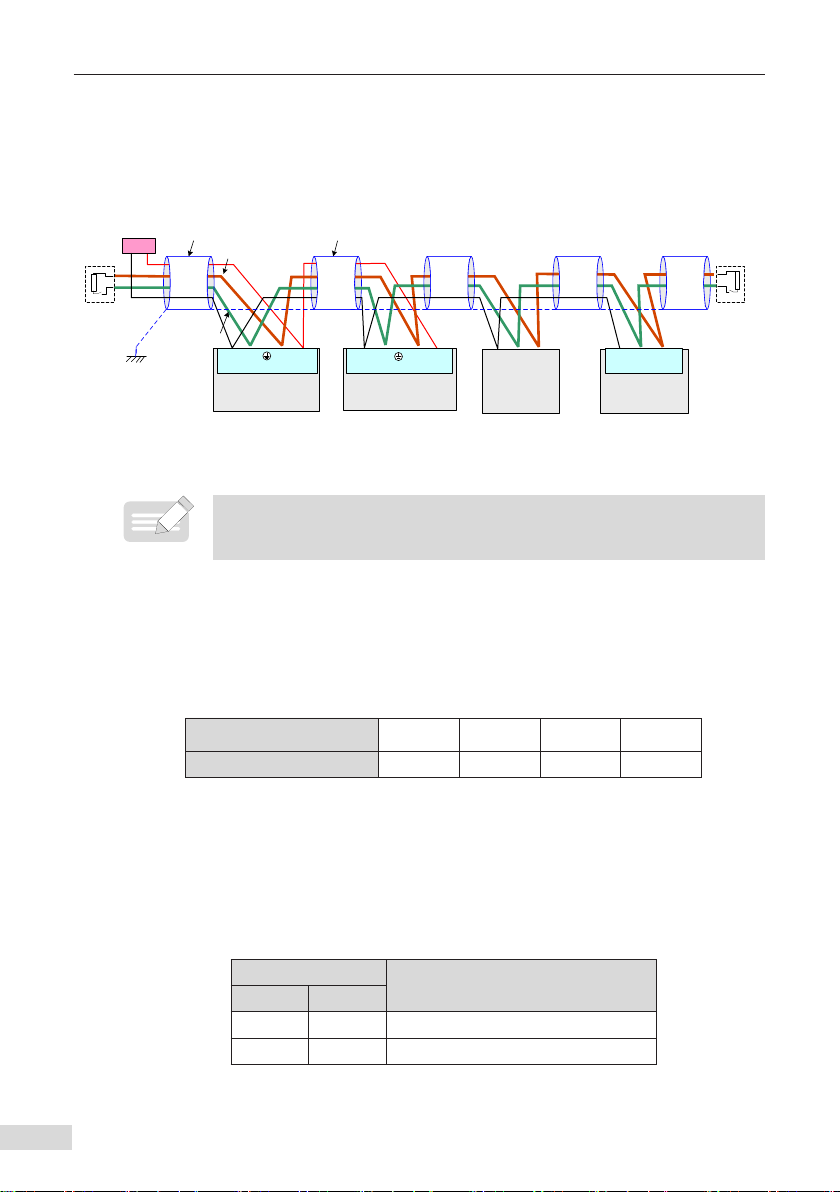
2.3 Interface Description ..................................................................................................... 3
3 Protocol Description of the MD38CAN2................................................................................. 7
3.1 Software Feature ........................................................................................................... 7
3.2 COB-ID ............................................................................................................................ 7
3.3 Parameter Operation of AC Drive.................................................................................. 8
3.4 SDO Read-Write Operations........................................................................................ 10
3.5 PDO AC Drive Operation.............................................................................................. 13
4 Parameters Related to CANopen Communication ............................................................. 15
4.1 CANopen Card Enabling.............................................................................................. 15
4.2 Parameters Related to Communication Control....................................................... 15
4.3 Parameters Related to Communication Monitoring................................................. 16
4.4 Emergency Message and AC Drive Fault Description................................................ 19
5 Simple Diagnosis................................................................................................................... 21
5.1 Brief Introduction ........................................................................................................ 21
5.2 Diagnosis...................................................................................................................... 21
5.3 Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................... 21
6 Overview of the CANopen Protocol ..................................................................................... 22
6.1 Brief Introduction ........................................................................................................ 22
6.2 Object Dictionary......................................................................................................... 22
6.3 Common Communication Objects............................................................................. 23
7 Format Description of CANopen Message........................................................................... 24
7.1 NMT Module Control Message.................................................................................... 24
7.2 NodeGuarding Message .............................................................................................. 24
7.3 Heartbeat Message...................................................................................................... 25
Revision History ....................................................................................................................... 26
Warranty Agreement................................................................................................................ 27