Keith & Koep GmbH Functional specification
MT6N (MT606) 5von 49
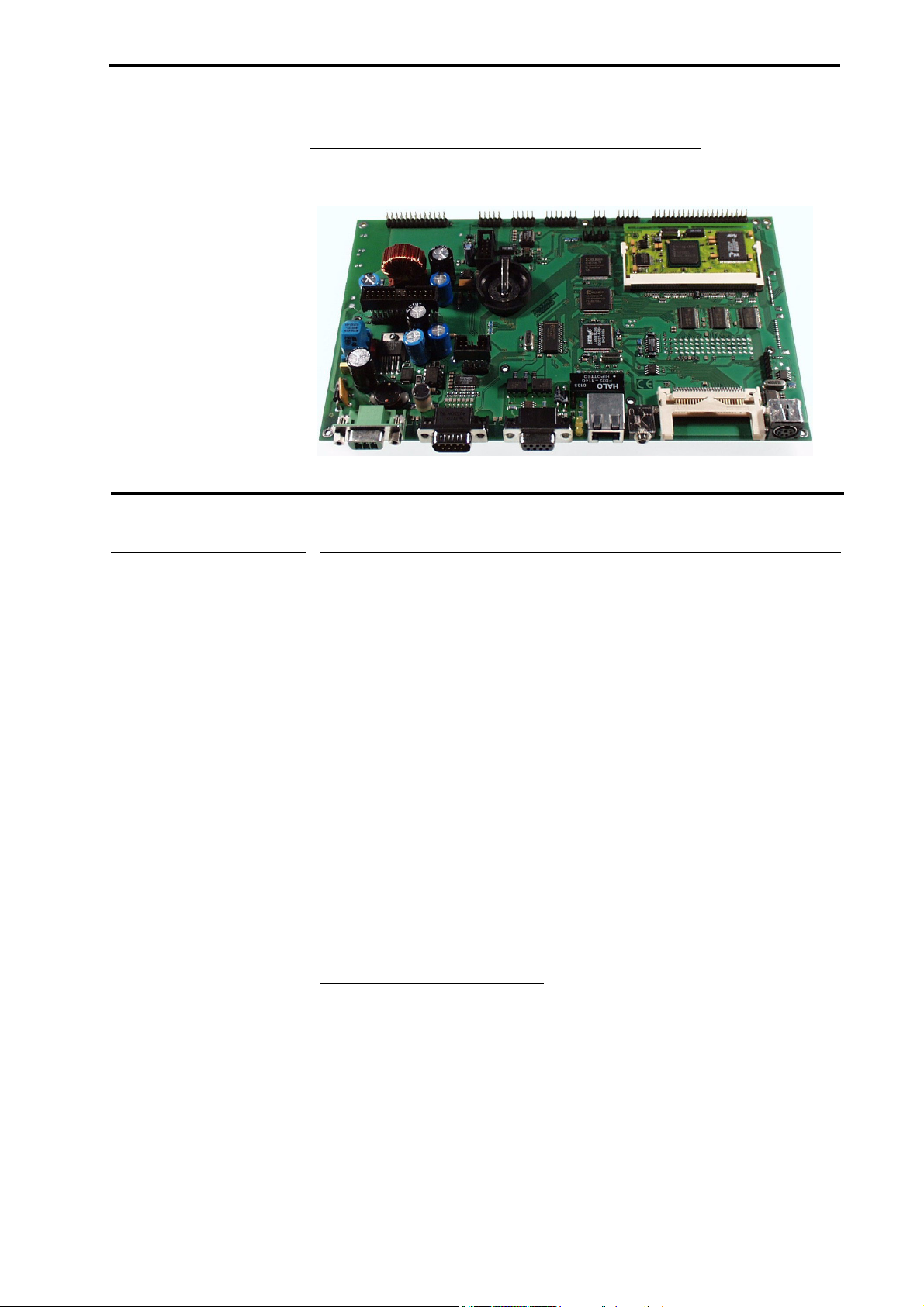
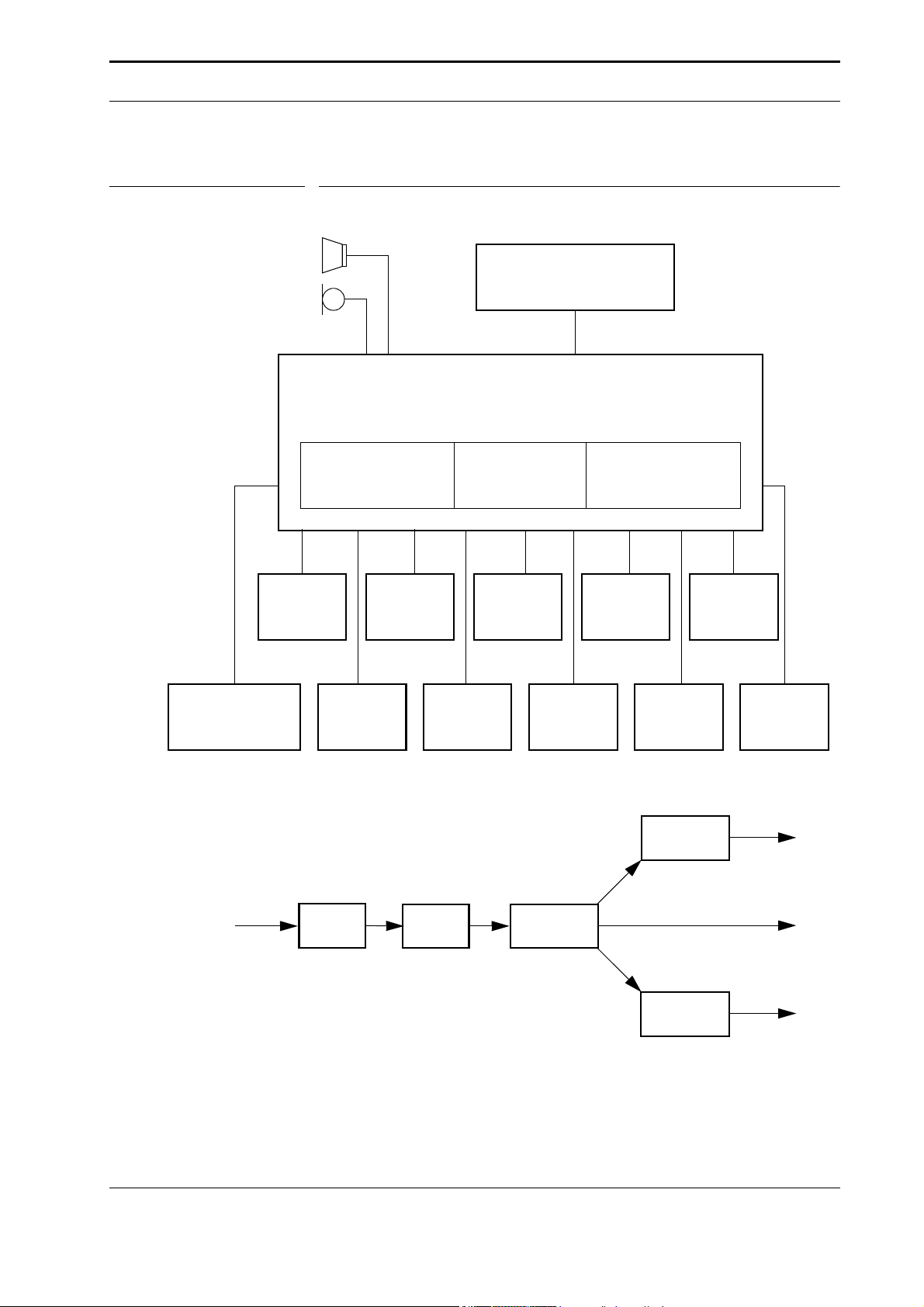
3.1 Trizeps
The MT6 board is fitted out either with the Trizeps I or the Trizeps II module.
3.1.1 Trizeps I
The Trizeps board is based on the Intel StrongArm SA-1110 Microprocessor - a
highly integrated communications microcontroller that incorporates a 32-bit Strong-
Arm Risc Processor core, system support logic, multiple communication channels,
an LCD controller, a memory and PCMCIA controller, and general-purpose I/O
ports.The SA-1110 is working very fast (150 Dhrystone 2.1 MIPS @ 133 MHz or
235 Dhrystone 2.1 MIPS @ 206 MHz) and needs very low power. Trizeps includes
also the Philips UCB 1200 (a single chip, integrated mixed signal audio and telecom
codec). The single channel audio codec is designed for direct connection of a micro-
phone and a speaker. The built-in telecom codec can directly be connected to a
DAA and supports high speed modem protocols. The incorporated analog to digital
converter and the touch screen interface provides complete control and read-out of
an 4 wire resistive touch screen.
3.1.2 Trizeps II
The Trizeps II Module is based on the Intel® XScale™ core-based CPU (200, 300
and 400 MHz) PXA250 - ARM Architecture v.5TE compliant and application code
compatible with Intel® SA-1110 processor which is used on the Trizeps I module.
The CPU based on Intel® Superpipelined RISC technology utilizing advanced Intel
0.18µ process for high core speeds at low power (480K Dhrystone 2.1 per second
@ 400 MHz). Some features of the XScale: Integrated memory and PCMCIA/Com-
pactFlash Controller with 100MHz Memory Bus, 16-bit or 32-bit ROM/Flash/
SRAM six banks, 16-bit or 32-bit SDRAM; System Control Module includes 17
dedicated general-purpose interruptible I/O ports, real-time clock, watchdog and
interval timers, power management controller, interrupt and reset controller, LCD
controller and two on-chip oscillators. Trizeps-II includes also the Philips UCB
1400, on a single chip it combines audio codec functions, a touch-screen controller
and power management interfaces. The incorporated A/D converter and the touch
screen interface provides complete control and read-out of a 4 wire resistive touch
screen.
3.2 Serial EEPROM (optional)
MT6N provides a serial EEPROM (X24C16- Xicor) to be used as a non-volatile
memory. It has a size of 16KBit and it is internal organized as 2048 x 8. The
X24C16 offers a serial interface and a software protocol allowing operation on a
simple two wire bus with I2C_CLK (GPIO26 of SA-1110) and I2C_DATA (GPIO27
of SA-1110). The EEPROM is optional and usually not placed.
FIGURE 2. The slave address of the EEPROM:
•Read address: A1
•Write address: A0
1010000R/W
Device Type
Identifier
High order
word address