Table of Contents Kübler Group
2 - EN HB Modbus Interface - R67048.0002 - 02
Table of Contents
1 Document ........................................................................................................................ 4
2 General Information........................................................................................................ 5
2.1 Target Group........................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Symbols used / Warnings and Safety instructions.................................................. 5
3 Product Description ....................................................................................................... 7
3.1 Technical Data Sendix F58xx ................................................................................. 7
4 Installation....................................................................................................................... 8
4.1 Electrical Installation ............................................................................................... 8
4.1.1 General Information for the Connection.................................................... 8
4.1.2 Information for EMC-Compliant Installation .............................................. 8
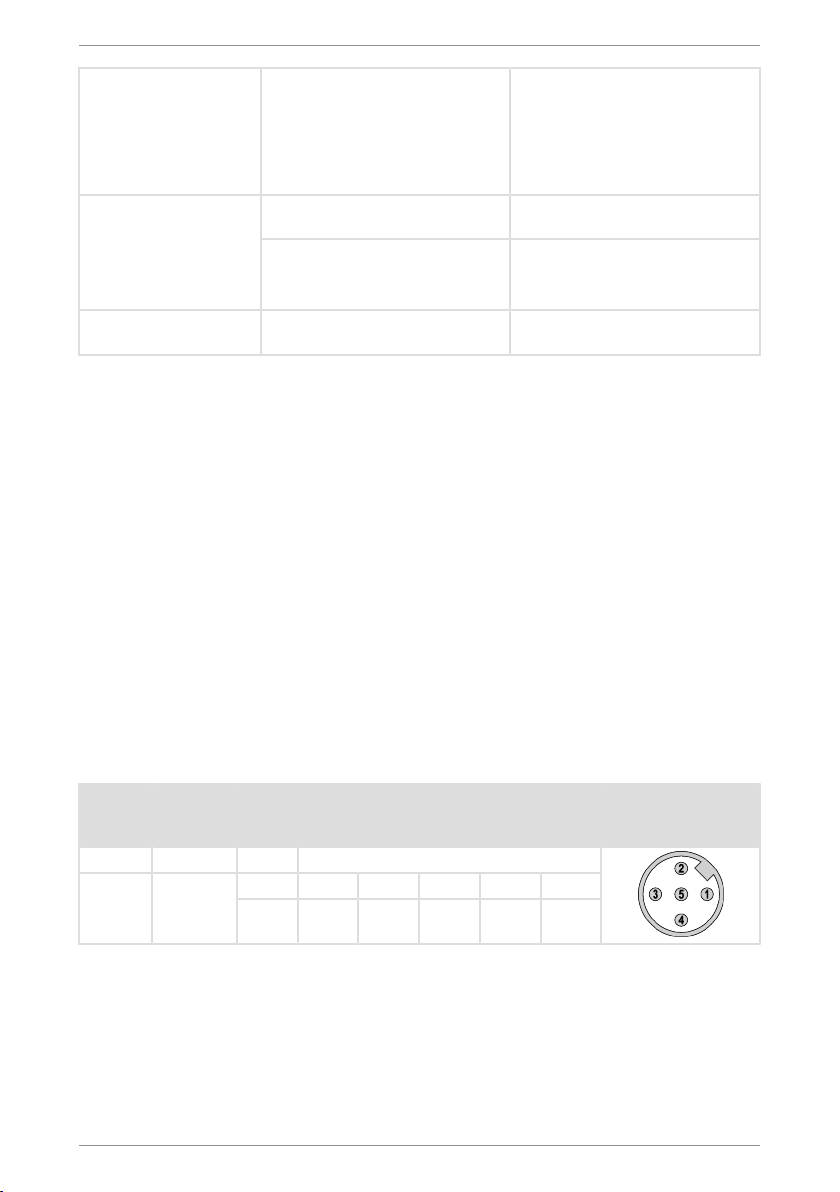
4.1.3 Terminal Assignment ................................................................................ 9
4.1.4 Network topology ...................................................................................... 10
5 Commissioning and Operation ..................................................................................... 11
5.1 Function and Status LED ........................................................................................ 11
5.2 Quick Start Guide.................................................................................................... 11
5.2.1 Changing the parameters ......................................................................... 11
5.2.2 Not supported Modbus function codes ..................................................... 12
5.2.3 Default settings ......................................................................................... 12
5.3 Protocol Features.................................................................................................... 13
5.3.1 Structure of the Modbus RTU frames ....................................................... 13
5.3.2 Function codes.......................................................................................... 14
5.3.3 LRC check................................................................................................. 16
5.3.4 Data Addresses......................................................................................... 16
5.4 Function code 03 - Reading the Holding Register .................................................. 16
5.5 Function Code 16 - Writing the Holding Register.................................................... 18
5.6 Function code 17 - Query of Device-Specific Information....................................... 22
5.7 Description of the Registers.................................................................................... 24
5.7.1 Reading the Holding Register ................................................................... 24
5.7.2 Writing the Holding Register ..................................................................... 27
5.8 Modbus Exception Codes ....................................................................................... 31
5.9 Examples ................................................................................................................ 31
5.9.1 Scaling Setting Example ........................................................................... 31
5.9.2 Count Direction Change Example............................................................. 32
5.9.3 Preset Setting Example ............................................................................ 33
6 Maintenance .................................................................................................................... 34
7 Annex............................................................................................................................... 35
7.1 Decimal / Hexadecimal conversion table ................................................................ 35
8 Contact ............................................................................................................................ 37