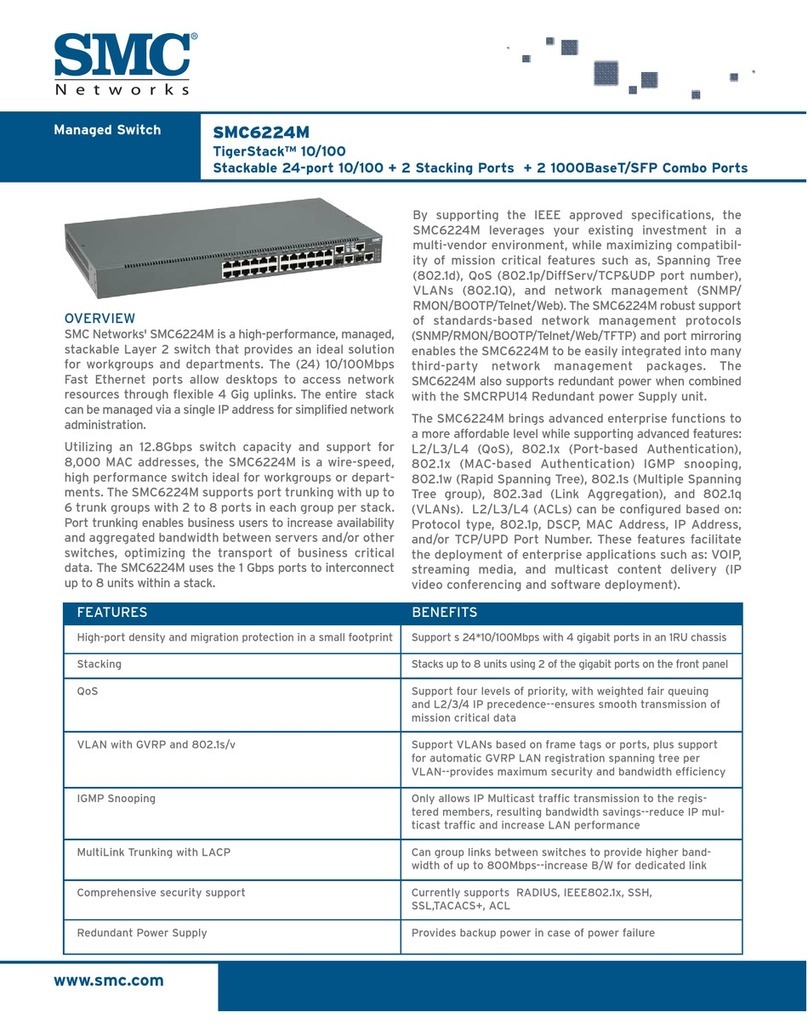
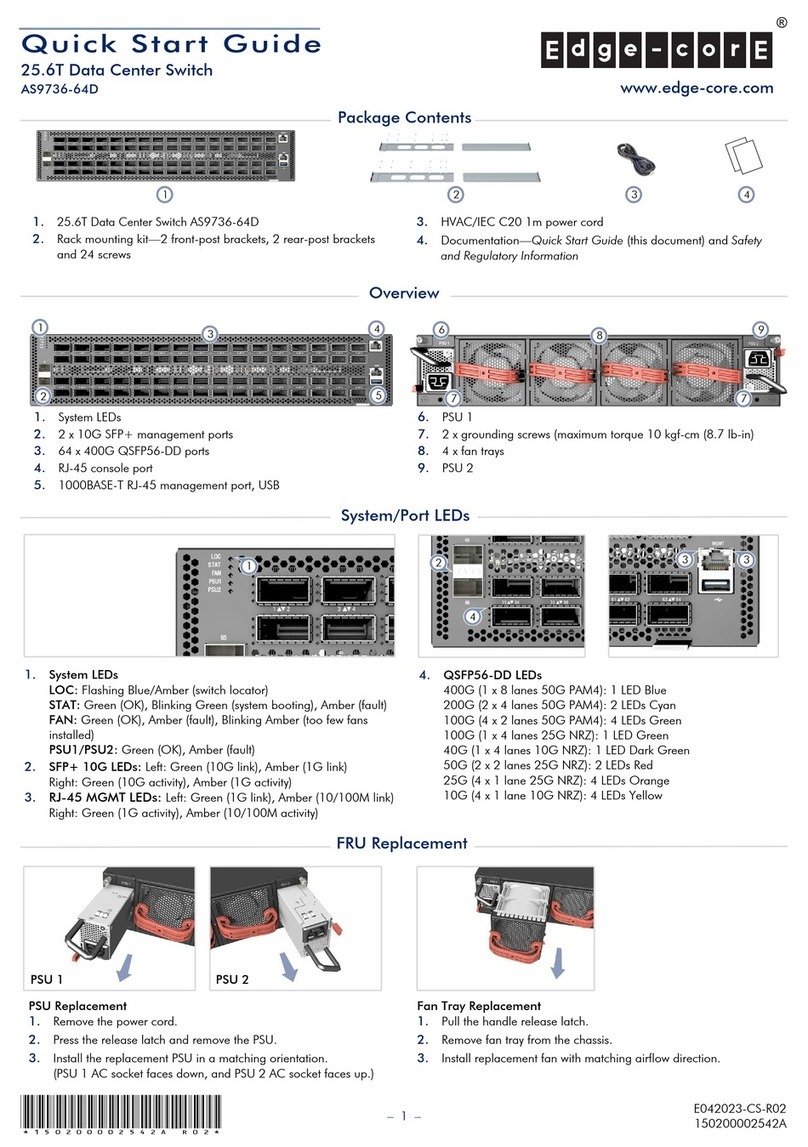
OPTICAL SYSTEMS DESIGN
DOC ID: 10111504
OSD2700F OPERATOR MANUAL
PAGE 3
INDEX 1
1
QUICK START GUIDE ............................................................................................................ 5
1.1
FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION .............................................................................................. 5
1.2
PHYSICAL
DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................... 6
1.3
CONSOLE
CONFIGURATION .............................................................................................. 6
1.3.1
CONNECT TO THE SWITCH CONSOLE:........................................................................ 6
1.3.2
CONFIGURATION SETTINGS OF THE TERMINAL-EMULATION PROGRAM:....... 7
1.4
WEB
CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................ 8
2
TECHNICAL SUMMARY........................................................................................................ 9
2.1
BRIEF
DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................ 9
2.1.1
PREFACE............................................................................................................................. 9
2.1.2
OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................... 9
2.1.3
APPLICATIONS.................................................................................................................. 9
2.1.4
FEATURES AND BENEFITS............................................................................................. 9
2.2
TYPICAL
CONFIGURATION.............................................................................................. 10
2.3
TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS ......................................................................................... 11
2.4
OSD2700F
FRONT
AND
REAR
PANELS............................................................................ 12
2.4.1
OSD2700F DIMENSIONS ................................................................................................ 12
3
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION................................................................................... 13
3.1
INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................. 13
3.2
INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.1
WARNING AND PRECAUTIONS................................................................................... 13
3.2.2
POWER SUPPLY CONNECTIONS ................................................................................. 14
3.2.3
DB9 CONFIGURATION CONNECTIONS...................................................................... 14
3.2.4
LED INDICATORS ........................................................................................................... 14
3.2.5
FITTING SFP CONNECTORS.......................................................................................... 15
3.3
OSD2700F
OPERATION....................................................................................................... 16
3.3.1
CABLE CONNECTIONS .................................................................................................. 16
4
SWITCH MANAGEMENT..................................................................................................... 17
4.1
M
ANAGEMENT
A
CCESS
O
VERVIEW
......................................................................................... 17
4.2
A
DMINISTRATION
C
ONSOLE
(CLI) .......................................................................................... 17
4.2.1
DIRECT ACCESS.............................................................................................................. 17
4.2.2
MODEM ACCESS ........................................................................................................... 18
4.3
W
EB
M
ANAGEMENT
................................................................................................................ 18
4.4
SNMP-B
ASED
N
ETWORK
M
ANAGEMENT
............................................................................... 18
4.5
P
ROTOCOLS
............................................................................................................................. 19
4.6
M
ANAGEMENT
A
RCHITECTURE
............................................................................................... 19
5
SNMP & RMON MANAGEMENT........................................................................................ 20
5.1
O
VERVIEW
.............................................................................................................................. 20
5.2
SNMP
A
GENT AND
MIB-2
(RFC
1213) .................................................................................. 20
5.3
RMON
MIB
(RFC
2819)
AND
B
RIDGE
MIB
(RFC
1493) ....................................................... 21
5.3.1
RMON GROUPS SUPPORTED........................................................................................ 21
5.3.2
BRIDGE GROUPS SUPPORTED..................................................................................... 21
6
WEB-BASED BROWSER MANAGEMENT........................................................................ 22
6.1
L
OGGING ON TO THE SWITCH
................................................................................................... 22
6.2
U
NDERSTANDING THE
B
ROWSER
I
NTERFACE
.......................................................................... 23
6.3
S
YSTEM
................................................................................................................................... 24
6.4
S
WITCHING
.............................................................................................................................. 37
6.5
T
RUNKING
............................................................................................................................... 41
6.6
STP
/
R
ING
.............................................................................................................................. 42