Contents
1EmStat development board features ................................................................................................. 2
Circuit protection ...................................................................................................................... 2
Power options .......................................................................................................................... 2
Communication options............................................................................................................ 3
Potentiostat interfaces .............................................................................................................. 3
Arduino Integration ................................................................................................................... 3
Other ........................................................................................................................................ 3
2First measurement using PSTrace ..................................................................................................... 4
3Getting started with the PalmSens Embedded SDK libraries ............................................................. 6
4Getting started with Arduino/Genuino................................................................................................ 7
Requirements ........................................................................................................................... 7
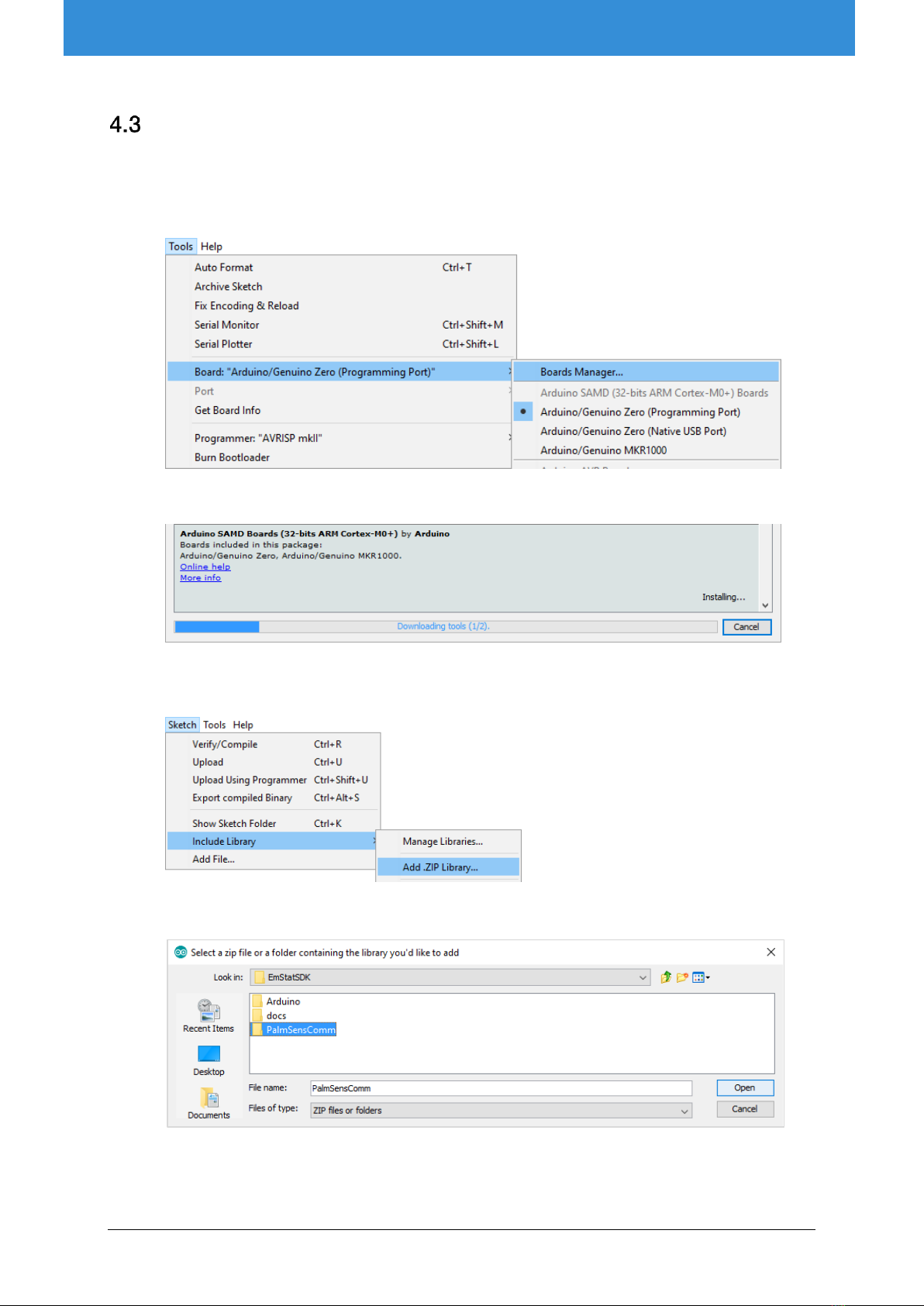
Preparing the EmStat dev. board for use with Arduino ............................................................. 7
Running the EmStat SDK Example for Arduino......................................................................... 8
4.3.1 Controlling the Arduino via terminal....................................................................................... 9
5Power supply options...................................................................................................................... 11
6Communication options .................................................................................................................. 11
PalmSens AUX pinout............................................................................................................. 12
RS232 communications ......................................................................................................... 12
Serial communication at TTL level........................................................................................... 12
7Pin descriptions............................................................................................................................... 13
Pinout of LEMO sensor socket (CON8)................................................................................... 13
Pinout of SPE connector (CON11) .......................................................................................... 13
CON4 pinout .......................................................................................................................... 13
CON5 pinout .......................................................................................................................... 14
8Adding a multiplexer........................................................................................................................ 15
9Noise considerations ....................................................................................................................... 16
Shielding can .......................................................................................................................... 16
10 Changing EmStat baudrate settings ............................................................................................ 17
11 Updating EmStat firmware........................................................................................................... 17
Programming the EmStat with custom firmware ..................................................................... 17
Updating the EmStat’s firmware via serial connection............................................................. 18
12 EmStat3 and EmStat3+ module specifications ............................................................................ 19
Appendix A: Change EmStat USB connection to virtual COM port ......................................................... 20