3
KX-TG4011LAT/KX-TG4012LAT/KX-TG4013LAT/KX-TGA403LAT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE PAGE
1 Safety Precautions----------------------------------------------- 4
1.1. For Service Technicians --------------------------------- 4
2 Warning -------------------------------------------------------------- 4
2.1. Battery Caution--------------------------------------------- 4
2.2. About Lead Free Solder (PbF: Pb free)-------------- 4
2.3. Discarding of P. C. Board-------------------------------- 5
3 Specifications ----------------------------------------------------- 6
4 Technical Descriptions ----------------------------------------- 7
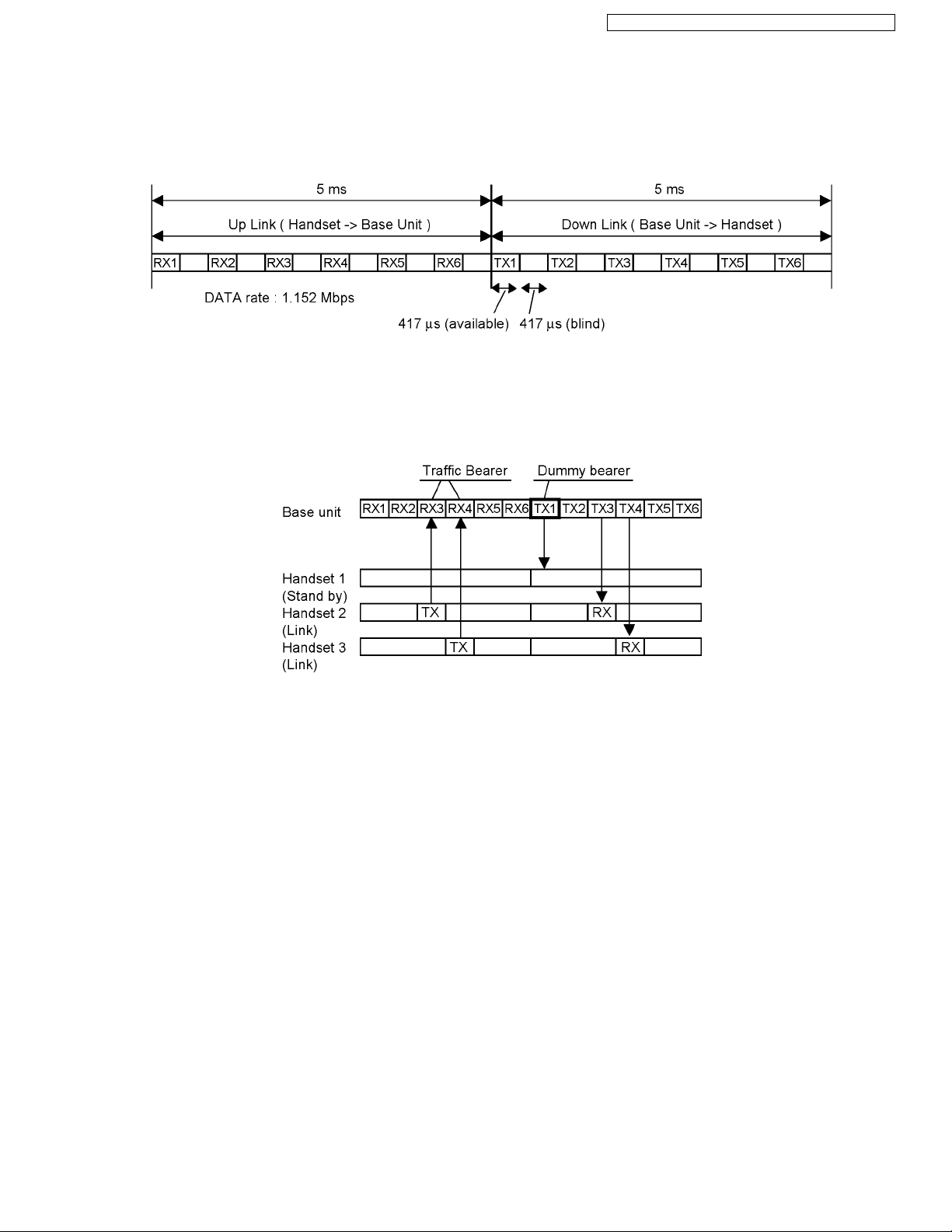
4.1. US-DECT Description ------------------------------------ 7
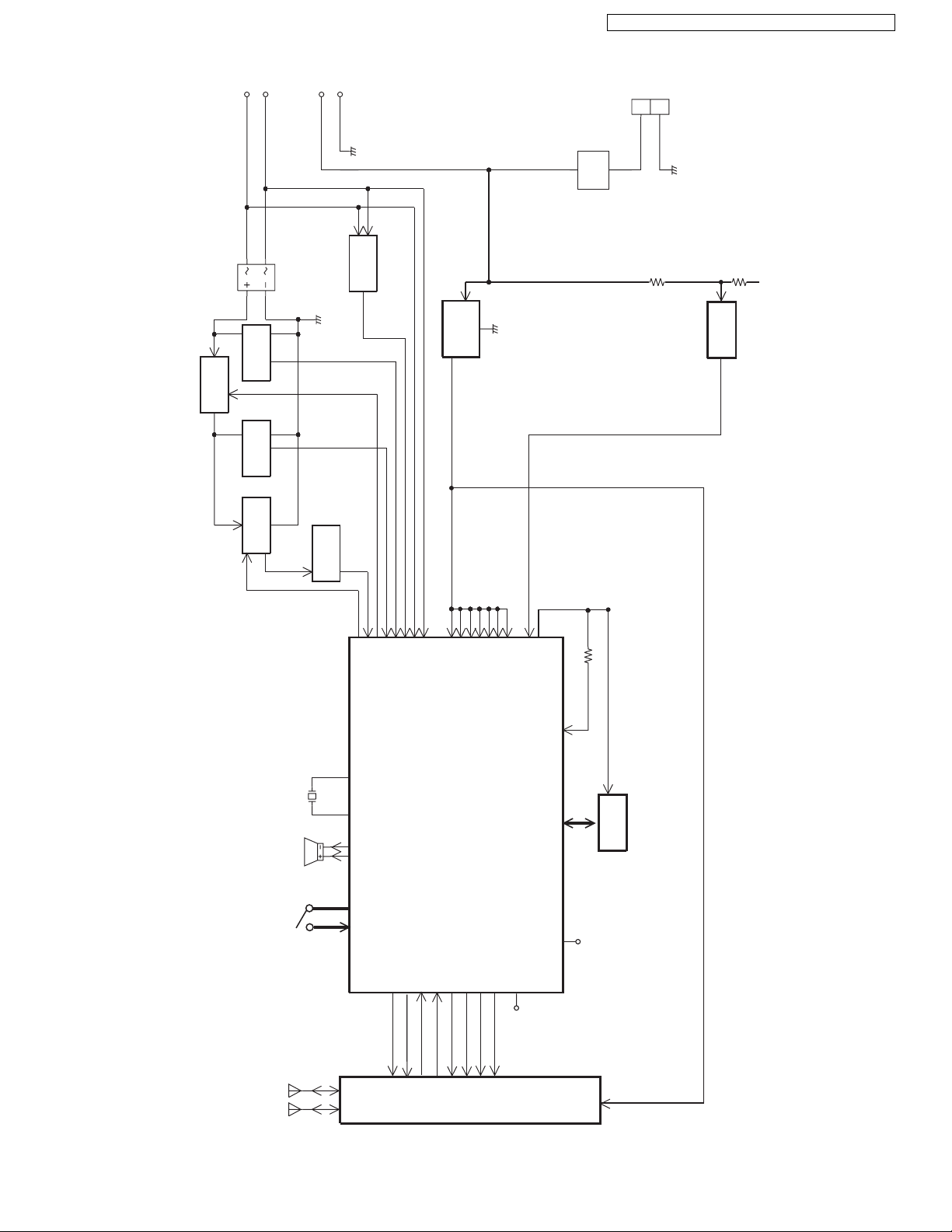
4.2. Block Diagram (Base Unit_Main)---------------------- 9
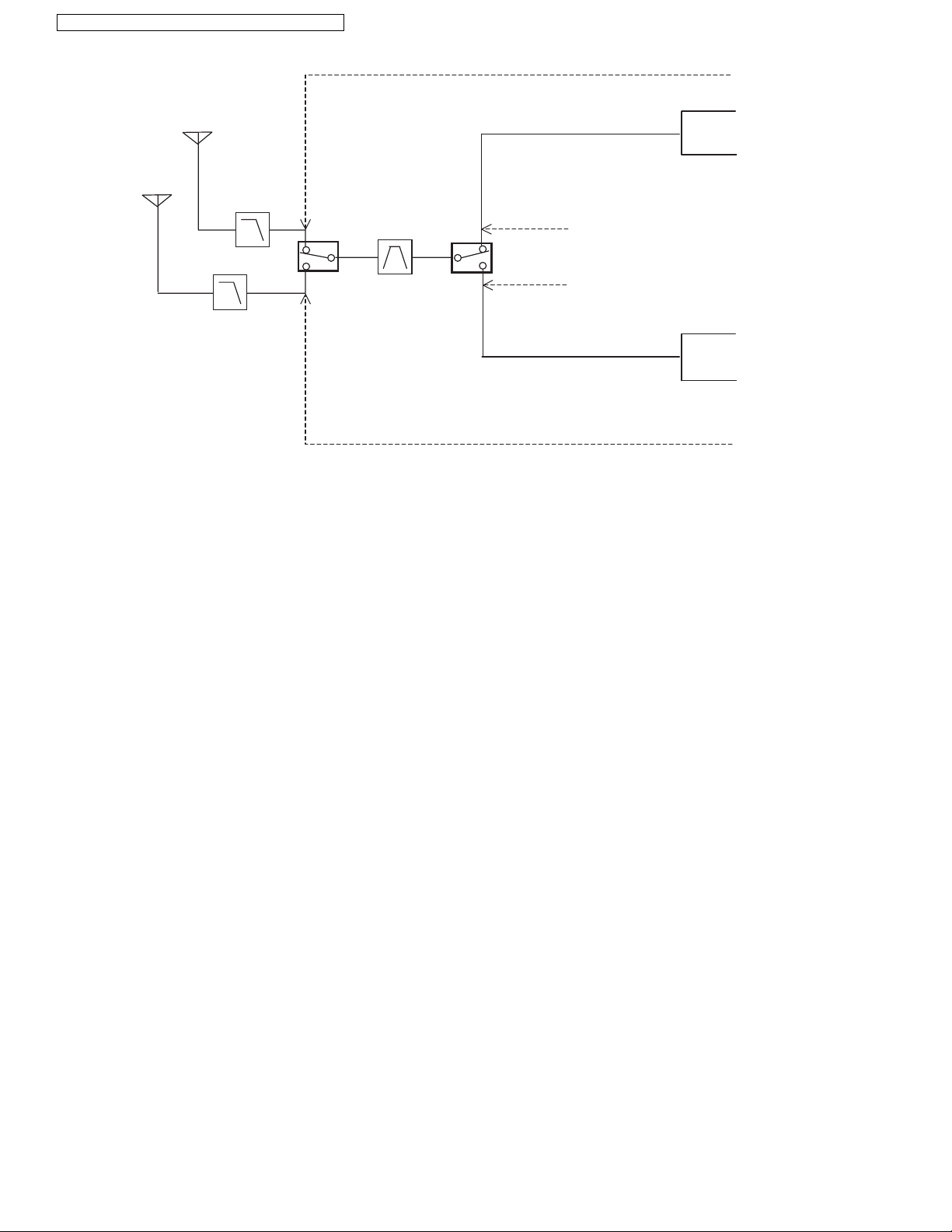
4.3. Block Diagram (Base Unit_RF Part) -----------------10
4.4. Circuit Operation (Base Unit) -------------------------- 11
4.5. Block Diagram (Handset)-------------------------------18
4.6. Block Diagram (Handset_RF Part)-------------------19
4.7. Circuit Operation (Handset)----------------------------20
4.8. Circuit Operation (Charger Unit) ----------------------22
4.9. Signal Route -----------------------------------------------23
5 Location of Controls and Components ------------------24
6 Installation Instructions ---------------------------------------24
7 Operating Instructions-----------------------------------------24
8 Test Mode ----------------------------------------------------------25
8.1. Engineering Mode ----------------------------------------25
9 Service Mode -----------------------------------------------------29
9.1. How to Clear User Setting (Handset Only)---------29
10 Troubleshooting Guide ----------------------------------------30
10.1. Troubleshooting Flowchart -----------------------------30
11 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions ---------------41
11.1. Disassembly Instructions -------------------------------41
11.2. How to Replace the Handset LCD -------------------44
12 Measurements and Adjustments---------------------------45
12.1. Equipment Required -------------------------------------45
12.2. The Setting Method of JIG -----------------------------45
12.3. Adjustment Standard (Base Unit)---------------------48
12.4. Adjustment Standard (Charger Unit)-----------------49
12.5. Adjustment Standard (Handset) ----------------------50
12.6. Things to Do after Replacing IC or X'tal ------------51
12.7. Frequency Table ------------------------------------------53
13 Miscellaneous ----------------------------------------------------54
13.1. How to Replace the Flat Package IC----------------54
13.2. How to Replace the Shield Case ---------------------56
13.3. How to Replace the LLP (Leadless Leadframe
Package) IC------------------------------------------------58
13.4. Terminal Guide of the ICs, Transistors and
Diodes -------------------------------------------------------60
14 Schematic Diagram ---------------------------------------------61
14.1. For Schematic Diagram---------------------------------61
14.2. Schematic Diagram (Base Unit_Main) --------------62
14.3. Schematic Diagram (Handset_Main) ----------------64
14.4. Schematic Diagram (Charger Unit) -----------------66
15 Printed Circuit Board-------------------------------------------67
15.1. Circuit Board (Base Unit_Main)-----------------------67
15.2. Circuit Board (Handset_Main)-------------------------69
15.3. Circuit Board (Charger Unit) ---------------------------71
16 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List -----------72
16.1. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Base Unit) -----------72
16.2. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Handset) -------------73
16.3. Cabinet and Electrical Parts (Charger Unit) -------74
16.4. Accessories ------------------------------------------------75
16.5. Replacement Parts List--------------------------------- 76