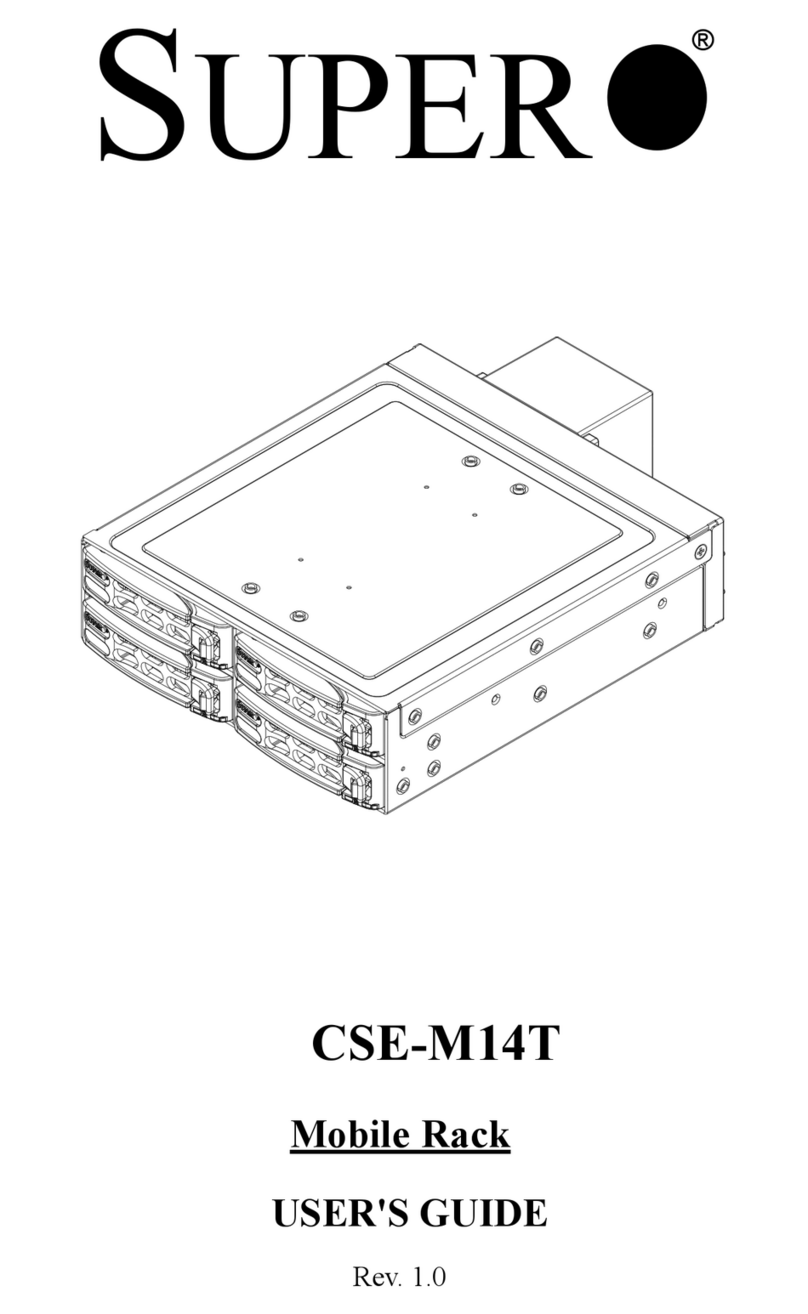
Pro-Log 7701 User manual

STD
7000
7701
16K
Static
Ram
Memory
Card
USER'S
MANUAL

o
c
7701
16K Static Ram Memory Card
USER'S
MANUAL
10/81
.......
J&P
••
ii4#".
hi.
, "
."
lRiP
;mAl;
iW4#4MA44QA

7701
16K
STATIC
RAM
MEMORY
CARD
USER~S
MANUAL
SECTION
SECTION
2
SECTION
3
SECTION
4
SECTION
5
SECTION
6
SECTION
7
SECTION
8
SECTION
9
SECTION
10
APPENDIX
A
TAB
LEO
F
CON
TEN
T S
Data Sheet
Functional
Description
Card Address
Mapp
i,ng
Read,
Wri
te,
and
Bus
Control
Electrical
Spec
if
i
cat
ions
Mechanical
Specificqtions
2114 1024 x 4
Bit
Stat
icRam
Description
Schematic
Assemb
1y Drawing
Series 7000
Memory
Card Timing
Plan
#133
Thermal
Application
Note For
Microprocessor
Systems
Using STD/Series 7000 Cards
o
o
o

o
o
•
gp
u@@@
7701
~l(lc')
[~;)UJJ®~~~~~~~~--~-·-·:MEMORY
CARD
16K BYTE STATIC RAM
MEMORY CARD
This card provides sockets for
up
to
16,384 bytes
of
Read-Write
or
PROM Memory. The card uses 2114
type RAMs
or
equivalent and has sockets for
16
pairs
of
RAMs. Alternately the card
wi"
accept
3625
type PROMs
or
equivalent. PROMs and RAMs can
not
be mixed on the same card.
The
7701
decodes 16 address lines, and can
be
mapped into either 8K
or
16K bytes
of
consecutive
address space. An on-card jumper system allows
users
to
establish which 16K segment
of
a 64K
microprocessor memory each
7701
occupies.
FEATURES
• Sockets
for
16K bytes
of
2114L RAMs
or
3625
PROMs
• User selectable card address
•
All
STO BUS lines buffered
• Minimal
logic
bus loading
•
All
Ie's
socketed
• Single
+5V
operation
• Use Pro-Log 01004, 1Kx8 memories (two
2114L's)
II
3-STATE
BUS
DATA
BUS
Do-D7 I CONTROL
¢
Q4
MEMRQ"
RD"
WR"
MEMU"
ADDRESS
A13-A15
ADDRESS
A10-A12
ADDRESS
Ao-A.
),.
-READ
,.
WRITE -
CONTROL
~
-CARD
3/
SELECT
P-
DECODER
I l CHIP
1.0..
SELECT
r-
31 DECODER
,
101
BUF
I
11K STATIC RAM
SHADING INDICATES SOCKETS ONLY
$
i,e
liM'
au
= ...-
"\
11/
,
101
,
1
DATA
1/
,
RAM ARRAY
IK.I
""IW
DATA
~
r
~"E"
~
••
AV
IKd
-RIW
DATA HU
/
-Ill
'"
ADORE
II
/
7701
"INDICATES ACTIVE LOW LOGIC

2.
FUNCT10NAL
DESCRIPTION
The
7701
1s
organized
to
accept
16
pair
(32
sockets)
2114L 1024 x
4-bit
statis
RAMs.
'Although
the
card
may
be
populated
with
less
than
the
full
complement
of
21l4L
chips,
the
data
bus
drivers
are
enabled
anytime a
valid
address
is
present
even
if
memory
chips
are
not
plugged
in.
The
card
address
range
is
chosen
to
prevent
bus
contention
with
other
system
memory
elements
including
processor
on-card
memory,
other
memory
cards,
and
memory
mapped
I/O. Each pai r
of
the
211lll's
add 1K
8-b
it
bytes
of
RAM,
wh
ich
are
designated
memory
blocks
0 -15
(MBO
-
MB1S).
Each
memory
block
consists
of2
each (1024
x4)
2l14L
RAMs.
(Reference
Assembly Diagram 102687)
PROM
OPTION
;
\..
v11.)
""
~
~
(V
2..0:;:
..
-~~----~
________
1
r----.....-..--
.......
~---~
-
......
_-,
,
(v
I~)
,v,,~+
.
<VLlj
,
......
---
-
----~
r-
,-
----
--
.............
---.----.-. ----.
I
(VIi)
M
BS
(V2.~;
~---
-
------t
r-
--------~~
......................
-.j
,
(YI
S)
N\
~~
(\.t
l..l)
,
~---------
......
-----~.J
,
................
.-
.....
...-._
......
1
---
1
:
tUI'-)
M117
(V:l.4):
~-
-----..,.
v('
P (::
~
"-o"""~"
r---M"Bi
----,
~
LV
lS)
lU33)
:
..
---
-------4
.,
-
-----
-........----
--
..-
~
.-~,
'''\l~
f
(,
+
~~~)
_~J~_:J
1--'
--
..-.
~~
-
~
......
_,
'(\I
1.'1)
M
~
'0
(...J
as)
,
~
__________
...J
-,----...-...........
.........
-........-,
'l
V2.
~
")
M
~I
f
(v
~
(,)
:
..:---
-----"
:
(v
1..,) --:'Vll\
,2:
-;-37):
...
_
-_
-----_..J
r
-----
.........
-
--
.....
.-.....-
-----;
'lv
~~)
M &
'1
C'"
t
~)
;
.--
-
---
--------
,---
......
------~
.-
.......
-.
---.
.---_,
I(\J~\)
1V1I~J"\-
(v~q)
I
~-_,
____
~--l
r--------,
I
(U'l'l.)
~AB
1.5
(1I~~
I
~---.
-..J
\I
f~'~(\'
~C'.y~\\...
The
card
is
designed
to
accept
type
3625
PROMs
in
place
of
2114
RAMs
with
an
increase
in
card
power consumption.
PROMs
and
RAMs
may
not
be mixed
on
the
same
card.
If
this
option
is
exercised
be
sure
to
cut
traces
and ground
pin
10
of
all
ch
ips.
2
o
o
o

IW4U!1j.ui\ly!n!!i'j!!
...
----.l_.~~
o
•
3.
CARD
ADDRESS
MAPPING
0000
3FFF
4000
7FFF
8000
BFFF
COOO
FFFF
o =
SX1~
(Lower
8K)
Sy~,:
(Upp'e
r
8K)
16K
BANKfl
=
SELECT
CARD
SELECT
~
ADDRESS
RANGE
'A'tsn4*
~
{
SO
0000"1
FFF
S1 2000
-t
3FFF
o 0 0
001
{
S2
4000 +5FFF
S3
6000~7FFF
o 1 0
o 1 1
{
S4
8000
+9FFF -
sx~'~
S5
AOOO
."BFFF
--Sy~;~
1 0 0
1 0 1
{
S6
COOO
-+DFFF
S7
EOOO
..,.
FFFF
1 1 0
1 1 1
CARD
SELECT
DECOD
I
NG
74LS42
(U4)
Lower
8K
Upper
8K
The
upper
three
(A15,
A14,
A13)
address
lines
are
decoded
by
an
74LS42
(U4)
for
card
address
selection.
A15
and
A14
are
decoded
to
select
one
of
the
four
16
banks. Address
line
A13
is
decoded
for
selection
of
the
lower
8K
(SX*)
and
the
upper
8K
(SV*)
of
the
16K
bank.
14-1...S+~
I'IIt"'~~@-~
D
(IJ~)
II
0-
16
} C
(:,'<>
'"
~.
f
I"Ff
AI5
,~
c.
s"
@
S5
~'4.@-~-.
'4,
.sc,...
&
~
~
()()<:)
""
~
f:~
t:
('S\\-ll'l'E~
POf:>I\loo-I~
S~
A1
3@-
IS
A
.$2..
S J
~o
3
} 'I-
<:)
~
»
'"]
1=1=='f.
J
o<::>~<:)...,
~\,<f'F
SY
*"
0PflE1<
~K
~t£eT\~
4-----.----;;
........
.s
X)t
LOw€R
cat<
s~LEc.·
..
noN
_==IM:",,,,,,·
41.

The
next
lower
three
addres:s 1t'nes'
(A12~
All~
Ala)
are
decoded
by.
two
each
'74LS42,
U5and
U6,
U5
is
strobed
bY'
S.X"~
ltne
and
select~
the
lower
8 addres:s
banks.
u6
is
strobed
by
Sy*
line
a~d
sel~cts
the
upper
8
addres~
6ank~,
U5
and
U6
are
designated
Chi'p
Select
Decoders
on
the
s:chematt'c
dt'agram,
CHIP
5ELECr
DECODER~
AI\
AIO @-'---";:+--
SKlf
Each
chtp
enable
1
ine
goes
to
ptn
8
(cE~'~l
of
a
patr
of
2114L
chi'ps~p
(1
K
block)
The
lower
ten
address
1
ines
are
used
for
dlrect
address
lng
of
the
1K
chi'p
pat
rs,
and
are
buffered
bY'
U3
and U7.
4
o
o
o

o
c
FROM
CARD
SELECT
DECODER
SX~~
LOWER
8K
FROM
CARD
SELECT
DECODER
SY~':
LOWER
8K
(U6)
CHIP
ENABLE
CE
t;.K~':
CE2K~~
CE3K1:
CE4K~':
CE5K~~
CE6K*
CE7K~~
CE8K
(U5)
CHIP
ENABLE
CE9K~':
CE
I
OK~':
CE11~'~
CE12K~'~
CE
l3K~':
CE
14K~':
CEI5K~':
CE
l6K~':
5
CHI.P
~ET
UPPER
LOWE~
U9
Ul7
UIO
Ul8
U
11
U19
Ul2
U20
Ul3
U21
U14
U22
Ul5
U23
Ul6
u24
CH
I,
P
SET
UPPER
LOWER
U25 U33
U26
U34
U27
U35
u28
U36
U29 U37
U30
U38
U3l
U39
U32
u40
BLQCK
MBa
MBI
MB2
MB3
MB4
MB5
MB6
MB7
BLOCK
MB8
MB9
MBIO
MBlI
MBl2
MBl3
MBl4
MBl5
SH
I.
PPED
ADDRESS
RANGE
8000
-
83FF
8400
-
87FF
8800
-
8BFF
8coo
-
8FFF
9000
...
93FF
9400
-
97FF
9800
-
9BFF
9COO
...
9FFF
AOOO
-
A3FF
A400
-
A7FF
A800
-
ABFF
ACOO
-
AFFF
BOOO
...
B3FF
B400
-
B7FF
B800
-
BBFF
BCOO
...
BFFF

-------'---------------------------
pAGE
.l[)MP:
e:
1\
~
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C 0 E F
~~t{t!J
O~
N\1
o 1
1M
~I
I I
Ml
~a
J
JM
SS,
~O
I
to
IN\
~Ll
I
'M
~51
r M I
1M
>7
I
\~
~'"
I
Sy
J I I J I I I o
2J(
I
M1
'9 1 I
\J.~
~q
T T M
B\OI
I
ht\E
I
&1
I I I f I I ( )l\ I
TO
3)( I
M1
)\'2.
I
1M
~\:,1
f
M1
~l4
I I
1M,'
~161
SX
I I I , , I , ,
1M
~o
I
1M
&,1
l
~2.
f
1M
I ,
~2,-
4)(
,M
~~
I
I I I I 1 r
;0
I
Ml
f
'M
oS'
'M
(pI
I~
I
Sx
)t1
I - I
~7r
4'1
I f ' I I I
(0'1.
'M]
~el
I
)G\
1
1M
BlOT
I Ml
l\1
10'3
I J I
Ml
J r
'J
f I
TO
1"1..
1M
I
1M
~l~,t
1M
01'-\
1 1
M~
)lS
1
-~'I(
I
~'21
I I I I I I
1M
J
1M
,1
I
1M
~2.
1
1M
~~
I
~"
~~
~D
I
I J I I I I I
"TO
q~
I Ml:
L\
l.
I
~t
J'M
~I
I I
~T
I _
>~1
1M
f I 1 I
MF"
t
Av..
t
M1
1
1M
eAt 1
fiJI
BIoi :
M~I\:
106
I
II
>9,
I I f I
TO
ax I
M(
"
IN\;
~,~T
1M
:W~:
l"M
~ISl
sx
f _
>\2
r I f r t J
<!.~
_IM1
I L'M
~'
I J ,
~'2..T
1
M1
_ 1
Sb
, 1 J
II
1M
1 I >3 I
TO
1M!
I I
MSSI
IM~
I 1M
~'1
I
DX
~J
)(p
,
SV
J I I I I I
o
E'(
1Mf,
I
'M
~T
I
M1
_ I
1M]
1 S7
I
)9,
I I I
~J
~\O,
I
~\\,
1 ,TO
F~
J~
I I M
?>l~
I
1Mf.
I
IMl
~15
I
~X
I ),2.. I , I I
)\~
I , ,
MEMORY
ADDRESS
MAP
&
JUMPER
SELECTION
TABLE
POR
lK
MEMORY
BLOCK
Card
Add,...
Selection o
6

4.
READ,
WRITE,
AND
BUS
CONTROL
o
,
Q.V
-S
~~
'f
f:-E.R S
?4L.S~~+
o'J
u2
~fMirt
~
L---------u
o 1 TO
WR\TE
EN~
wE*"
(p,~
\0)
($
MJ...
~\\A.\'-
(!,H-\P$
The
write
strobe
to
the
2114L chips.
qnd
the
read/wrrte
control
s(gnals
for
BUS
BUFFER
di
recttonql
control
is,
the
implementati"on
of
the
followi'ng Booleqn
Logic:
ROM;'·
=:
[(SX
+
Sy)
•
MERQ
•
READ]
WRM;'·::=
[(SX
+
Sy)
•
MERo.
•
WR
ITE]
If
Intel
Mask
ROM
3625
is
to
be
used,
It
is
necessary
to
cut
the
two
traces
of
the
WRM*
line
and ground
pin
10
of
qllmemory
sockets!
Pads
qre
provided
for
this
option.
(PROMs.
and
RAMs
may
not
be
mixed
on
the
same
card).
NOTE:
The
Card's
data
bus
drivers
(74LS244)
Ul
and
U2
are
enabledanytlme
a
valid
address
is
present
even
if
memory
chips
qre
not
plugged
in.
The
card
address
range
is
chosen
to
prevent
bus
content
ion wi'th
other
system
memory
elements
including
processor
on-card
memory,
other
memory
cards,
and
memory
mapped
I/O.
7
, Ii';
«"
A
4M¥
4 4
1#;
M,
$I;;; ;;
U;
4&14&tel#....1
MMW_,
••
ij'i&iiMUk£l\iW&GiWJj$d&lld

5.
ELECTRICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
Vcc
:::;
+5V
±5%
Icc = 2.08A
maximum
(l.6A
typical)
with
RAM
Power
8.0
watts
(typrca
1)
~'d~
Sockets
fully
loaded
(65mA
per
RAM
maximum)
Address, Data, and Control Busses meet
all
STD
BUS
general
electrIcal
specifications
except:
A10,
All
~
A12
~
These
address
bus
Inputs
present
2
LSTTL
loads
maximum
each.
STD/7701 EDGE
CONNECTOR
PIN LIST
PIN NUMBER PIN NUMBER
OvrPUT
(.DtU"e.) LS.,
.....
OUTPUT
(DRIVE)
L4S.
'\II..
INPUT
(LOADING)
~L
INPUT
(LOADING)
~1tt.
MNEMONIC
',"
MNEMONIC
+5
VOLTS VCC 2 1 VCC
+5
VOLTS
GROUND GNO 4 3 GNO GROUND
-5V 6 5 -5V
07
1
55
I---
8 7
f---
65
1
03
06
1
5~
10 9
~!;
1
02
05
1
56
12
11
~'$
1 01
04
1
55
14
13
~5
1
DO
A15 1 16
15
1 A7
A14 1 18
17
1
AS
A13 1 20
19
1 A5
A12 2 22
21
1 A4
A11
2 24
23
1 A3
A10 2 26
25
1 A2
A9 1 28
27
1
A1
A8 1 30
29
1
AO
RO'
1 32
31
1
WR'
MEMRO'
1 34
33
IORO'
MEMEX'
1 36 35
IOEXP'
MCSYNC'
38
37
REFRESH'
STATUS
0'
40
39
STATUS
l'
BUSRO'
42
41
BUSAK'
INTRO'
44
43
INTAK'
NMIRO'
46
45
WAITRO'
PBRESET'
48
47
SYSRESET'
CNTRl'
50
49
CLOCK'
PCI
IN
52
51
OUT
PCO
AUX GNO
54 53
AUX GNO
AUX
-v
56 55
AUX
+V
"Designates Active Low Level
Logic
Edge Connector Pin List
**
See Appendix
A,
Thermal
Considerations
8
o
o
o
--~-----------------------------
----

o
o
6.
MECHAN,CAL
$PEClF~CAT{QN$
The Series 7000 cards
conform
to the STD BUS standards, with the
following
additional requirements,
including those
shown.
STD
BUS
CONNECTOR
CARD
EDGE
.600
(1.52
CM)
6.5
(16.51
CM)
.250
(.64 CM)......
.-
CARD
.250
(.64
CM)
[.
EJECTOR
-+--~A------------------------------------~,'--~----~
DATUM
4.48
I/O
.0150x45°
MIN
BEVEL
(11.38
CM)
INTERFACE
CARD
EDGE
4.1
BOTH
SIDES ENTIRE
LENGTH
.06
R,
2 PL
5.7
(14.48
CM)
TOLERANCES: .XX=+.025, .XXX=+.0050
(10.41
CM)
Series 7000 STD BUS Standard Card
Outline
3.375±.002
(8.57 CM)
.300+.005
-.000
(.76 CM)
Series 7000 STD BUS Edge Card Finger Specifications
9
.........
1"=414# 4 ; ¢
PM
44
MMfAiiliiliiiM'+\"':;&\Ik i J I
Jli.lI¥rlIM
i

7. 21141024 x 4
BIT
STATIC
RAM
DESCRIPTION
o
Ac,
As
PIN
C£)l'-.\F1QVRf»i'~"'"
2114
RAM
PIN
NAMES
ACTIVE
STATE
AO
-
A9
Address tnputs· High
DO
-
03
Data tnput/Output
High
CE"~
Chip
Enable
Low
WE"~
Wri
te
Enable
High
Read/Low
Write
Vee
Power
(+5V)
-
-:!:-
Ground
..
10
b,;
(D?)
01
lo(.j
0;
t!)~)
I}~
(M')
o
o
o

~~"
..
:~:'"
'*
A'5
",4-
"13
Ale
Ail
AID
PCO
PC'
A9
AS
A"J
A4-
,.3
112
AO
Reo;
CIIRO
bELECT
pO:CC/,..R
+5
\I
12.
~
t:ll
18)
...
,
~Z/))
- .
13
iUS:
7 ;
CE/~J('"
l.EISK
.j:-
14
a
..
s ..
CEI4K'R
51
S
!:.E.I~I(1-
15
A
53
...
C.E\2t:
....
~
c.£.'Ji<.:#
c.E'K.
..
CEa~~
C£'1K*
C'E6k.lf-
':ESk"~
C.f4-~'"
CE3,:::
.....
c.t:~<'*
®;
CE,K1t
~
AOORE&5
WfFERS
~.·=!V\RC4:0~r------------=
G~'>-I
-------
Cr-
I
~::/
1""-' !
+i.el
1.
C.Z.-CII
~
T~~a'
T6
.:.
d:
Cir-,-.-~
Er-l
~
o
(TYP)
r
N/
'1.!·LS00
--1
NO~~!
5 . I
.'V'5.0'.----'
m::"'f
;"I~~;~~li:Y~;~\~J;->'
i~:i
~
-----~------~~----~.~.~----~--------------~--~
TYP
(-TYP)
wr;M,.
'rID
WRM",---l
--------.
TYP
(TYP)
+5V
C
'-c---o-
V'J.'Rr..l
*
~s
~~;;.c:c.
~.~~~~·~~~~·~s~~~~~~'~.;·~~,.~VI.~
'J~EO
P.":;.&..
~.:N1
~L·~.W
il
:~_
~x
l(
; i "
;lj~.
_'.
t.'::
j")
l'iAr
;!~l.]
i;!":O
'll
.£Ie
.C:!.':.,;JI,.;'.:/."rs
I
o
(TYP)
(TYP)
'T';O
VIRM-~
-.l
,-
D7
BUS
BUFFE:.R
-@D'
~
/9'
I
18
2
r'
JI I
·---DR>-IHEmiENCE
ONLY
I
p.SSr../~E·L'r'
?AJ?TS :...r:.i
!()?!r.87
Ir;L:J;~8
~f~~~~:~~~rJ
-~~
...
-:--;---'--~
o
T"""
T"""

D
......
I\)
21
-.J
t3l
(,,)
&
SEE
DETAIL A
~REF
DETAil A
/5:;,
LDENTIFY
WITH
AS5fJ1t3/Y
?EV wrER
thiNG
iiUgE£R
5Tl>MP.
4.
REF
DF.~::h/:..;(QNS
MT
~6K.
U:CA"N6
'PlJRPC·-::ES
:NLY
A\lO
MA,(
~.J6T"
AFFEAR
CN
A~n..A.L
;;0..1<,
......
&
\,'PPED
AT
80')(l-
<erFF.
A'l:D
:·M.P;>E:D
AT
A:lJO-
bFFF.
&,-INOICATE.S
PiN
NO.
I
m:
SOCKETS ('1'(p).
1 ;:C)R
AS&'Y
PRDGF.
CUQES
~tE
,~~
iDi.)4
..
,
NOTE5:
UI\LESf:>
OTHE.R\-Vl~£
t?EC.,F\ED.
o
~~
-
e>--QD-o
~
fQSm
~
t:£~:J
F.~1j
b.~
~r~:::
~~~::
f
[::~o::j
t:~~]
t:7t:J
[::~;:J
[::0::]
.rz:j
Gd
~:J
~
0 0 0
00
0 0
~j
11
10
1
U20
t
~
Coo
0
~2~0
0
':1
00000000
~~
18
10
1
U37
•
~
~
00
0
:2:
00
~
ErJ
r°:E:J
00000000
00000000
200000000
L:::J
00000000
~
.
")
U23
~
0 0
;)
0
;) ;) ;)
~
k0 0 0
:3:
0-0
:1
00000000
~
U31-~
100000003
~t:-
0 0 0
:\6'
0 j
~E:::s:J
~[
0 0 0 U
0
3:
0
']
~[OTO
u::o
o
:
000000000
00000000
00000000
00000000
~
(2)
c:
o
A
r
, '
,-'
>-
<II
CI)
co:
2S
8
(32)
~
SC'"'~IVIATIC
NO.
102686
PA:n
S LIST
NO.10<='6B3
?
_....
:..;,
7"'.
eo
1"."-\,::.,,0
Pf.:H'LN",}ii>3.1
:-;:1
)/i;
c.
I ;'::"I:';:D
yER
peu 811.
h-/·q~I~\u.
REFERENCE
ONLY
1:
r·
iK
,
1/4~~~
~
~_cc
I:~
c
~~
~~
___
_
.-!
!O.L.
....
~
7 I
~~~,(.
I
C·l
ITEl.:1
DESCR!PTlON
I
REF.
Of.SiGNATlOtl~
PRO-LOG CORPORATION I
~~~~~r1;~~i~~~"c:~~
_ 1 A
o
~.~

10.
o
o
•
SERIES
7000
MEMORY
CARD
TIMING
Series 7000 cards are designed
to
communicate over the STD BUS backplane in any combination
without
usertiming considerations. The following information is provided
to
accommodatethe
useof
pincompatible
memory
chip
variations which can be used in the Series 7000 memory cards.
Figure
lO-'
showsthe functional blocks
of
the7700 Memorycards. Thedelayscontributed bythese blocksare
added to the memory chip delays and access times todeterminethe
AC
characteristics
of
the card. Thetable
in Figure
,o~
gives maximum propagation delays for the memory card. For exact delays use the IC
manufacturer's data sheets and the appropriate schematics.
MEMlX·
ADDIIISI
BUI(HIGH,
ADDAESI
IIUS
(LOW)
ADONSI
MIll
OIl
MIl
AIItIA'I
DATA
DECODIIIS
IlUfnU
o---c
fl
a.-.
aw
I
1)
~
......
DATA
,
~
ADOIIEIII
_._.
DATA
BUS
AOOIIESS
IlUfnIlI
'--<
-,
_TI
CONTIIOl
<>-¥-
~
~~l
?c
=D-
&,
(T"'"
MI_-'"
~
110-
~
WIIITI
CIIICUlTIIY
_lENT
ONLY
ON
IIAM
CAIIDI.
.,..
NOTU
F'cau.re
\0-1
Memory Card Functional Blocks
PROPAGATION DELAY LOAD CONDITIONS
CIRCUIT FROM TO . TpD MAX CL RL
MEMORY CHIP
ADDRESS ADDRESS BUS ENABLE
DECODERS
OR
OR
75 ns
15
pF -
MEMEX' READIWRITE
ENABLE
ADDRESS ADDRESS MEMORY CHIP 35 ns
160
pF -
BUFFERS BUS ADDRESS
MEMORY CHIP DATA 20 ns
45
pF
4.7Kn
DATA (OUT) BUS
DATA
DATA MEMORY CHIP
25
ns 80 pF
BUFFERS BUS DATA (IN) -
READ WRITE VALID OUTPUT
30
ns
CONTROL ENABLE
READ DECODER
ROM'
100
pF
4.7Kn
WRITE OUTPUT
OR
70 ns
CONTROL RD', WR',
WRM'
(RAMs ONLY)
OR
MEMRQ'
f
1C\0C't.
\C)-
a.
Generalized Maximum Delays For Memory Cards
For
example,
the
2114
RAM
chlpts
speclfted
Data
Read
a.cce~s~
ttJ1)e
from
em
addre~s
change (AO-A9)
is
450ns.
In
the
7701.
th
is
increased
by
the
addres's
buffers
(35ns}
and
data
buffers
(20ns)
to
505n5.
In
thts
case
the
decoding
of
A1Q-A15 and
the
Data
Bus
buffer
control
are
presumed
to
occur
during
the
RAM
data
access'
ttme,
13
=££;14#11,,;
4,I'iM4"I
\AMM,
,Wi
*
Z$SZAW#

o
o
o
14
---~-------~------.-~--

o
c
•
PLAN
#133
-
THERMAL
APPL1'CATION
NOTE
FOR
MICROPROCESSOR
SYSTEMS
USING
STD/SERIES
7000
CARDS
TABLE
OF
CONTENTS
SECTION
1
SECTION
,2
SECTION
3
SECTION
It
SECTION
5
SECTION
6
SECTION
7
ILLUSTRATIONS
FIGURE
1
FIGURE
2
TABLES
TABLE
1
TABLE
2
TABLE
3
INTRODUCTION
THERMAL
CONSIDERATIONS
FOR
STD
SYSTEMS
CONFIGURING
A
TYPICAL
SYSTEM
FAILURE
RATE
ACCELERATION
DUE
TO
TJ
THERMAL
RESISTANCE
OF
ICs
FORCED
AIR
COOLING
CONCLUSION
THERMAL
AND
ELECTRICAL
ANALOGY
HEAT
FLOW
IN
ENCLOSED
DIGITAL
SYSTEM
TYPICAL
NOMINAL
POWER
DISSIPATION
FOR
SERIES
7000
CARDS
THERMAL
RESISTANCE
OF
TYPICAL
IC
PACKAGES
FAILURE
RATE
AS
A
FUNCTION
OF
TJ
15
__
."'11:;
; 1 I
G##¢#¢MP
4% k
••
4,.

THERMAL
APPLICATION
NOTE
FOR
MICROPROCESSOR
SYSTEMS
USING
STD/SERIES
7000
CARDS
SECTION
1 -
INTRODUCTION
The
failure
rate
of
many
electfical
components
is
an
exponenti~l
function
of
junction
temperature.
Temperature
rise
from
ambient
to
Junction
temperature
depends
on
many
factors
such
as
power
density
i.e.
watts/inch
3,
air
velocity
over
the
high
dissipating
components,
thermal
·resistance
.(junction-to-case)
and
dissipation
of
the
component, and
the
thermal
characteristics
of
the
cabinet
which houses
the
system.
This
application
note
is
intended
to
aid
the
user
in
estimating
and
solving
his
thermal
problems.
Sample
analyses
of
two
Series
7000
Systems
are
included,
as
well
as
suggestions
for
minimizing
thermal
effects.
Heat flow
is
analogous
to
current
flow in
an"
electrical
circuit.
The
electrical
and thermal
equivalent
are
presented
in
Figure
1.
AT
TH£R.nAL
CIRCuIT
=
p,
I:l
V"~
I.
Ii
llT
-
'Re
THE~"1AL
EGuf-lTIONS
I
THERMAL
ELECTRICAL
!
SYMBOL
NAME
UNITS
/SYMBOL
NAME
UNITS
I
i
P
POWER
(HEAT
WATTS
I
CURRENT
AMPS
FLOW)
T
TEMPERATURE
°c
DIFFERE;NCE
I V
VOLTAGE
01
FF~:
VOL
TSI
j
-
i
R'
THERMAL
°C/W
e
RESISTANCE
j R
ELECTRICAL
OHMS!
I
RESISTANCE
i
~
I
r
FIGURE
1 -
THERMAL
AND
ELI
16
o

o
.-
c I
L
__
o
Figure
2 shows
STD
cards
as
heat
sources
in
an
enclosed
.digital
system.
The
heat
generated
by
a
card
is
the
sum
of
numerous
heat
sources:
the
heat
generated
by
ICs
plus
any
singular
components. Most
heat
is
generated
in
the
different
junctions
within
the
IC.
An
average
thermal
resistance
between
any
junction
and
the
case
is
assumed. Heat flow from an
IC
with
a
junction
te~perature
TJ
encounters
the
junction-to-case
thermal
resistance
ReJC
and
raises
the.
case
temperature
to
TC'
From
the
IC
case,
the
heat
flows
through
ReCAI
to
the
ambient
air
in
the
enclosure,
and
finally
through
ReA
to
give
TA
the
ambient
temperature·outside
the
enclosure
--
JUNCTION
enclosure
HEAT
SOURCES
Tc..
ReJC
IC
CASE
ReCAI
I
l
r
I
I
I
(
AMB
I
ENT
IN
ENCLOSURE
l
f
ReA
.J
---
--
TA
AMBIENT
OUTSIDE
ENCLOSURE
TJ -
IC
junction
temperature
TC
-
IC
case
temperature
TAl';" Ambient
temperature
in
enclosure
TA
-Ambient
temperature
outside
enclosure
ReJC
-Thermal
resistance,
junction-to-case
R
eCAI
-Thermal
resistance,
junction-to-ambient
in
enclosu~e
ReA
-Thermal
resistance,
ambient
in
enclosure
to
ambient
outside
enclosure
FIGURE
2 -
HEAT
FLOW
IN
ENCLOS£D
DIGITAL
SYSTEM
When
many
heat
sources
are
involved,
the
thermal
circuit
becomes
quite
complex.
The
use
of
analysis
with
assumptions,
approximations,
and
experimental
techniques
is
necessary
to
understand
the
problems
and
find
practical
solutions.
17
_
..
au
..
"~A
i
fP/!ihT#Mp
# 4