5
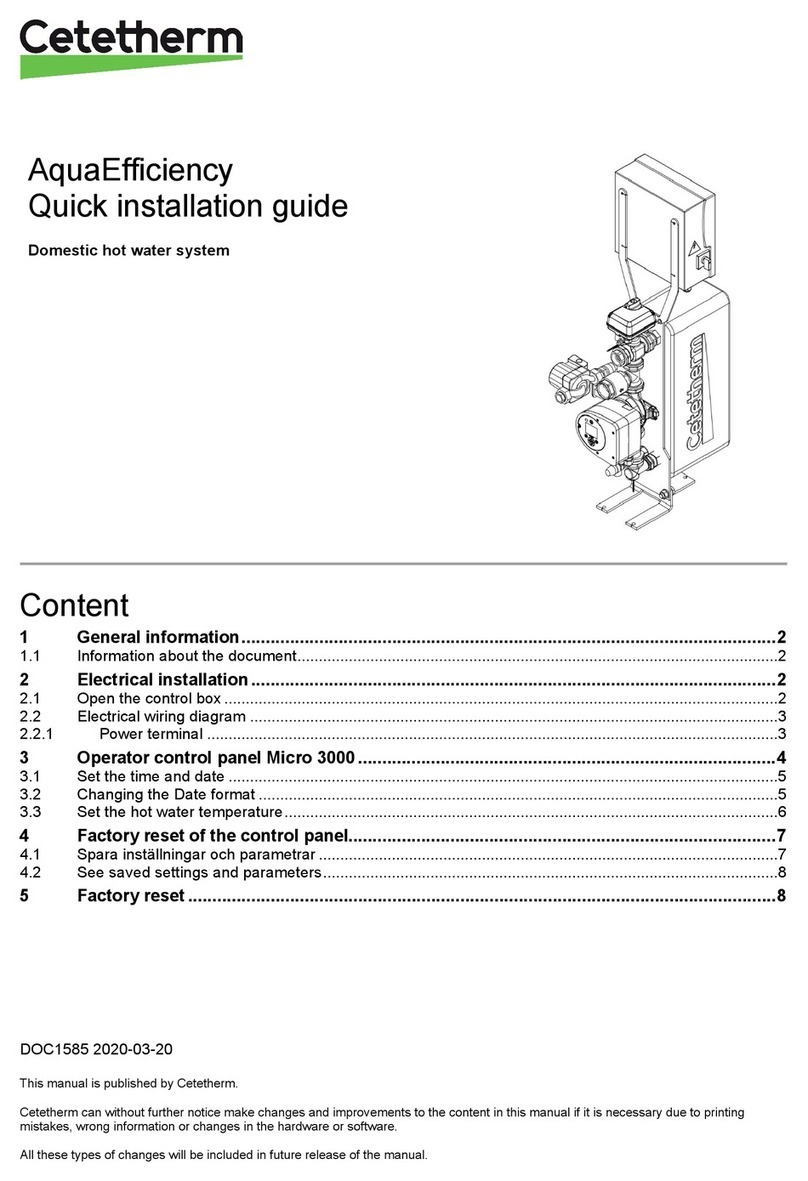
Overview of the PURA Quick Change RO System’s Components
Manifold Assembly
The manifold assembly serves as the functional hub of the PURA system by
directing the flow through each of the system’s main components.
Sediment Filter
The sediment filter screens out particulate material, such as dirt, sand, or rust,
which may clog the other filters in the system.
Activated Carbon Filter
The activated carbon prefilter reduces chlorine which may damage the RO
membrane filter. The activated carbon postfilter serves as a final polishing
step to improve the water quality. They must be regularly checked and/or
replaced to prevent premature membrane failure and poor water quality.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The RO membrane (4) reduces dissolved substances and other microscopic
impurities. It consists of a membrane envelope wound around a perforated
tube. Product water diffuses through the membrane to the inside of the
envelope where it flows to and is collected by the tube. Impurities are flushed
away in the drain stream.
The RO membrane featured in the PURA system offers exceptional
contaminant rejection, application versatility, and long life. The membrane
material is sensitive to an attack by chlorine. The activated carbon filter must
be maintained properly to prevent premature failure of the RO membrane.
For long term storage the RO membrane should be refrigerated to maximize
performance once used. DO NOT ALLOW TO FREEZE.
NOTE: This preservative must be flushed from membrane before use. If
ingested it may cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract, colic, diarrhea,
or other similar symptoms. The manufacturer recommends discarding all
the product water for at least one hour of operation before drinking or
use in food preparations. WaterGroup highly recommends discarding the
product water for a full 24 hours to flush the preservative and to properly
hydrate the membrane for maximum performance.
Drain Line Flow Control
The flow control assembly or concentrate flow control (5) regulates the flow rate of the flushing (drain) stream and to
maintain pressure in the RO membrane filter.
Automatic Shutoff
The automatic shutoff (6) automatically stops the flow of water through the PURA system when the storage tank is full.
Storage Tank
The storage tank (7) collects and stores the water produced by the RO system. A compressed air diaphragm drives the
water to the polishing filter and faucet. The ball valve (11) provides a convenient way to lock water in the tank during
transport and filter changes.
Dispenser Faucet
The PURA faucet (8) allows the product water to be drawn from the system with a simple rotation of the handle. This air
gap style faucet prevents the unit from siphoning drain water back into the system. It features a built-in siphon break
for concentrate discharge as required by most plumbing codes.
NOTE: Cleanliness is essential in the Preparation procedure. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before handling
filters. The use of surgical gloves is strongly recommended.
Figure 2