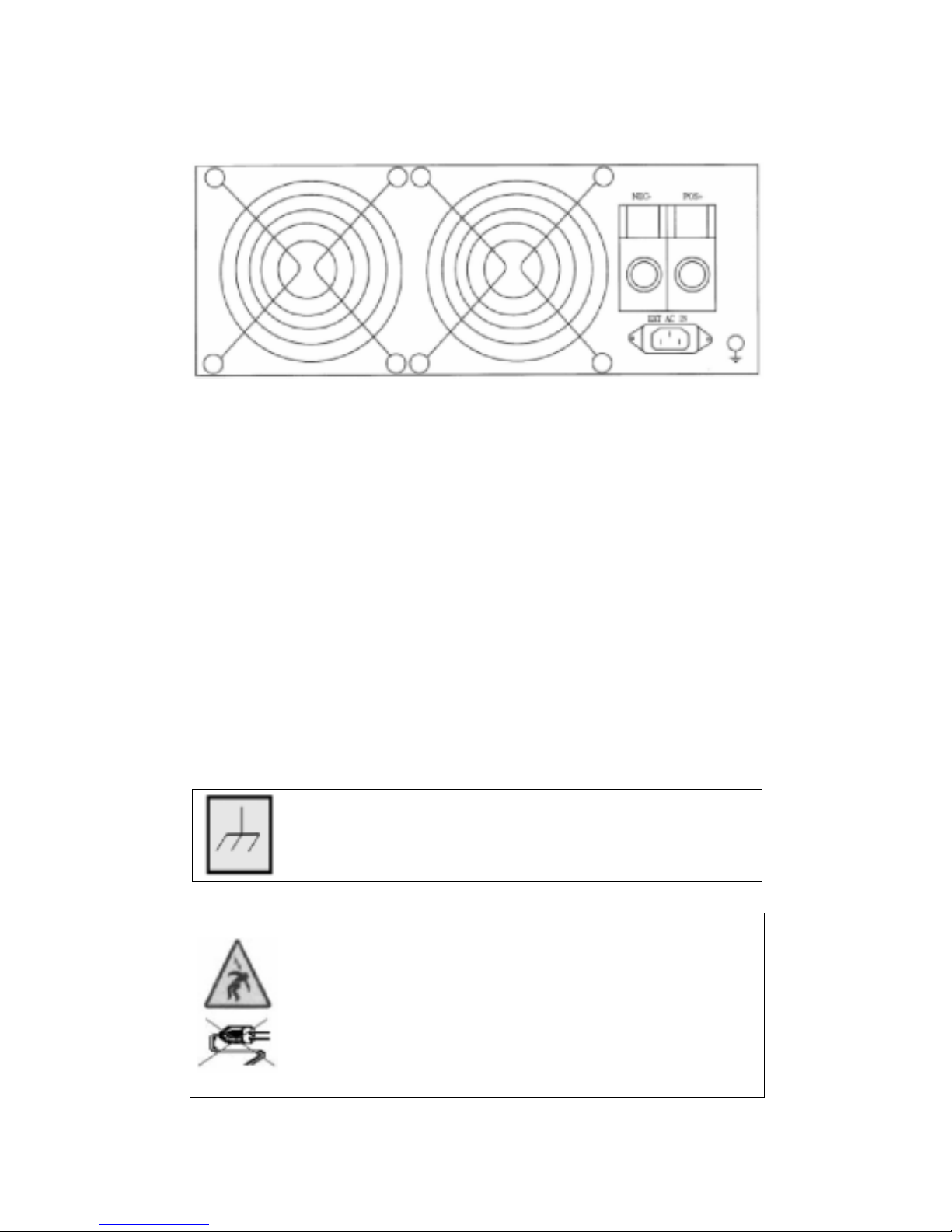
- -
1
Safety Instructions
WARNING!
Before installing and using your Inverter, read the
safety instructions.
A. General Safety Precautions
A-1. Do not expose the Inverter to rain, snow, spray, bilge or
dust. To Reduce risk of hazard, do not cover or obstruct
the ventilation openings. Do not install the Inverter in a
zero-clearance compartment. Overheating may result.
A-2. To avoids a risk of fire and electronic shock. Make sure
that existing wiring is in good electrical condition; and
that wire size is not undersized. Do not operate the
Inverter with damaged or substandard wiring.
B. Explosive Gas Precautions
This equipment contains components, which can produce
arcs or sparks. To Prevent fire or explosion do not install in
compartments containing batteries or Flammable materials
or in locations which require ignition protected equipment.
This includes any space containing gasoline-powered
machinery, fuel tanks, or joints, fittings, or other connection
between components of the fuel system.
C. Precautions When Working With Batteries
If battery acid contacts skin or clothing, wash immediately
with soap and water. If acid enters eye, immediately flood
eye with running cold water for at least 20 minutes and get
medical attention immediately.
C-1. NEVER smokes or allow a spark or flame in vicinity of
battery or engine.