Ritual Electronics Diviser User manual

Clock
Ritual Electronics
Diviser

2
Summary
03................Warranty
04................Installation
05................Overview
06.................Controls
07.................Divisions
08.................Counting
09.................Reset
10.................Patches

3
Diviser
Thank you for purchasing Ritual Electronics Diviser.
Your module has been assembled with care in our
studio in Marseille, France.
You can find your module on Modulargrid:
https://www.modulargrid.net/e/ritual-electronics-diviser-
For any remarks and informations, contact us at:
For video demos and patch ideas check:
https://www.youtube.com/ritualelectronics
https://www.instagram.com/ritualelectronics
Limited warranty
Ritual Electronics warrants this product to be free of defects in
materials or construction for a period of one year from the date
of purchase.
Malfunction resulting from wrong power supply voltages, backwards
or reversed eurorack bus board cable connection, abuse of the
product or any other causes determined by Ritual Electronics to be
the fault of the user are not covered by this warranty, and normal
service rates will apply.
During the warranty period, any defective products will be repaired
or replaced, at the option of Ritual Electronics, on a return-to-Ritual
Electronics basis with the customer paying the transit cost to Ritual
Electronics. The return of your module is on us.
Ritual Electronics implies and accepts no responsibility for harm to
person or apparatus caused through operation of this product.

4
Installation
Always turn your eurorack case off before installing
a module.
Do not touch any electrical terminals when attaching any
Eurorack bus board cable.
Diviser does not have a shrouded header. Please connect it
with care. Align the power cable’s red stripe with the “Red”
text on the module.
Ritual Electronics Diviser does require 25mA on +12V, 3mA
on -12V and 0mA on 5V.
You will need 14HP of free 1U space in your Eurorack case
to install Diviser. The module is 35mm deep.

5
Overview
Diviser is a 1U clock divider with odd & even outputs.
It can divide a signal by 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 16 and 32
simultaneously.
Being based on CMOS chips it can run at audio speed (and
higher) to create subharmonics and/or rhythms from an
oscillator.
The reset input resets all the outputs to a high state.
Comparators are built in both the Clock and Rest inputs
with threshold set at 2.5V. It means you can use any type of
signals in these inputs.

6
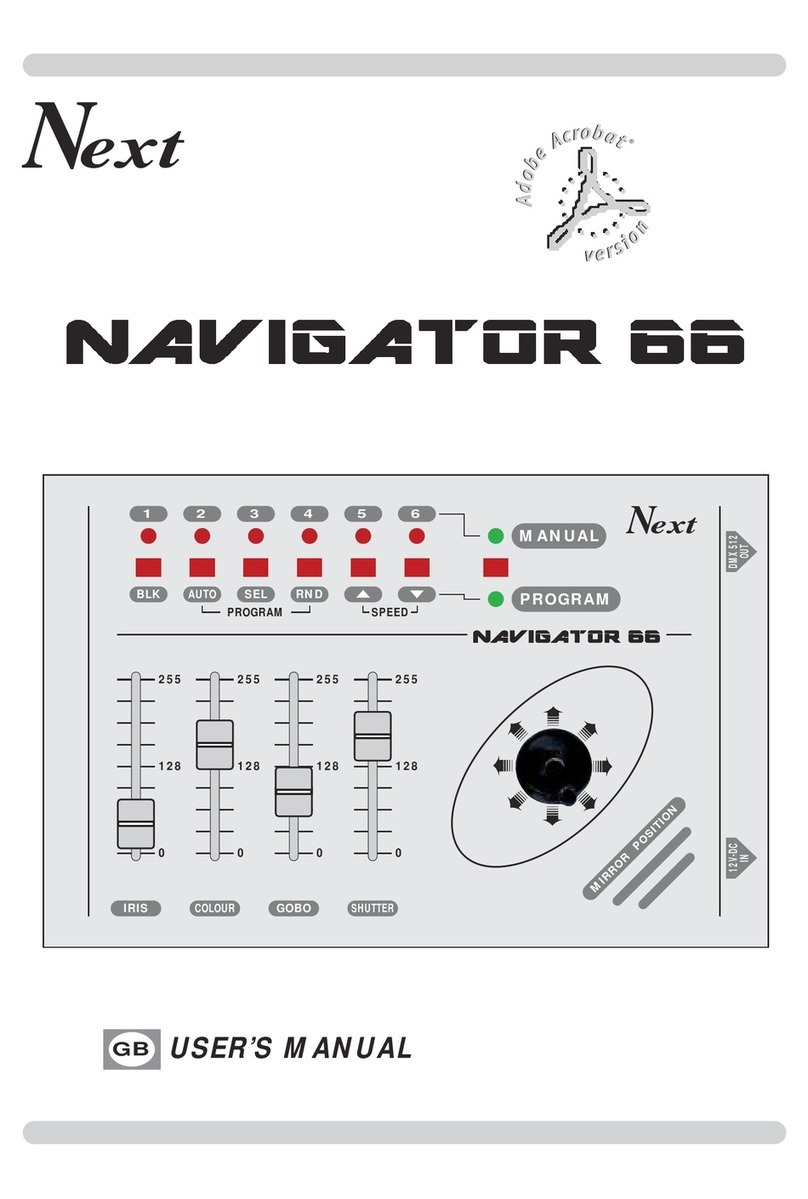
Diviser controls
Divided outputs
50% duty cycle
0-10V squares
Reset Input
Resets the divider on a High
Built in comparator going into a
gate to trigger convertor
Clock Input
Signal to be divided
Built in comparator
Clock

7
Divisions
Clock Input
/2
/3
/4
/5
/7
/8
/16
/32
Diviser outputs 8 different clock divisons. Each output has a 50% duty cycle (equal time spent on and off).
Here is a visual representation of the different outputs in relation with the clock input.

8
Counting
Sequence input
/2
/3
/4
We are referring to devices as Diviser as clock dividers. When using a straight clock it is
indeed the effect we observe. See diagram above, in Divisions.
If we use a gate sequence in place of the steady clock we can discuss another aspect of
Diviser. The chips used in the module are marketed as electronic counters. They do not
divide per say, they count the pulses and output accordingly.
Diviser counts the rising edges of incoming pulses. You can then generate slowed down
sequences related to your input. Resets can be used to add more pulses to the resulting
sequences - see next page.

9
Reset
This shows how the Reset input behaves.
No effect if it is during a high. It will create
a High if the effect is triggered during a
Low. Here we have a straight clock, an
unrelated trigger pattern in the Reset in,
and the resulting pattern is taken from the
/2 output.
When using an odd division output, you
can make use of an even division to reset it
back when a bar starts for example. Here
you can see a straight beat, a reset signal
taken from the /8 output and the resulting
pattern at output /3.
Diviser follows what has been known as “musical reset”. Instead of dropping to a Low when the divider
receives a reset input, Diviser goes High. It is the expected behavior when you want to reset a divider/
sequencer/... You usually want your module to start the first beat/whatever of the sequence when it receives
a trig in Reset.
On top of this there is a gate to trigger in the Reset input. Meaning the signal you put in the Reset can be as
long as you want, it will only reset the divider at its rising edge. If you want to pause Diviser we recommend
doing it at the Clock input.

10
Patches
Patch #1 - Harmonic oscillator
Diviser can take high frequency audio at its input and act as
a sub oscillator. Mixing the outputs together with the oscillator
you can get a really thick sounding oscillator.
Note that Diviser outputs unipolar gates, you may want to
offset them by -5V for best results. Or as pictured, inverse the
phase of one of the divisions.
The odd divisions will give you second, forth and sixth
intervals, octaves down.
You may want to use a faster than usual oscillation.
You can play with the reset input to find beating patterns.
Patch notes
Oscillator, Out ------------ Mixer, In
Oscillator, Square Out ------------ Diviser, Clock In
Diviser, Clock Outs ------------ Mixer, Ins
Anima
Attack
Curve
Decay
_+
_+_+
_+_+_+
Attack
Curve
Decay
_+
Unipolar
Bipolar
Attack I Curve I
Out I
Out I
EOC I
EOC I
Decay I
Gate I 1V/Oct I
Attack II Curve II
Out II
Out II
EOC II
EOC II
Decay II
Gate II 1V/Oct II
Clock
Mix
In I
In
In II
In III
O
u
t
O
ut
I
O
ut III
O
ut II
Ø I
Ø II
Multiple
II
I

11
Patches
Patch #2 - More complex sequencing
Try switching from different reset divisions with the help of
Pointeuse. Clock Diviser from a clock or a sequence of gates.
Clock Pointeuse with an unrelated clock for more variations.
Patch notes
Diviser, Clock Outs ------------ Pointeuse, Out/In I & II
Pointeuse, In/Out ------------- Diviser, Reset In
Clock
Trig In
LatchMom
Pointeuse
Table of contents